2. After passing the control valve, vapors from the fuel tank through the evaporation hose enter the adsorber, where they are adsorbed into the activated carbon filler and retained. When the operating parameters for which the system is programmed are reached (the engine is running, its temperature has reached a certain limit, etc.) a signal is sent from the PCM to open the purge valve and the ventilation valve. Fuel vapors are carried through the purge hose from the adsorber into the intake manifold (due to the created vacuum), where they are mixed with the air-fuel mixture before entering the combustion chambers.
3. The intensity of the flow of fuel vapors directed from the canister into the intake manifold is adjusted in the PCM when the EVAP purge valve cycle is changed. When the engine is running cold or when the start time of a warm engine is delayed, the PCM does not send a control signal to the valve solenoid. After the power unit has warmed up to operating temperature, a signal is sent from the PCM control unit to the purge valve solenoid, and vapors are supplied to the intake manifold at a flow that depends on the operating mode of the engine. Purge Valve Duty Cycle (switching on and then switching off) occurs 5 to 10 times per second. The flow of gases is controlled by changing the pulse width of the valve (duration of the signal to the solenoid).
4. When starting a cold engine, the EVAP system performs self-diagnosis. When certain operating parameters are reached, a signal is received from the PCM to open the purge valve, and the ventilation valve remains closed at this time. In this case, the EVAP system is informed of the vacuum created in the engine. When a certain degree of vacuum is reached, the purge valve closes, and thus the system is sealed. The PCM analyzes the signal from the pressure sensor in the fuel tank, and when it is determined that the system is depressurized, the corresponding diagnostic trouble code is recorded in the electronic memory of the microprocessor.
5. The operating principle of the fuel tank pressure sensor is similar to the operating principle of the manifold absolute pressure sensor (IDA). In the PCM, the 5-volt circuit of the sensor, as well as its ground loop, is closed. The sensor sends a signal to the PCM, which changes depending on the vapor pressure in the fuel tank. When equalizing the pressure in the tank with atmospheric pressure (like when the gas cap is removed) The sensor output signal has a potential of approximately 1.5V. With a vacuum in the tank of 356 mm Hg. Art. The output potential of the sensor is 4.5V.
Note: the fuel vapor recovery system, like all emission reduction systems, has a guarantee of uninterrupted operation (At the time of creation of this manual, the warranty was provided for 5 years or 80,000 km).
Replacing elements
6. All EVAP system hoses have quick-release couplings. Before disconnecting, you must clean the coupling and the area around it. Rotate the coupling elements relative to each other to release the seal. When disconnecting the coupling of a larger diameter hose, it is necessary to compress the protrusions of the clamp and pull it off the tube. To disconnect a smaller diameter hose, you need to press in the locking tab and pull the coupling off the tube.
Adsorber
7. The EVAP canister is attached to a bracket next to the fuel tank.
8. Raise the vehicle and install vertical supports.
9. If necessary, remove the fuel tank protective panel.
10. Disconnect the hoses from the adsorber (see illustration).

15.10. The EVAP system canister is located near the gas tank
11. Unscrew the bracket bolt and remove the adsorber.
12. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
Purge valve
13. The purge valve is located on the left side of the engine. It is mounted on a bracket that is located above the starter (see illustrations).

15.13. The EVAP purge valve/control solenoid is located on the left side of the engine block
14. Disconnect the electrical connector.
15. Press in the retaining tab and disconnect the hose from the purge valve.
16. Unscrew the fastening bolt/nuts.
17. Remove the purge valve.
18. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
Ventilation valve
19. The ventilation valve is mounted on a bracket near the gas tank (see illustration).
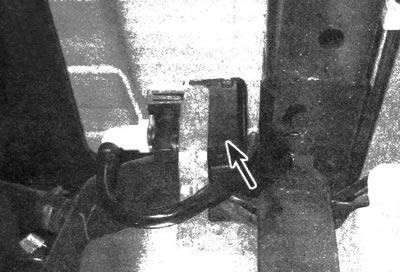
15.19. EVAP Vent Valve/Control Solenoid Location
20. Raise the vehicle and install vertical supports.
21. Disconnect the electrical connector.
22. Disconnect the hose from the vent valve (see paragraph 9).
23. Disconnect the fasteners and remove the ventilation valve from the bracket.
24. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
Fuel tank pressure sensor
25. The gas tank pressure sensor is located in the fuel pump module (see illustration).

15.25. Location of the sensor in the fuel tank; to remove it, it must be squeezed from the sides
26. Remove the fuel tank (see chapter 4).
27. Disconnect the electrical connector from the fuel tank pressure sensor.
28. Disconnect the retainer and remove the sensor from the top of the fuel pump module.
29. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
