Warning: Certain precautions should be taken when inspecting and servicing the battery. The battery contains hydrogen, so do not expose it to open flames or sparks from a burning cigarette or ignition system. The electrolyte in the battery has the solvent properties of sulfuric acid, and if it comes into contact with the skin or eyes, it causes serious injury; The electrolyte is also aggressive towards clothing fabrics and paint coatings. When disconnecting the battery, disconnect the negative cable first and connect it last when connecting.
1. Carrying out timely preventative maintenance of the battery allows you to ensure quick and reliable engine starting in any weather. Before working on the battery, make sure you have the necessary tools and materials (see illustration).
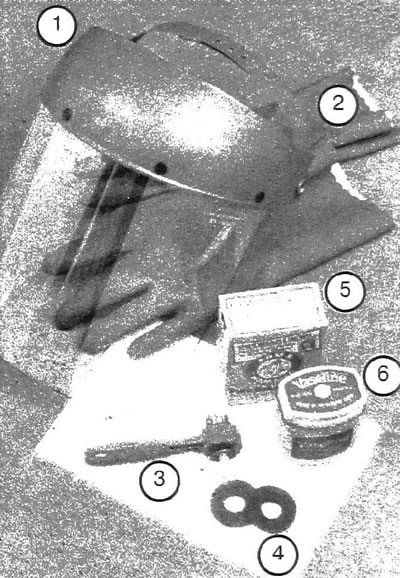
11.1. Tools and materials required to service the battery: 1. Eye and face mask - When cleaning the battery terminals from traces of corrosion using a wire brush, acid crystals may get into the eyes 2. Rubber gloves Another safety measure when servicing the battery. Do not forget that the battery is filled with acid 3. Battery Terminal and Wire Cleaner - Use this tool to remove corrosive deposits from the battery terminals and wires 4. Protective washers - Placing washers on the battery terminals under the wire clamps reduces the formation of corrosive deposits 5. Food grade soda - An aqueous solution of soda is used to neutralize acid crystals 6. Technical petroleum jelly - Applying a layer of petroleum jelly to the battery terminals prevents them from becoming covered with corrosive deposits
Note: Some of the models described are equipped with an additional battery. In this case, the safety requirements and maintenance procedures described below apply to both batteries.
2. There are several safety requirements that must be followed when working with the battery. Before servicing the battery, stop the engine and turn off all electrical sources on the vehicle, then disconnect the wire from the negative terminal.
3. The battery produces hydrogen gas, which is both flammable and explosive. Do not expose the battery to sparks from the ignition system, and do not smoke or allow open flames near the battery. Charge the battery in a well-ventilated area.
4. The electrolyte contains poisonous and corrosive sulfuric acid. Do not allow electrolyte to come into contact with the skin, eyes or clothing, or penetrate into the body. Wear eye and face protection before working with the battery. Keep children away from the battery.
5. Inspect the battery. If there is a protective rubber cover on the positive terminal, make sure it is intact. The housing must completely cover the terminal. Inspect the terminals for signs of corrosion or looseness, and also make sure there are no cracks in the housing. Check the battery clamp is secure. Inspect the cables along their entire length for chafing and cracking of their insulation (see illustration).
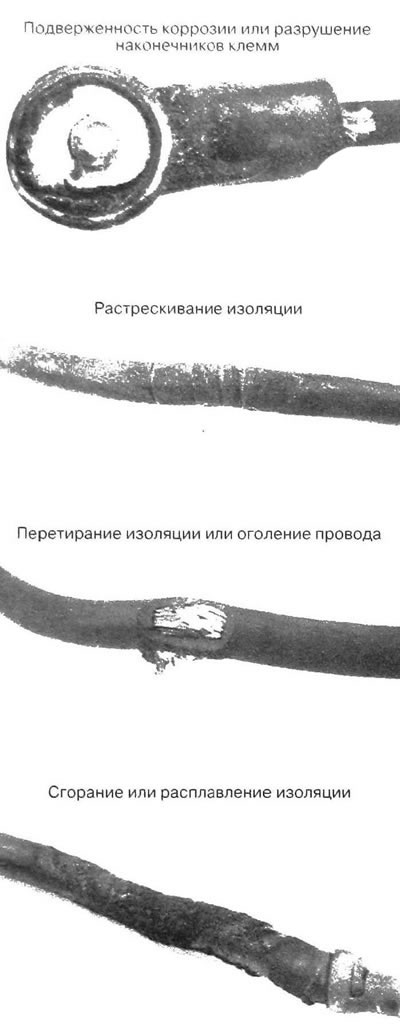

11.5. Typical battery cable defects
6. If there are signs of corrosion in the form of white, loose deposits around the terminals, the battery should be removed for cleaning. Loosen the cable terminal bolts using a wrench and, disconnecting the negative terminal first, remove the cables from the battery terminals. Then unscrew the retaining clip, remove the clip and remove the battery from the engine compartment.
7. Clean the battery terminals using a special brush or tool and a warm water solution of baking soda. Wash the contacts and top panel of the battery with the same solution, preventing the solution from penetrating into the battery. When cleaning the terminals, contacts and top panel of the battery, wear a protective mask and rubber gloves to protect your eyes, face and hands from electrolyte and corrosive deposits. To perform these procedures, wear old work clothes, as the electrolyte will burn holes when it gets on the fabric. If the terminals are highly corroded, use a special tool to clean them (see illustrations). Wash all cleaned areas and parts thoroughly with plain water.

11.7a. Fixture shown (available in car dealerships) used for cleaning contacts on batteries with side terminals

11.7b. For finishing, a brush is used, located on one side of the device

11.7c. When using any type of device, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the battery contacts until a shine appears on their surface
8. Make sure the battery tray is in good condition and the battery clamp bolts are tight. If the battery is to be removed from the tray, make sure that there are no tools or parts on the bottom of the tray when reinstalling it. Do not use excessive force when tightening the battery clamp bolts.
9. Metal brackets for attaching the battery to the body that are exposed to corrosion should be treated with sandpaper, coated with a zinc or copper-based primer, and painted.
10. A detailed description of the procedure for removing and installing the battery is given in chapter 5. The procedure for starting the engine with an additional battery is given at the beginning of this manual.
Charger
Warning: Charging a battery produces gas containing flammable and explosive hydrogen. Do not smoke near a battery that is charging or has recently been charged, and do not allow open flames near the battery. Staying near a charging battery is only permissible while wearing a protective mask or goggles. Before connecting or disconnecting the battery from the charger, make sure it is unplugged.
Note: Manufacturers recommend that you always remove the battery from the vehicle for charging, as the gas released may damage the paintwork. Emergency charging without disconnecting the battery cables may result in damage to the electrical system.
11. Slow current charging is the best way to restore a battery that is so discharged that it has lost the ability to start the engine. This method is also recommended for charging the battery of a car that is used for short trips. Maintaining a proper battery charge level is especially important in winter, when more energy is required to start the engine and the vehicle's electrical equipment is used more intensively.
12. Chargers with a current of two amperes are most suitable (sometimes they are called «jet»), Such devices are safe and charge the battery evenly with a low current. These chargers are also relatively cheap. For fast charging, you can use devices with a higher current intensity, but do not charge the battery with devices with a current intensity of more than 10 Ah. Forced charging, which restores battery voltage in 1-2 hours, has a strong impact on the battery and can damage an old or worn battery. Charging in this mode should only be used in emergency situations.
13. The average time required to fully charge the battery is usually indicated in the instructions for the charger. Usually «inkjet» devices charge the battery in 12-16 hours.
14. Remove the caps of all cans (if their presence is provided for by the design) and cover the holes with a clean cloth to prevent electrolyte from splashing. Disconnect the negative battery cable and connect the charger electrodes to the battery terminals (positive electrode to positive terminal and negative electrode to negative terminal), then turn on the device. Make sure the charger switch is in the "12 Volt".
15. When using a device with a charging rate of more than 2 Ah, you must constantly monitor the battery for overheating. When using an inkjet device, it is possible to monitor the battery for overheating during the first two hours of the process, after which you can leave the battery to charge overnight.
16. If the battery has removable caps on the cans, in the last hours of the charging process the density of the electrolyte should be monitored with a hydrometer. A hydrometer is an inexpensive and accessible device that can be purchased at most auto stores (When using, follow the accompanying instructions). Charging is considered complete if the density does not change within two hours and the electrolyte in the jars boils. The density of the electrolyte after charging the battery should be almost the same in all banks. If this condition is not met, the battery banks may be damaged.
17. Some batteries do not have cell caps, but are designed to have a built-in charge indicator. As a rule, the indicator of a fully charged battery is bright. If the indicator is dark, the battery still needs charging.
18. If the design of the battery does not provide for the presence of cell caps and a built-in charge indicator, then to assess the degree of charge it is necessary to connect it to the contact terminals of a voltmeter. The voltage of a fully charged battery is more than 12.5V.
19. For more information about the battery and the method of starting the engine from an additional battery, see chapter 5, and also at the beginning of this manual.
