Each axle shaft has two constant velocity joints: internal and external. The outer pivot has a double cage design with balls to allow for angular movement (see illustration). The inner joint has three pins with rollers allowing for angular movement and allowing the axle shaft to move in and out.
The CV joints are protected by rubber boots, which are held in place by clamps so as to protect the joints from water and dirt. Protective covers should be checked periodically (see chapter 1, section 13). Damaged boots must be replaced immediately, otherwise the hinges may be damaged. When replacing protective covers, remove the axle shafts (see section 2). It is also recommended to disassemble, clean, inspect, sort out the constant velocity joint at each boot change and ensure that it does not become contaminated with moisture or dirt, which can cause premature failure of the joint.
The most common symptom of wear or damage to constant velocity joints other than lubrication leaks is crackling and clicking noise when turning, a dull metallic sound when accelerating, or vibration when driving.
Note. If the vehicle is equipped with a Delco Loc II audio system, be sure to disable the system lock before carrying out any operation to disconnect the battery.
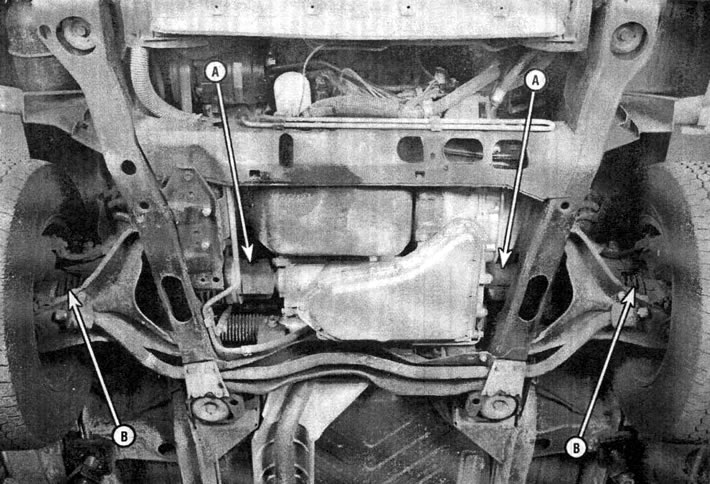
1.2. Two types of constant velocity joints used on each of the axle shafts: A - internal constant velocity joint, B - external constant velocity joint
