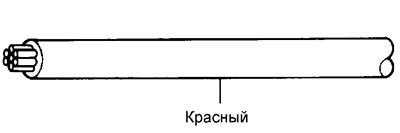
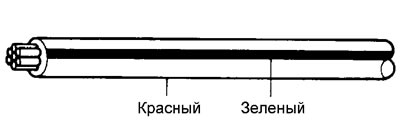
Wire Color Codes
Wire colors are indicated in capital Latin letters. The first letter indicates the main color of the wire, the second letter indicates the color of the strip.
| Designation | Color | |
| VC | BLK | black |
| OG | ORN | orange |
| BN | BRN | brown |
| RK | PNK | pink |
| GN | GRN | green |
| TN | TAN | yellow-brown |
| LB | LT BLU | blue |
| RD | RED | red |
| PU | PPL | purple |
| GY | GRY | grey |
| VT | violet | |
| BU | BLU | blue |
| WH | WHT | white |
| L-GN | LT GRN | light green |
| YE | YEL | yellow |
| D-BU | LT BLU | Navy blue |
| D-GN | DKGRN | dark green |
 |  |
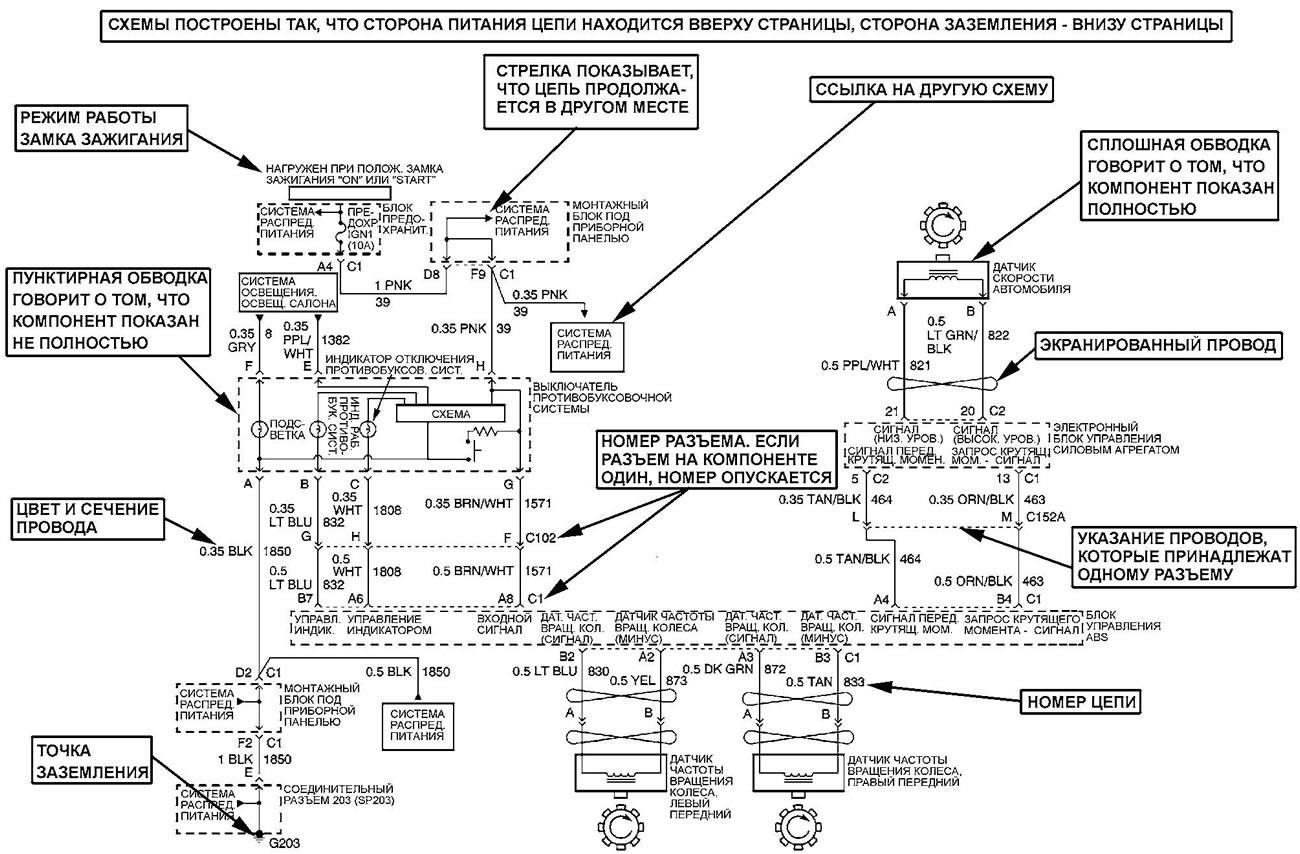
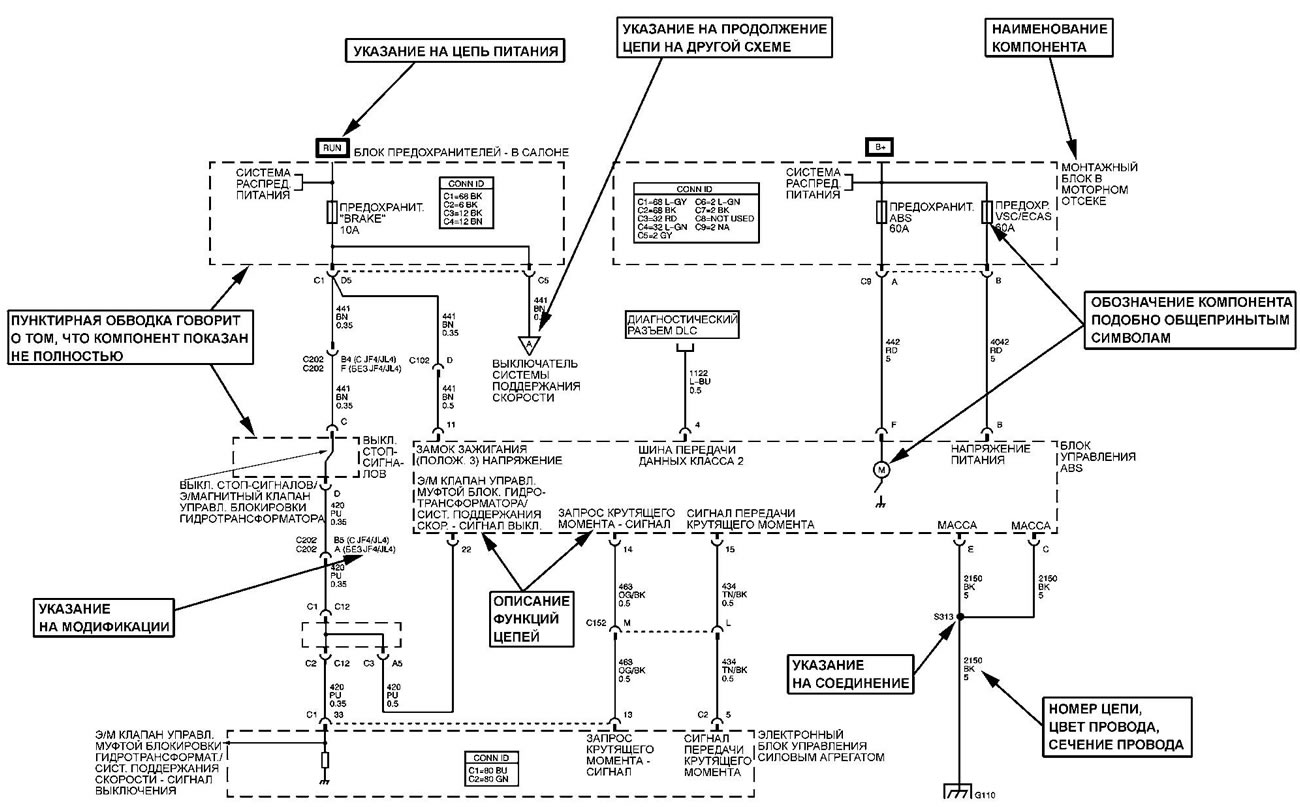
Connectors, grounding points and connections
Note: Not all connectors can be repaired. Some connectors are only replaced with the wiring harness. A typical example is the wiring connectors of the passive safety system. Always check the ownership of the connector.
The connectors are numbered as follows:
- Connectors located in the engine compartment are numbered C100 series.
- Connectors located in the instrument panel area are numbered C200 series.
- The connectors located on the body are numbered in the C300 series.
- Remote connectors are serial numbered C400.
- Grounding points and grounding sockets are identified by the letter "G" and have a serial number like the wiring connectors.
- Places of permanent connections are indicated by the letter "S" and have a serial number like the wiring connectors.
- Component connectors are identified by the name of the component instead of numbers. If a component has more than one connector, additional numbers are used for identification, such as C1, C2, etc.
Diagnostics and verification
When troubleshooting an electrical circuit, you need to have a few common tools. These tools are listed below.
A jumper is a single wire used to connect two points in a circuit. Used to bypass an open circuit.
Voltmeter - used to check the voltage in the circuit. Always connect the black probe to a good "earth", the red probe - to the positive point of the circuit.
Attention: the voltmeter must have an input resistance of at least 10 MΩ.
An ohmmeter is used to test the resistance between two points in a circuit. Low or no resistance in a circuit means good conduction.
Attention: the ohmmeter must have an input resistance of at least 10 MΩ. Also, when testing resistance, always turn off the power to the part under test, otherwise the instrument may be damaged or incorrect data may be obtained.
Adapters - these tools are used when checking terminals (conclusions) connector (pic. 1). Select an adapter according to the size of the terminal and install it on the probe of the meter.
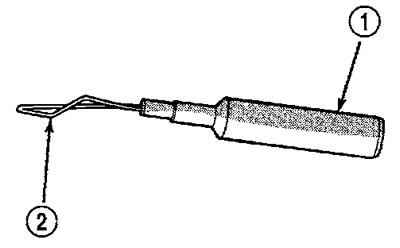
Pic. 1. Adapter. 1 - probe end, 2 - terminal end
Lost and bad contact
Most problems in electrical circuits are caused by faulty connectors or wiring. Check the following before making a judgment on a component or wiring fault:
- Reliability of connection of connectors.
- Connector pin status (landing in the connector, dirt, corrosion).
- Connector housing condition.
- Wire insulation condition (cuts, abrasions).
Troubleshooting in the wiring
Note: When troubleshooting the wiring, try to follow the steps below, it will make the troubleshooting easier. Before any diagnostics, always check self-installed equipment included in the problem circuit, it is advisable to disable this equipment altogether.
1. Correctly formulate the problem.
2. Check for any related symptoms. To do this, check all the components included in this circuit, use the circuit diagrams.
3. Analyze the symptoms of a malfunction, determine the section of the circuit in which a malfunction with these symptoms is most likely to occur.
4. Isolate the problem area.
5. Make any necessary repairs.
6. Check the operation of all components of this circuit.
Voltage measurement
1. Connect the negative voltmeter probe to a known good "earth" (pic. 2).
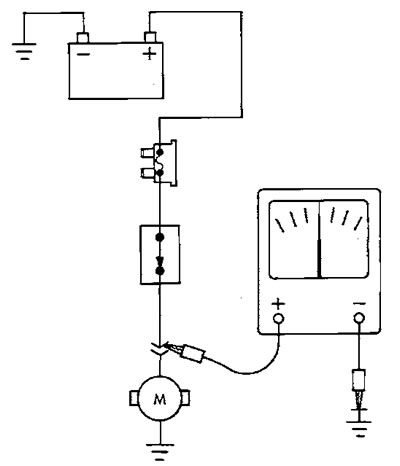
Pic. 2. Voltage measurement
2. Connect another voltmeter probe to the point in the circuit to be tested. In some cases it will be necessary to turn on the ignition.
Conductivity test
1. Remove the fuse for the circuit under test or disconnect the battery.
2. Connect the ohmmeter probes to the test points of the circuit (pic. 3). Low or no resistance means good conduction.
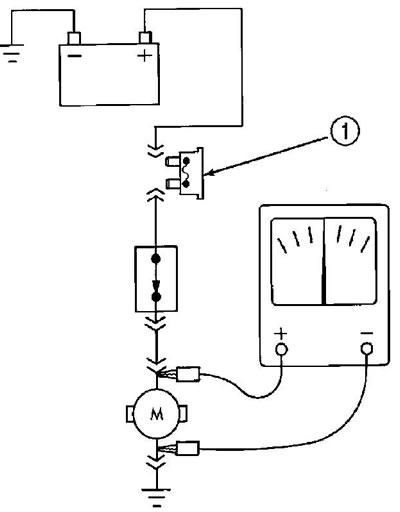
Pic. 3. Conductivity test. 1 - removed fuse
Search for a short circuit on "earth"
Method 1
1. Remove the fuse and disconnect all components of the circuit protected by the fuse.
2. Connect a control lamp or the voltmeter to contacts of a socket of a safety lock.
3. Starting at the fuse box, wiggle the wire harness approximately every 15 to 20 cm and observe a voltmeter or test light.
4. If the voltmeter reads voltage or the test light comes on, there is a short to power in that area of the wiring harness "earth".
Method 2
1. Disconnect all components of the circuit whose fuse has blown.
2. Replace the blown fuse.
3. Turn on the ignition.
4. Start connecting circuit components one by one. When the fuse burns out, we can say that a section of the circuit with a short circuit has been found.
Voltage drop test
1. Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the side of the circuit closest to the battery (pic. 4).
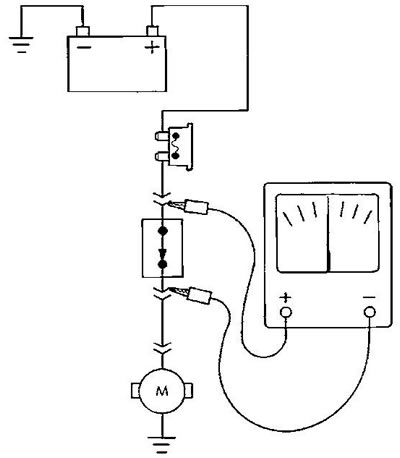
Pic. 4. Voltage drop test
2. Connect another voltmeter probe to the point in the circuit to be tested.
3. The voltmeter will show the voltage difference between the two points.
Connectors
Terminal replacement
1. Disconnect the battery.
2. Release the connector lock.
3. Disconnect the halves of the connector.
4. Remove the protective cover (if applicable) (pic. 5).
5. If necessary, release the secondary clamp on the connector terminals.
6. Using the special tool, release the primary retainer of the connector terminal, pull on the wire and remove the terminal from the connector housing.
7. Installation is carried out in the reverse order.
8. After connecting the battery and check the operation of the system.
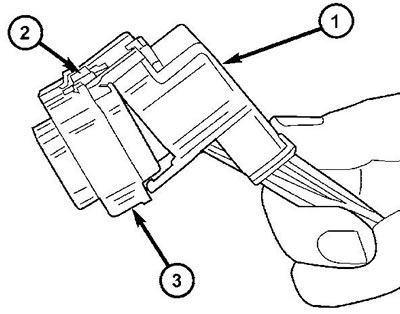
Pic. 5. Removing the connector cover. 1 - cover, 2 - connector lock, 3 - connector
Diode
Withdrawal
1. Disconnect the battery.
2. Locate the diode in the wiring harness and remove the protective cover.
3. Remove the diode. Pay attention to the direction of electric current flow (pic. 6).
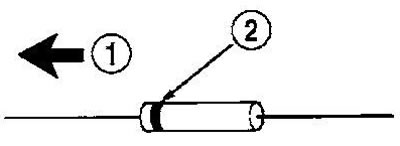
Pic. 6. Diode identification. 1 - electric current, 2 - the strip around the diode indicates the direction of the electric current
Installation
1. Remove the wire insulation so that you can solder a new diode.
2. Install the diode in the wiring harness in the direction of current flow. If necessary, refer to the corresponding circuit diagram.
3. Solder the diode. Use only rosin as a flux. Do not use acid flux.
4. Secure the diode to the harness with electrical tape.