2. Visually inspect the block for cracks and corrosion. Check the condition of the threads, if necessary, restore the stripped thread. It is recommended to check for internal defects in the cylinder block in a car service. If defects are found, replace the cylinder block.
3. Check up presence of chips and scuffs on internal surfaces of cylinders.
4. Measure the inner diameter of the cylinder at the top (right under the ridge), in the middle and in the lower part parallel to the axis of the crankshaft. Check the ovality and taper of the cylinders (see photo).

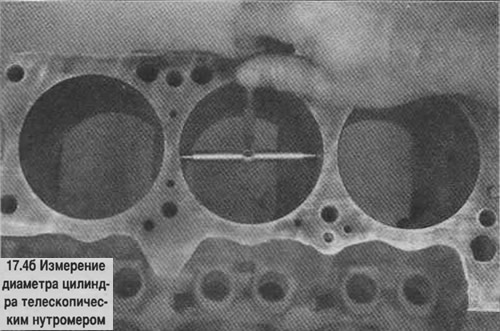
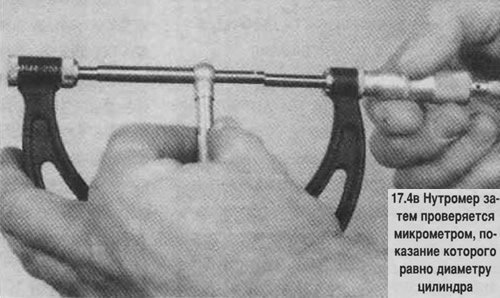
Attention! For measurements, the cylinder block must be removed from the stand, otherwise the measurements will be inaccurate due to block deformation.
5. The taper of the cylinder is defined as the difference between the diameters in the upper and lower planes. Cylinder out-of-roundness is defined as the difference between diameters measured perpendicular to and parallel to the crankshaft axis. Compare the measurement results with the standard values.
6. If there are severe scuffs and scratches on the surfaces of the cylinders, or the ovality and taper of the cylinders exceed the norm, then the block must be handed over to the workshop for boring and honing. After restoring the block, pistons and rings of repair sizes will be needed.
7. If the condition of the cylinders is acceptable, the wear of the cylinder does not exceed the norm, and the gap between the cylinder and the piston can be restored by replacing the piston, then only the cylinders need to be honed.
