Removal and installation. If only the oil pump needs to be repaired, remove the engine from the vehicle (see subsection «Removal and installation of the engine»), place on a turntable, drain the crankcase, turn the engine over and remove the crankcase. Then turn away bolts of fastening of the oil pump and remove it together with a receiving branch pipe.
Install the oil pump on the engine in the reverse order of removal.
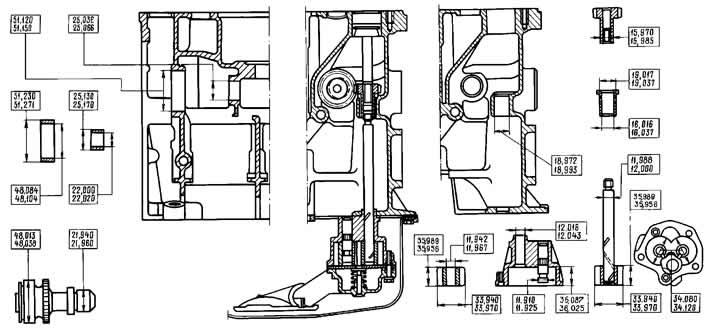
Pic. 2-68. The main dimensions of the parts of the oil pump and its drive.
Disassembly and assembly. Secure the oil pump in a vise, being careful not to damage the housing, and then:
- unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the intake pipe together with the oil pressure reducing valve;
- remove cover 3 (pic. 2-69) pump housing and remove the pump shaft with drive gear and driven gear from the housing.
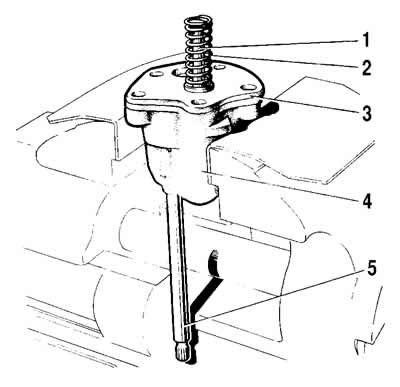
Pic. 2-69. Oil pump disassembly:
1 - pressure reducing valve;
2 - valve spring;
3 - cover;
4 - body;
5 - roller.
To assemble, secure the pump housing carefully in a vise and proceed as follows:
- install the drive gear with the roller in the pump housing, put the driven gear on the axle in the housing;
- install the pump cover, pressure reducing valve with spring and attach the suction pipe to the pump body.
Note. After assembling the pump, when turning the drive shaft by hand, the gears should rotate smoothly and without jamming.
Checking pump parts. After dismantling, wash all pump parts with kerosene or gasoline, blow with compressed air, and then inspect the pump housing and cover; if there are cracks, replace the parts with new ones.
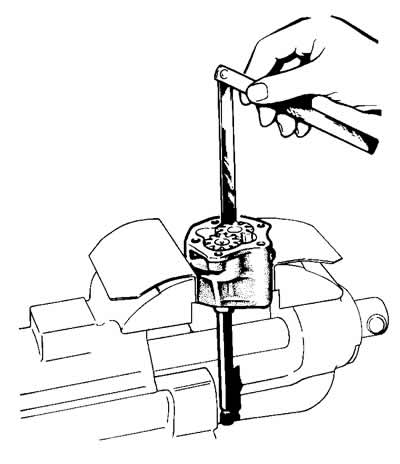
Pic. 2-70. Checking the radial clearance in the oil pump.
Check with a set of feelers the gaps between the teeth of the gears, as well as between the outer diameters of the gears and the walls of the pump housing (pic. 2-70), which should be respectively 0.15 mm (maximum allowable 0.25 mm) and 0.11-0.18 mm (maximum allowable 0.25 mm). If the clearances exceed the maximum allowable values, then replace the gears, and, if necessary, the pump housing.
Feeler and ruler (pic. 2-71) check the gap between the ends of the gears and the plane of the housing, which should be equal to 0.066-0.161 mm (maximum allowable 0.20 mm). If the clearance is greater than 0.20 mm, replace the gears or pump housing, whichever is worn.
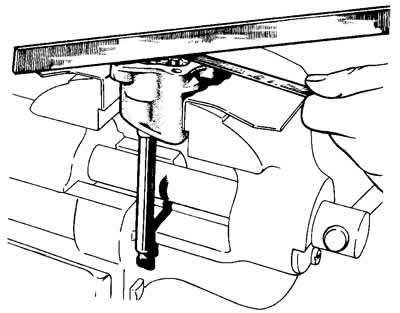
Pic. 2-71. Checking the axial clearance in the oil pump.
After measuring the details, determine the gap between the driven gear and its axis, which should be 0.017-0.057 mm (maximum allowable 0.10 mm), as well as between the pump shaft and the hole in the housing. This gap should be 0.016-0.055 mm (maximum allowable 0.10 mm). If the clearances are out of tolerance, replace the worn parts.
Pressure reducing valve check. When repairing the oil pump, check the pressure reducing valve. Pay attention to the surfaces of the valve and the orifice in the suction pipe, as possible contamination or deposits on the mating surfaces can cause the valve to stick.
The mating surfaces of the valve and pump cover must be free of nicks and burrs, which can lead to a decrease in oil pressure in the system.
Check up elasticity of a spring of the reducing valve, compare the received data with resulted on fig. 2-72.
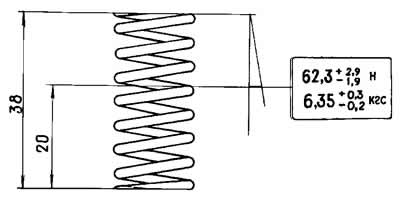
Pic. 2-72. Basic data for checking the pressure reducing valve spring.
