Device Features
The main dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group are given in fig. 2-34.
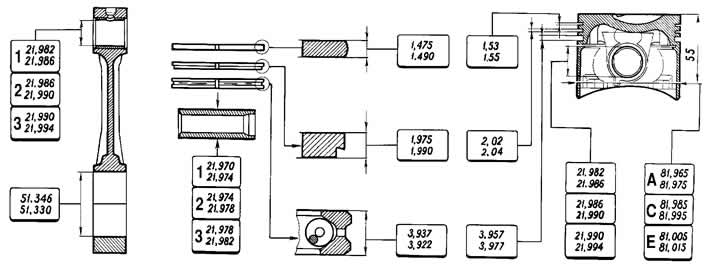
Pic. 2-34. The main dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group
The piston is cast aluminium. In the manufacture of the mass of pistons is strictly maintained. Therefore, when assembling the engine, it is not required to select pistons of the same group by weight.
The outer diameter of the pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) through 0.01 mm. The outer surface of the piston has a complex shape. It is barrel-shaped in height and oval in cross-section. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 55 mm from the piston crown.
According to the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, pistons are divided into three classes (1, 2, 3) through 0.004 mm. Piston diameter classes and piston pin bores are stamped on the piston crown (pic. 2-35).
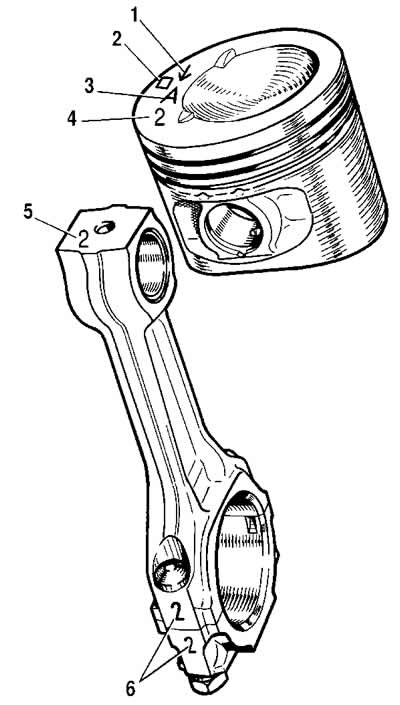
Pic. 2-35. Piston and connecting rod markings:
1 - arrow for orienting the piston in the cylinder;
2 - repair size;
3 - piston class;
4 - hole class for the piston pin;
5 - connecting rod class according to the hole for the piston pin;
6 - cylinder number.
Pistons of repair dimensions are manufactured with an outer diameter increased by 0.4 and 0.8 mm. On the bottoms of these pistons, markings are made in the form of a triangle or square. A triangle corresponds to an increase in the outer diameter of 0.4 mm, and a square corresponds to 0.8 mm.
The arrow on the bottom of the piston shows how to correctly orient the piston when it is installed in the cylinder. It should be directed towards the camshaft drive.
Piston pin - steel, hollow, floating type, i.e. rotates freely in the piston bosses and the connecting rod bushing. The pin is fixed in the piston with two steel retaining rings.
According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three classes through 0.004 mm. The class is marked with paint on the end of the finger: the blue mark is the first, the green mark is the second, and the red mark is the third class.
Piston rings are made of cast iron. The top compression ring is with a chrome-plated barrel-shaped outer surface. Bottom compression ring scraper type. Oil scraper ring - with chrome-plated working edges and with an expanding coil spring (expander).
On rings of the repair sizes digital marking is put «40» or «80», which corresponds to an increase in the outer diameter of 0.4 or 0.8 mm.
Connecting rod - steel, forged. The connecting rod is machined together with the cover and therefore they are not interchangeable individually. In order not to confuse caps and connecting rods during assembly, the number 6 is stamped on them (see fig. 2-35) the cylinder in which they are installed. When assembling, the numbers on the connecting rod and the cover must be on the same side
A steel-bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod. According to the diameter of the hole of this bushing, the connecting rods are divided into three classes through 0.004 mm (just like pistons). Class number 5 is stamped on the upper head of the connecting rod.
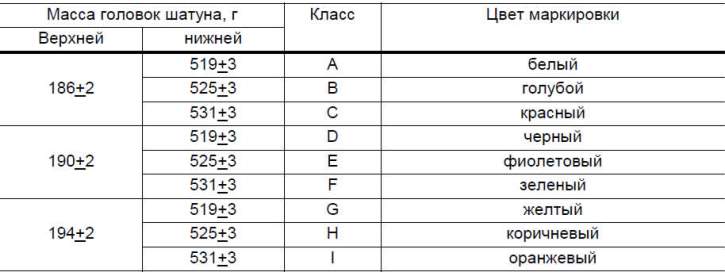
By the mass of the upper and lower heads, the connecting rods are divided into classes (tab. 2-1), marked with paint on the rod of the connecting rod. Connecting rods of the same weight class must be installed on the engine. You can adjust the mass of connecting rods by removing metal from the bosses on the heads to the minimum sizes of 16.5 and 35.5 mm (pic. 2-36).
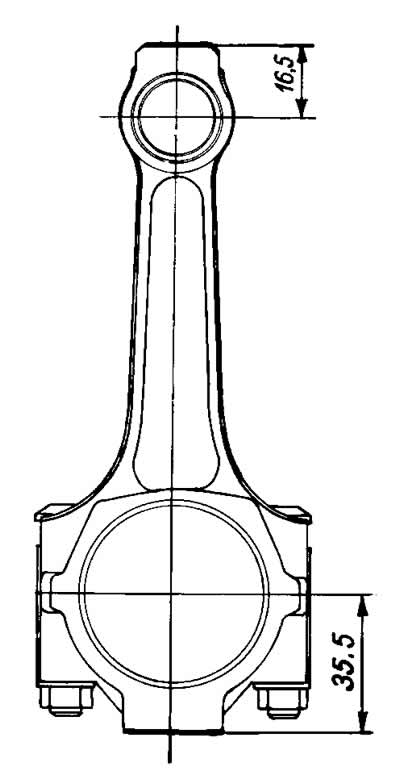
Pic. 2-36. Places where it is allowed to remove metal, when adjusting the mass of the upper and lower connecting rod heads.
Table 2-1. Connecting rod classes by weight of the upper and lower heads
Piston to cylinder selection
Estimated minimum clearance between piston and cylinder (for new parts) equal to 0.025-0.045 mm. It is defined as the difference between the minimum cylinder size and the maximum piston size and is provided by installing pistons of the same class as the cylinders. Maximum allowable clearance (when parts are worn) - 0.15 mm.
If a used engine has a clearance greater than 0.15 mm, then it is necessary to reselect the pistons to the cylinders so that the clearance is as close as possible to the calculated one.
Pistons of classes A, C, E are supplied as spare parts. These classes are sufficient for selecting a piston for any cylinder during engine repair, since pistons and cylinders are divided into classes with a small overlap in size. For example, class B and D cylinders can be fitted with a class C piston.
Disassembly and assembly
Disassembly. Remove the piston pin circlips from the piston, remove the pin and disconnect the connecting rod from the piston. Remove piston rings.
Connecting rod bolts are pressed into the connecting rod. Therefore, in order not to disturb the fit of the bolt in the connecting rod, it is not allowed to press out the bolts from the connecting rods when disassembling the engine and the connecting rod and piston group.
If some parts of the connecting rod and piston group are not damaged and slightly worn, then they can be reused. Therefore, when disassembling, mark them in order to assemble a group with the same parts in the future and install them in the same engine cylinder.
Assembly. Before assembling, pick up a finger to the piston and connecting rod. For new parts, the class of the pin holes in the connecting rod and piston must be identical to the class of the pin. For used parts, for proper mating, it is necessary that the piston pin, lubricated with engine oil, must enter the piston bore from pressing the thumb (fig.237) and smoothly exit under its own weight from the holes of the piston bosses, while in a vertical position, as shown in Figure 2-38. If additional force is required to push the piston pin out of the piston boss holes, replace the piston pin with a smaller grade.
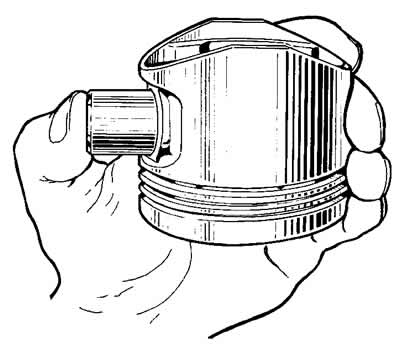
Pic. 2-37. Piston pin installation.
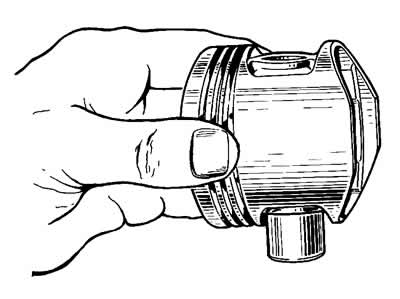
Pic. 2-38. Check piston pin fit.
If a pin of the first category was inserted into the piston, then replace the piston pin and connecting rod. The assembly of the connecting rod and piston group is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly. After installing the piston pin, lubricate it with engine oil through the holes in the piston bosses.
Install piston rings in the following order:
- Lubricate the piston grooves and piston rings with engine oil. Orient the piston rings so that the top compression ring lock is at a 45°angle to the piston pin axis, the lower compression ring lock is approximately 180°to the top compression ring lock axis, and the oil scraper ring lock is approximately 90°to the lock axis upper compression ring
- install the lower compression ring with the groove down (see fig. 2-36). If the ring is marked «Top» or «TOR», then install the ring with the mark up (to the bottom of the piston).
Before installing the oil scraper ring, check that the joint of the spring expander is located on the side opposite to the ring lock.
Checking the technical condition
Clean the piston from carbon deposits and remove all deposits from the lubrication channels of the piston and connecting rod.
Check the details carefully. Cracks of any nature on the piston, piston rings, pin, on the connecting rod and its cover are not allowed. If there are deep marks on the working surface of the liners, replace the liners with new ones.
Check the clearance between the piston rings and grooves with a set of feeler gauges, as shown in fig. 2-39 by inserting the ring into the corresponding groove. Estimated clearance (rounded to 0.01 mm) for new parts it is 0.04-0.07 mm for the upper compression ring, 0.03-0.06 mm for the lower one and 0.02-0.05 mm for the oil scraper. The maximum allowable wear gaps are 0.15 mm.
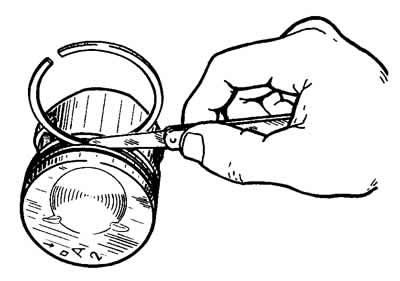
Pic. 2-39. Checking the clearance between piston rings and grooves.
Check the gap in the lock of the piston rings with a set of probes, inserting the rings into the cylinder (pic. 2-40), having a hole diameter equal to the nominal diameter of the ring with a tolerance of±0.003 mm.
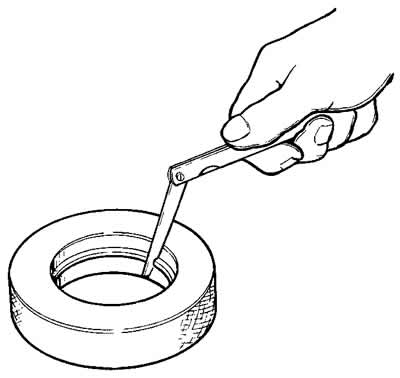
Pic. 2-40. Checking the gap in the lock of the rings.
The gap should be within 0.25-0.45 mm for all new rings. The maximum allowable wear clearance is 1 mm.
