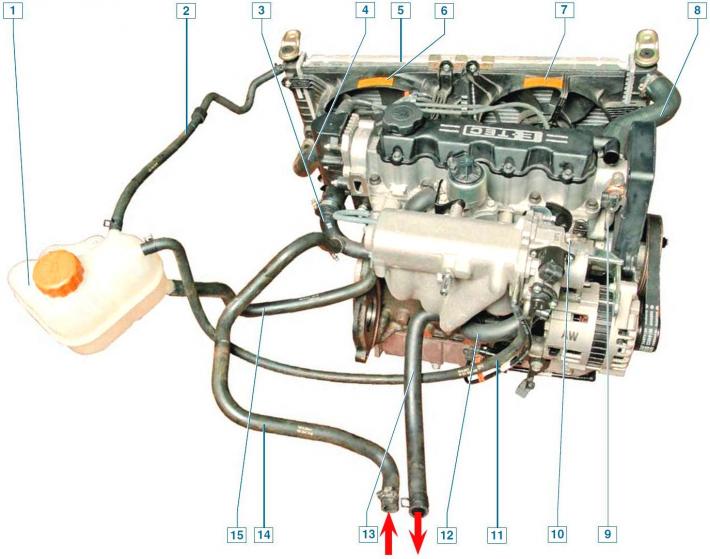
Cooling system: 1 - expansion tank; 2 - steam outlet hose of the radiator; 3 - inlet pipe of the pump of the cooling system; 4 - outlet hose of the radiator; 5 - radiator of the cooling system; 6 - fan casing; 7 - additional fan cover (only on vehicles with air conditioning); 8 - radiator inlet hose; 9 - outlet pipe of the cylinder head; 10 - coolant temperature indicator sensor; 11 - hose for draining fluid from the heating unit of the throttle assembly; 12 - bypass hose; 13 - heater supply hose; 14 - outlet hose of the heater; 15 - inlet hose of the expansion tank
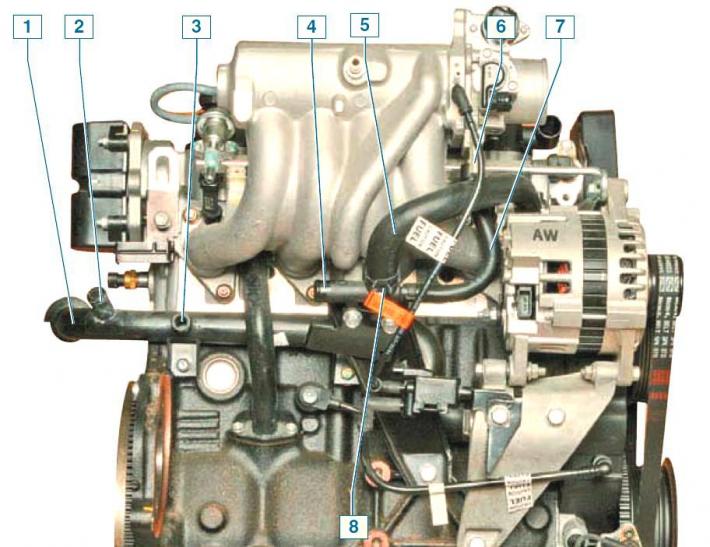
The nodes of the cooling system located on the rear of the engine: 1 - inlet pipe of the pump of the cooling system; 2 - branch pipe of the inlet hose of the expansion tank; 3 - branch pipe of the outlet hose of the heater; 4 — a branch pipe of a supply hose of a heater; 5 - bypass hose; 6 - branch pipe of the hose for draining fluid from the heating unit of the throttle assembly; 7 - hose for supplying fluid to the heating unit of the throttle assembly; 8 - tee
The cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation.
It consists of an expansion tank, a coolant pump, an engine cooling jacket, a thermostat, connecting hoses and a radiator with an electric fan.
The heater core is connected to the cooling system.
The system is filled with coolant through the neck of the expansion tank.
The expansion tank is made of translucent plastic, which allows you to visually control the coolant level.
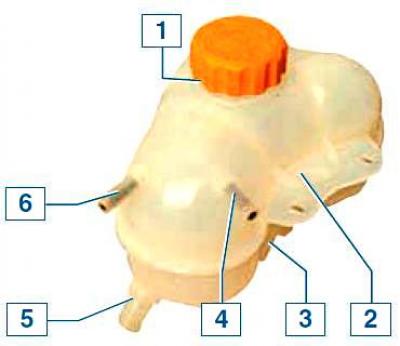
Expansion tank elements: 1 - filler cap; 2 — the top bracket of fastening of a tank; 3 — the bottom bracket of fastening of a tank; 4 - branch pipe of the radiator steam outlet hose; 5 - branch pipe of the inlet hose; 6 - branch pipe of the hose for draining fluid from the heating unit of the throttle assembly
On the wall of the expansion tank there are marks MAX and MIN, between which there should be a liquid level on a cold engine.
A steam outlet hose connecting the tank to the radiator is connected to the upper left branch pipe of the tank, and a hose for draining liquid from the throttle assembly heating unit is connected to the upper right branch pipe.
The lower branch pipe of the tank is connected by a filling hose to the inlet pipe of the pump.
The tightness of the cooling system is ensured by inlet and outlet valves in the cap of the expansion tank.
Replacing the expansion tank cap with a cap without valves, even of a suitable size and thread, will lead to an unacceptable increase in pressure in the cooling system (on a hot engine) and, as a result, to the leakage of coolant in the hose connections with nozzles.

The circulation of liquid in the cooling system is provided by a coolant pump.
The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven by a toothed timing belt.
The liquid enters the pump through a supply pipe located on the rear wall of the cylinder block under the intake manifold.
From the pump, liquid under pressure is supplied to the engine cooling jacket, and from there to the outlet pipe of the cylinder head, under which there is a thermostat.
On a cold engine, the thermostat valve is closed and blocks the outlet pipe leading to the radiator of the cooling system.
In this case, all the liquid from the cylinder head through the bypass hose (mounted on the intake manifold) enters the tee, and from it - into the heater radiator and the throttle assembly heating unit, bypassing the cooling system radiator, and then returns to the pump - a small circulation circle.
As the engine warms up, at a fluid temperature of 87°C, the thermostat valve begins to move, opening the outlet pipe of the cylinder head and passing the flow of fluid into the radiator of the cooling system.

Thermostat
At a temperature of 102°C, the thermostat valve opens completely and the liquid enters the radiator of the cooling system, where it gives off heat to the surrounding air.
The movement of fluid through the engine cooling jacket and the cooling system radiator forms a large circulation circle.
Through the heating unit of the throttle assembly and the heater radiator, the liquid circulates constantly and does not depend on the position of the thermostat valve.
The radiator of the cooling system consists of two vertically located plastic tanks connected by aluminum tubes with cooling plates arranged in one row.
The liquid enters the radiator through the pipe of the right tank, and is discharged through the pipe of the left tank.
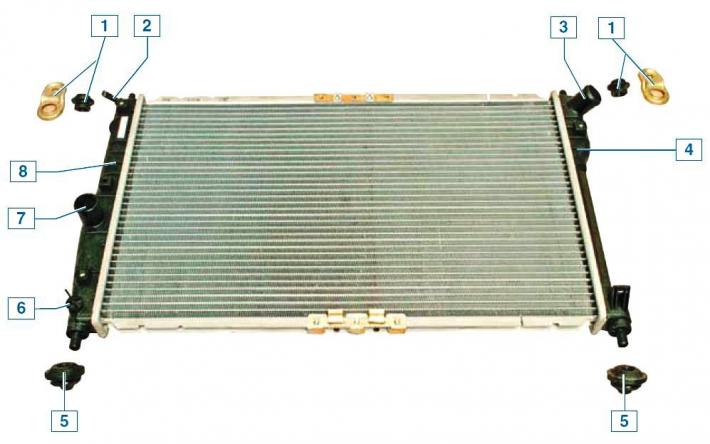
Radiator: 1 - bracket with top mounting cushion; 2 - steam outlet pipe; 3 - inlet pipe; 4 - right tank; 5 - rubber cushion of the lower mount; 6 - drain plug; 7 - outlet pipe; 8 - left tank
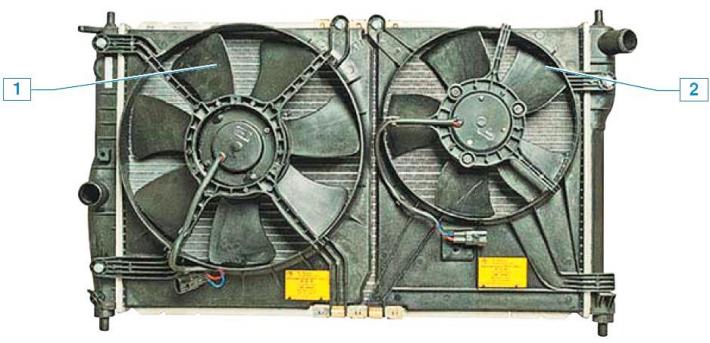
Cooling fans: 1 - main fan; 2 - additional fan (car with air conditioning system)
There is a drain hole for removing coolant.
The electric fan is installed in a casing behind the radiator.
On vehicles with an air conditioning system, two fans are installed - the main (bigger size) and additional.
The work of the main and additional (if available) fans are controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU) motor, which, through the corresponding relay, ensures the rotation of the fan impeller at two speeds.
The ECU turns on the main fan at low speed at a coolant temperature of 93°C, at high speed at 97°C, switches the fan from high to low speed at 94°C and turns it off at 90°C.
The additional fan is turned on by the computer at a low speed when the air conditioning system is turned on, and at a high speed when the coolant temperature is 97°C or the pressure in the air conditioner discharge line reaches 1882 kPa.
The coolant temperature indicator sensor is installed on the intake manifold on the right side in the direction of the vehicle (see Removal of the gauge of the index of temperature of a cooling liquid.

Coolant Temperature Gauge Sensor
The sensor provides information to the temperature gauge in the instrument cluster.
