Wheels
Automobile wheels are distinguished by design, manufacturing technology and dimensions that determine whether the wheel belongs to a given vehicle, as well as the sizes and types of tires that can be used on it.
Passenger car wheels are usually made of steel or light alloys. Light alloy cast and forged wheels are made entirely from a single piece. At the same time, cast wheels are machined directly from the casting, and forged wheels are machined from a pre-forged billet (forgings), which provides them with higher strength.
The dimensions determining for the wheel are the mounting (landing) diameter «A» and width «b» rim profile. Rim dimensions may be in millimeters, but inch is more common, such as 5.5J x 14. In both cases, the first number indicates the width of the rim, the letter J indicates its profile shape (there are also designations E, L, K), and the last digits are the mounting diameter of the wheel corresponding to the same tire size.
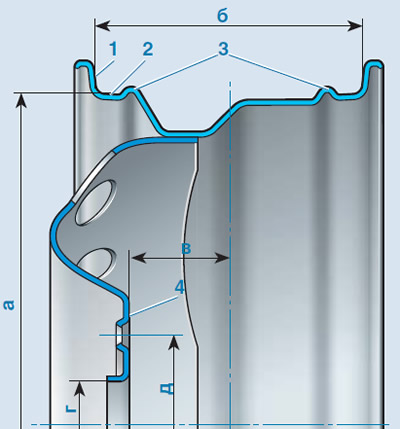
The main elements and dimensions of the wheel: 1 - rim flange; 2 - shelf; 3 - annular protrusions (humps) for additional fixation of the sides of a tubeless tire; 4 - mounting plane; a - mounting diameter; b - rim width; c - departure (distance between the plane of symmetry of the rim and the mounting plane of the wheel); d is the diameter of the central hole for the hub; d - diameter of the circle of the location of the mounting bolts
Possible additional designation H (H2) means the presence of one or two humps on the rim. Humps are called annular protrusions along the edges of the wheel rim, designed for tubeless tires. The main purpose of the humps is to securely fix the tire bead in turns in order to prevent depressurization of the wheel.
In the designations of wheels that have one hump along the outside, there is one letter H. But many wheel models are equipped with a hump along the inner edge of the rim, as indicated by the H2 index. Two humps increase the reliability of fixing the tire on the wheel, but create problems during its installation.
wheel offset (size «V») in the wheel marking it is designated as ET and is given in millimeters. Center hole diameter (size «G») and diameter of holes for fixing bolts («d») are given in millimeters and are designated, respectively, DIA and PCD.
On «Lanos» install wheels with a dimension of 5.5Jx14. Dimension of steel wheel «Lanos»...

...marked on the outside of the disc between the mounting holes.

The wheel offset is additionally marked on the wheel rim (ET49).
Complete wheel specification «Lanos» 5.5J x 14H2 4 x 100 x 56.6 ET49, where: 5.5 - rim fit width; J - profile symbol; 14 - landing diameter (in inches), on which the tire rests; H2 - the presence of two humps; 4 - the number of mounting holes; 100 - diameter of the circle of the centers of the mounting holes (PCD), mm; 56.6 - diameter of the central hole (DIA), mm; ET49 - wheel offset, mm.
The main advantage of alloy wheels over steel wheels is their lighter weight. Reducing the mass of the wheel assembly with the tire leads to a decrease in unsprung inertial masses and improves the working conditions of the vehicle suspension, since the wheel is faster «obeys» return action of the elastic suspension elements and restores lost contact with the road. This improves driving comfort and driving safety. Vehicle handling, braking dynamics are improved, slightly, but fuel consumption is reduced. Due to high manufacturing precision and material characteristics, alloy wheels better hold the tubeless tire on the rim.
Forged wheels weigh even less than cast wheels. They have a smaller wall thickness - up to 3 mm, while cast walls should be no thinner than 5.5 mm. However, forged wheels are better able to withstand bumps in the road and are more resistant to breakage and deformation.
Alloy wheels are made primarily from aluminum alloys. Magnesium is used less frequently, although wheels made of it are 0.5-1.5 kg lighter than aluminum wheels and have a better (100 times) damping ability. In addition, due to the high thermal conductivity of magnesium, it can further reduce the heating of the brake mechanisms and vehicle hubs while driving.
Aluminum and especially magnesium are highly corrosive metals. To protect the wheels, their manufacturers use expensive coatings - special varnishes of complex compositions, but this protection is not eternal, and it is very difficult to restore it. It is possible to damage the varnish not only on a bad road or under the influence of winter salt, but also due to inept mounting / dismounting of the tire. In addition, alloy wheels are balanced with special weights that are glued to the surface of the rim. Ordinary caliper weights may simply not fit on the rounded rim flange, and rebalancing the wheel may leave scratches and corrosion spots from contact with the caliper steel.
The increased thickness of the light-alloy wheel disk does not allow the use of regular wheel bolts for its fastening. Instead, they require longer ones, which, as a rule, are purchased complete with wheels. The impact resistance of alloy wheels is higher than that of steel wheels. However, a steel wheel never collapses when deformed, and on it, if it is able to hold air in the tire, you can get to the place of repair. Light-alloy wheels with a strong impact, as a rule, simply split. In addition, if the bent steel wheel can be straightened («roll») on a special machine, then light alloy is much more difficult to restore.
Particularly dangerous in this regard are counterfeit, uncertified wheels that have not passed special strength tests. in metal «left» products may well turn out to be hidden shells, cracks, delaminations, which significantly reduces their strength. Therefore, when buying wheels in a store or on the market, you should carefully consider their markings, be interested in information about the manufacturer, and require sellers to provide a certificate for the goods.
Tires
The tire design has the following main elements.

Structural elements and main dimensions of tires: D - outer diameter; H is the height of the tire profile; B - tire profile width; d - landing diameter of the tire; 1 - frame; 2 - breaker; 3 - protector; 4 - sidewall; 5 - board; 6 - bead wire; 7 - filling cord
Carcass 1 is the main strength element of the tire, which gives it strength and flexibility, and also determines many performance properties. Represents several (usually four) layers of rubberized cord: textile or a combination of textile and steel. In the carcass of a radial tire, all the cords are parallel - along the radius from one side to another.
Breaker 2 - cushion layer (belt), which is a rubber-fabric or metal-cord layer around the entire circumference of the tire between the carcass and tread.
Protector 3 — «running» the part of the tire that is in direct contact with the road. It is a thick layer of wear-resistant rubber, the inside of which is a solid strip, and the outside is embossed, i.e. covered with pattern.
This figure determines the purpose of the tire and its suitability for operation in certain road conditions.
According to the type of tread pattern, tires can be divided into road, all-season (universal), winter tires, including those designed to install anti-skid studs, tires for off-road driving, as well as sports and racing tires.
Sidewall 4 - thin (1.5-3.0mm) rubber layer on the sidewalls of the tire. Together with the carcass, it performs a bearing function, protects the carcass from mechanical damage, moisture penetration, and also serves to mark the tire.
Bead 5 - part of the tire, designed to fix it on the wheel rim. It consists of a layer of cord wrapped around a wire bead ring 6 and a rubber filler cord 7. The beads prevent the tire from stretching and provide its structural rigidity at nominal internal air pressure.
For tubeless tires, the internal volume is sealed with an airtight rubber layer applied to the inner layer of the carcass, and the valve is inserted into the hole in the wheel rim.
Tubeless tyres, when punctured, especially small ones, do not lose air as quickly as tube tyres. However, in some cases, the puncture can be sealed without removing the tire from the wheel.
We recommend that you purchase a tubeless tire repair kit and carry it with you in your car, especially when traveling away from tire shops. In this case, you should definitely take a tire pump or an electric compressor with you.
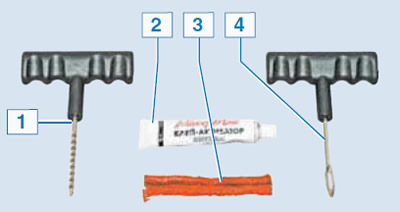
Tubeless Tire Repair Kit: 1 - a tool for cleaning the hole; 2 - glue-activator; 3 - repair inserts (flagella); 4 - tool for inserting a repair insert
In this way, only small punctures in the tread area can be repaired. For tire sidewall repair, this method is unacceptable.
To determine the puncture site, it is necessary to inflate the tire and moisten its surface with water. The puncture site will be better seen if car shampoo is added to the water or a soapy solution is applied.

We remove the object that pierced the tire. By applying a few drops of activator glue to the hole cleaning tool.

... we clean the walls of the hole by introducing into it (3-4 times) tool approximately at the same angle at which the object that pierced the tire was located.
We insert the flagellum into the needle head of the tool for inserting the repair insert and align the ends of the flagellum. We apply glue-activator on the flagellum.
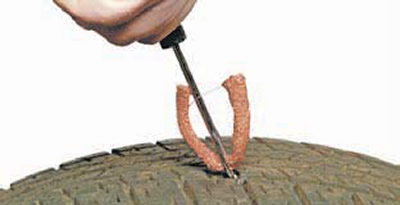
We insert the tool with the flagellum into the repaired hole so that the ends of the flagellum protrude outward by about 10-15 mm.
Carefully remove the tool from the hole, making sure that the flagellum remains in the hole.

Cut off the protruding ends of the flagellum «flush» with tread surface.
We bring the pressure in the tire to normal with the pump - the wheel is ready for operation.
For cars «Lanos» tubeless radial tires with a dimension of 185/60 R 14 are installed.

Vehicle tire marking «Lanos»
Deciphering the designation 185/60 R 14 82H: 185 - conditional width of the tire profile (IN), mm; 60 - tire profile height ratio (H) to width (IN), %; R is the designation of the radial tire; 14 - landing diameter in inches; 82 - conditional tire load capacity index (475 kgf); H - tire speed index (210 km/h).

The sidewall of the tire is also marked «Radial» - radial tire and «Tubeless» - tubeless tire design.
The dimensions of the wheels and tires are determined by the car manufacturer, and these standards should not be deviated from, since they contain the nominal indicators of stability, handling, and cross-country ability of the car in the entire range of its speeds. Only the tire tread pattern is not stipulated, which each owner chooses independently, based on specific operating conditions, season, driving style, as well as their financial capabilities. However, in any case, the tires used must strictly comply with the parameters specified by the car manufacturer: geometric dimensions, load capacity and maximum speed.
Checking the condition and caring for tires
Wheels and tires should be inspected regularly for damage (cuts, punctures), remove foreign objects stuck in the tread blocks or between them. On the outer sidewalls of tires, cracks, scuffs on curbs during unsuccessful parking can occur. Tires should also be inspected for tread wear, especially one-sided or uneven tread wear.
In motion, the condition of the tires is monitored by the vehicle's ability to «keep the road» at high speed. If vibrations, lateral slip or «yaw» vehicle, stop immediately and check the condition of the tires. Most often, the cause is a decrease in pressure in one or more tires, which must be brought to normal, since under reduced pressure, the tire structural elements do not work correctly, overheating, accelerated wear and destruction of the tire from the inside occur. It is recommended to check the tire pressure daily before the first ride. In practice, drivers do this much less often, however, modern tire designs make it possible to maintain pressure at the required level for quite a long time and «forgive» inattention to the run even in 2-3 thousand km. However, at least once every one to two weeks, the tire pressure (including the spare wheel) it is recommended to check and bring to the norm.
The pressure should be controlled only on «cold» tire, because after a trip, especially a long trip, at high speed and in hot weather, the pressure is usually higher than normal. In this case, it should not be reduced.
The service life of tires is usually not specified by the manufacturers of the tires themselves and automobiles, since it strongly depends on the operating conditions and driving style. The average driver, buying new tires, has the right to count on about 40-50 thousand km of their run, neat, thrifty - on 70-80 thousand km. Driving on rough roads, on over-inflated or under-inflated tires, hitting obstacles, frequent sharp accelerations and braking, high speeds, vehicle overloads accelerate tire wear by 20-50%.
Operation of tires with detached tread, carcass, breaker, swelling on the sidewalls («hernias»), with deep damage exposing the cord, is prohibited. A worn tire should be immediately, without waiting for its emergency destruction, replaced with a new one.
Tire storage
It is not recommended to rearrange sets of tires on a single set of wheels every season: the bead ring is stretched, rubber damage is inevitable, it is not easy to maintain the accuracy of the initial installation, as a result, balance is disturbed, wear progresses. It makes sense to purchase a separate set of wheels for winter (or summer) tires. By the way, this will speed up «changing shoes» car, and at the same time it will save the wheels, especially if it is equipped with light-alloy ones - beautiful and expensive. Of course, it is desirable to use them in summer: in winter, the advantages of light wheels for high-speed driving are not so noticeable, and their appearance may suffer from contact with deicing agents or objects invisible in the snow.
If the wheels are still beaded, we recommend that you mark each tire and the wheel on which it is installed. It is best to store the tires removed from the wheels in a standing position, not hanging or stacking. Tires mounted on wheels, on the other hand, should not be stored upright. It is better to store them hung on wire hooks or stacked. especially «greenhouse» Tire storage conditions are not required. The ideal temperature for them is 15-25°C, the absence of nearby sources of heat and direct ultraviolet radiation, including sunlight. Avoid contact of tires with oils, greases, paint, fuel and other similar substances, as well as the formation of condensation on them - take care of ventilation of the storage. Upright tires should be rotated every four months.
When the car is parked on wheels for a long time, it is sometimes necessary to check the tire pressure and roll the car a short distance so that the surface of the tires does not deform.
