
We mark the relative position of the covers and the generator stator.

With an awl or scriber, we push two pins fixing it inside the plastic cover..

... and remove the cover.

Using the same tool, we push two fixing pins inside the protective cover of the rear bearing of the generator..

... and remove the cover.

With the "E8" head, we unscrew the three screws that tighten the front and rear covers of the generator.

We remove the rear cover assembly with the stator, pushing the bearing out of the cover.
Loosen the pulley mounting nut.
This work can be done in two ways.
In the first method, we put a "24" head on the pulley fastening nut.
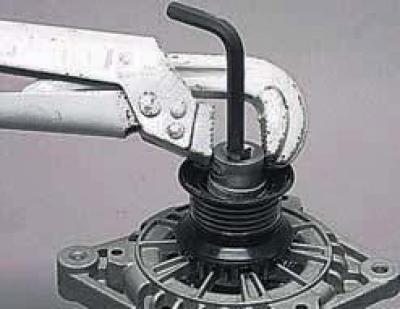
Holding the rotor shaft with an "8" hexagon and turning the head with a pipe wrench, unscrew the nut.
In the second method, we put a "24" head with a collar on the nut.

Holding the rotor from rotation by hand, we strike with a hammer on the knob and unscrew the nut.

We remove the pulley from the rotor shaft..

...and a bushing.

With a hammer with a plastic striker, we knock out the rotor shaft from the bearing.

We remove the spacer sleeve from the rotor shaft..

...and a fan impeller.
Using a screwdriver, we unbend the ends of the leads of the rectifier unit..

... and solder the leads of the stator winding from the leads of the rectifier unit.

We disconnect the stator and the rear cover of the generator.

Pushing out two pins..

... and remove the plastic reflective washer.

Using the "8" head with an extension, unscrew the nut securing the output of the "BAT" terminal (contact bolt) …

... and take out the contact bolt.

Using the "E6" head with an extension, we unscrew the four screws securing the rectifier unit and the brush holder with a voltage regulator and remove them from the cover.
We unbend the end of the output of the rectifier block..

... and solder the output of the voltage regulator from the output of the rectifier unit.
Remove the voltage regulator.

Releasing the three latches with a screwdriver,

... remove the brush holder cover.

We take out the brush assembly from the brush holder.

To remove the second brush, solder its output from the output of the voltage regulator.
To replace the front cover bearing..

... we press out the bearing with a suitable piece of pipe or a tool head, transferring force only to the outer ring of the bearing.
To check the rotor winding for open and short circuit..

... we connect the ohmmeter probes to the slip rings.
We measure the resistance of the rotor winding, which should be in the range of 1.7–2.3 ohms.
If the resistance is less than specified, then the rotor windings are closed to each other, if the resistance is very large (tends to infinity), which means that there is a break in the rotor windings.
In both cases, the generator rotor must be replaced.
To check if the rotor windings are shorted to ground..

... we connect the ohmmeter probes to the rotor housing and alternately to the slip rings.
The measured resistance must be very large (strive for infinity).
If the ohmmeter shows a small resistance, then the rotor windings are shorted to ground.
In this case, the generator rotor must be replaced.
To check the stator windings for an open..

... with an ohmmeter we alternately measure the resistance between all the terminals of the windings.
If the measured resistance tends to infinity, then there is an open in the stator windings and the generator stator must be replaced.
To check if the stator windings are shorted to ground..

... we connect the ohmmeter probes to the stator housing and in turn to each output of the windings.
The measured resistance must be very large (strive for infinity).
If the ohmmeter shows a small resistance, then the stator windings are shorted to ground.
In this case, the generator stator must be replaced.
To check the rectifier unit..

... we connect the ohmmeter probes to the output of the rectifier unit, which is connected to the phase winding of the stator, and to the air diode radiator..
...and measure the resistance.
Then we change the probes of the ohmmeter in places and measure the resistance again.
If the ohmmeter readings are the same in both cases, then the rectifier unit is faulty and must be replaced.
Similarly, we check the other two diode circuits of the rectifier.
To test the diodes of the rectifier unit..

... we connect the ohmmeter probes to the output of the rectifier unit, which is connected to the phase winding of the stator, and to the base plate..
...and measure the resistance.
We change the probes of the ohmmeter in places and measure the resistance again.
If the ohmmeter reading does not change, then the rectifier unit is faulty and needs to be replaced.
Similarly, we check the other two diode circuits.
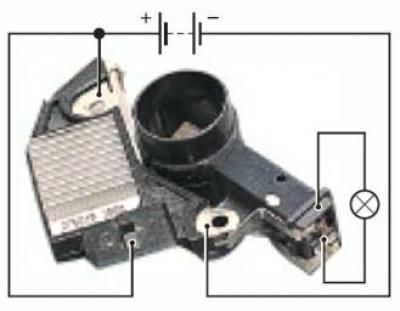
To check the voltage regulator, connect a test lamp (1-5W, 12V) between the brush holders.
We supply a voltage of 12 V from a DC source: "+" to the "L" terminal and at the same time to the "BAT" output of the voltage regulator, "-" to the second output of the voltage regulator.
We recommend inserting a screw into the hole of this output of the voltage regulator and tightening the nut to ensure contact between the outputs of the regulator and the brush.
The lamp should light up.
Then we apply a voltage of 15–16 V, while the lamp should go out.
If the lamp is lit in both cases, then the regulator is damaged; if it does not light up, there is an open in the circuit or the contact between the brushes and the regulator leads is broken.
In both cases, the regulator should be replaced.
We assemble the generator in reverse order.
For the convenience of installing brushes on slip rings when connecting the rear cover assembly with the stator and the front cover assembly with the rotor, we sink the brushes into the brush holder and..

... insert a suitable pin into the hole in the back cover of the generator (wooden stick or piece of wire) and fix the brushes in the recessed position.
After assembling the generator, remove the pin.
Brushes, under the action of springs, are displaced to slip rings.
After installing the generator, adjust the belt tension.
