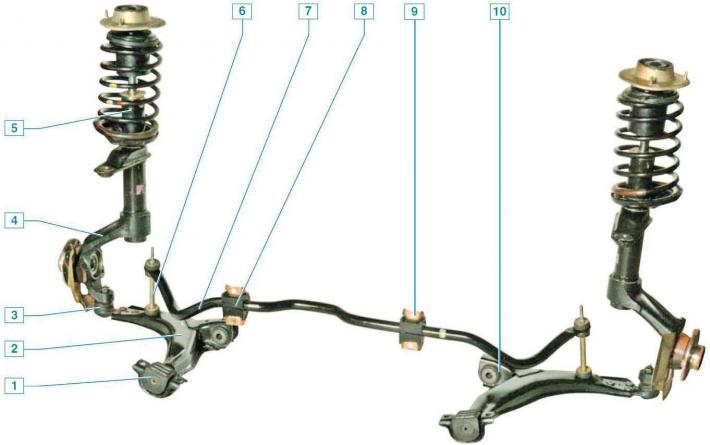
Front suspension: 1 - lever pad; 2 - lever; 3 - ball bearing; 4 — a rotary fist with a nave; 5 - shock absorber; 6 - anti-roll bar; 7 - bar stabilizer bar; 8 — a pillow of a bar of the stabilizer; 9 - bracket for attaching the stabilizer bar to the front panel; 10 - silent block of the lever
The front suspension is independent, MacPherson type with wishbones and anti-roll bar mounted on the front panel.
The basis of the suspension is a telescopic shock absorber strut, which allows the wheels to move up and down when driving through bumps and at the same time dampen body vibrations.
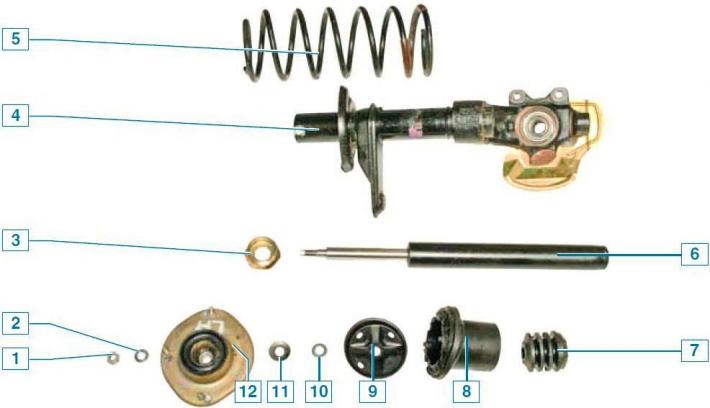
Strut strut details: 1 — a nut of fastening of a rod of the shock-absorber; 2 - washer; 3 — a nut of the case of a rack; 4 - shock absorber housing with a steering knuckle; 5 - spring; 6 - shock absorber; 7 - compression stroke buffer; 8 - cover; 9 - upper support cup; 10 - flat washer; 11 - disc washer; 12 - top support
The rack is made as a single unit with the steering knuckle.
A spring support cup and a swivel lever are welded to the middle part of the rack body, which is connected to the steering rod through a ball tip.
A helical coil spring with an upper coil of reduced diameter, a rubber buffer for the compression stroke, and an upper support assembly with a bearing are installed on the telescopic strut.
A telescopic hydraulic shock absorber is installed in the rack housing.
The upper support is attached with three self-locking nuts to the mudguard cup of the body.
Due to its elasticity, the support allows the strut to swing during the suspension strokes and dampens high-frequency vibrations of the suspension.
The bearing pressed into it allows the rack to turn along with the steered wheel.
Braking and traction forces during the movement of the car are perceived by the suspension arms connected through ball bearings to the steering knuckles and - through silent blocks and pillows - to the body.
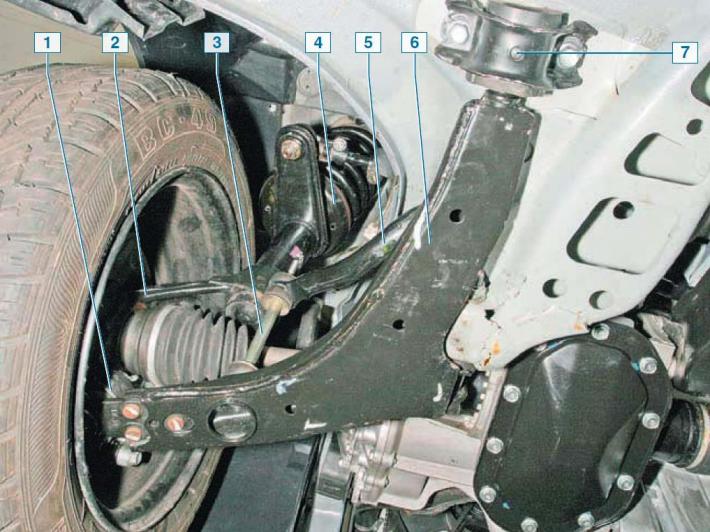
Elements of the front suspension on the car, bottom view: 1 - ball bearing; 2 - steering knuckle; 3 — stabilizer bar; 4 - shock absorber; 5 - bar stabilizer bar; 6 - lever; 7 - bracket for mounting the lever cushion
The lower part of the steering knuckle is connected to the front suspension arm through a ball joint.
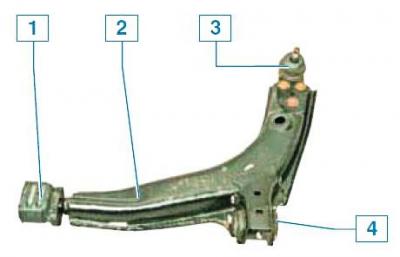
Front suspension arm: 1 - pillow; 2 - lever; 3 - ball bearing; 4 - silent block
The ball joint pin is attached to the steering knuckle with a nut, and the support body is riveted to the lever with three rivets.
To replace the ball joint, you will need to drill three rivets and replace them with bolts and nuts.
A closed-type double-row angular contact ball bearing is pressed into the hole of the steering knuckle, and the wheel hub is pressed into the inner rings of the bearing.
Inner rings shrink (through the hub) nut on the threaded part of the shank of the outer hinge housing of the wheel drive.
In operation, the bearing is not adjustable and does not require relubrication.
Wheel bearings are interchangeable.
Nuts of bearings of naves of both wheels identical, with the right carving.
The anti-roll bar is made of spring steel.

The bar of the stabilizer of transverse stability: 1 - left side; 2 - right side
The bar in its middle part is attached to the bulkhead plate through rubber pads.
Both ends of the stabilizer bar through the rack with rubber bushings are connected to the suspension arms.
The stabilizer bar has an asymmetrical shape.
To ensure good stability and controllability of the car, the front wheels are set at certain angles relative to the body and suspension elements.
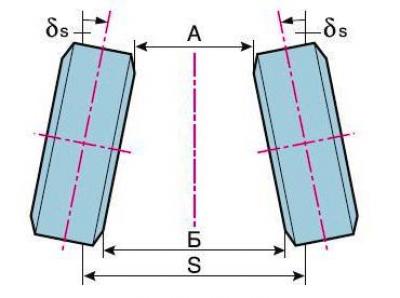
B–A — convergence of the front wheels; A and B - distance (mm) between the edges of the wheel rims in front and behind; δs is the toe angle of the front wheels; S - track
Only the toe angle is adjustable.
Other parameters (camber angle, caster angle) are structurally made by the manufacturer and are not subject to adjustment.
Toe-in is the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle.
Wheel alignment contributes to the correct position of the steered wheels at various speeds and angles of rotation of the car.
Signs of deviation of the toe angle from the norm: severe sawtooth tire wear in the transverse direction, tire screeching in corners, increased fuel consumption due to high rolling resistance of the front wheels.
The toe-in is adjusted by turning the adjusting screw with the terminal connections of the tie rod ends loose.
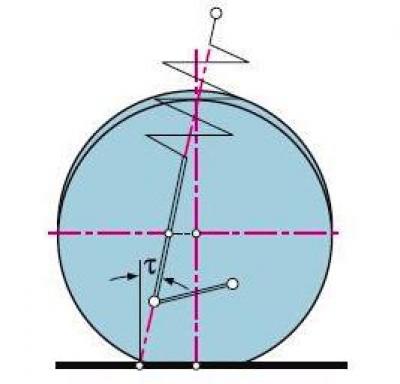
T - angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheel
Caster angle - the angle between the vertical and the line passing through the centers of rotation of the ball joint and the bearing of the upper support of the shock absorber strut in a plane parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle.
It contributes to the stabilization of the steered wheels in the direction of rectilinear motion.
Symptoms of deviation of the angle value from the norm - car pulling to the side while driving, different efforts on the steering wheel in the left and right turns, one-sided wear of the tire tread.
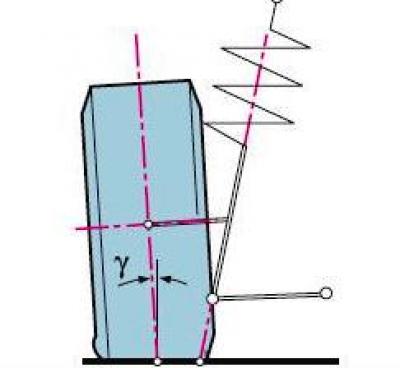
Y - camber angle
Camber is the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the vertical.
It contributes to the correct position of the rolling wheel during suspension operation.
With a strong deviation of this angle from the norm, the car can be pulled away from rectilinear movement and one-sided wear of the tread.
The camber angle of the wheels and the angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheel are set by the geometry of the suspension parts and are not subject to adjustment in operation.
Checking the angles of the front wheels and adjusting the toe-in is recommended to be carried out at a service station.
Before adjusting the wheels must be set to the position of the rectilinear movement of the car.
The car must be installed on a horizontal platform and loaded in accordance with the recommendations of the manufacturer.
With normal tire pressure and no excessive play in the front suspension units, the installation angles should correspond to the following values:
- – convergence: 10'±10'
- – camber angle: –1°10'±20'
Pitch Angle:
- – with power steering 2°45'±1°
- – without power steering 1°30'±1°
