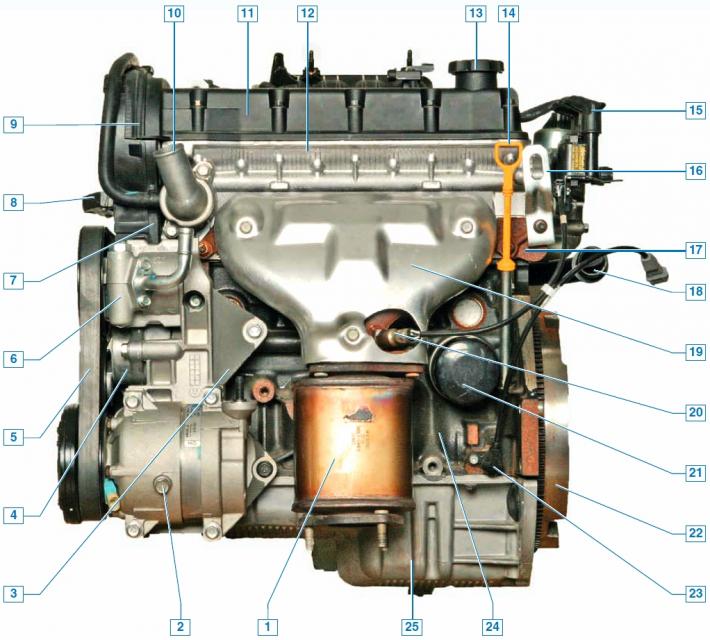
Engine (front view of the car): 1 - catalytic converter of exhaust gases; 2 - air conditioning compressor; 3 - bracket for mounted units; 4 - tensioner of the auxiliary drive belt; 5 - drive belt for auxiliary units; 6 - power steering pump; 7 - rear cover of the timing drive; 8 - bracket for the right support of the power unit; 9 - upper front cover of the timing drive; 10 - thermostat cover; 11 — a cover of a head of the block of cylinders; 12 - cylinder head; 13 - oil filler cap; 14 - oil level indicator (oil dipstick); 15 - ignition coil; 16 - eye; 17 - exhaust manifold; 18 - inlet pipe of the coolant pump; 19 - heat-shielding casing of the exhaust manifold; 20 - control oxygen concentration sensor; 21 - oil filter; 22 - flywheel; 23 - crankshaft position sensor; 24 - cylinder block; 25 - oil pan.
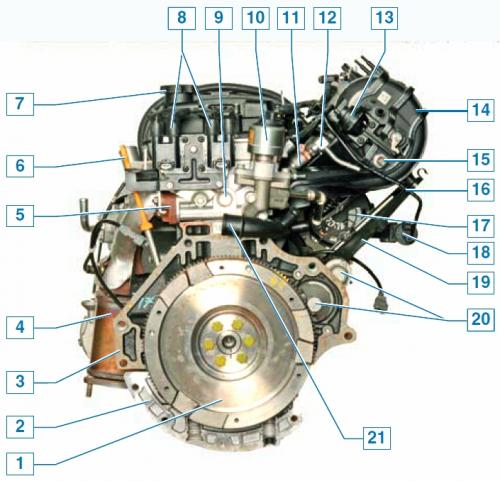
Engine (left side view of the car): 1 - flywheel; 2 - oil pan; 3 - cylinder block; 4 - catalytic converter of exhaust gases; 5 - exhaust manifold; 6 - oil level indicator; 7 - oil filler cap; 8 - ignition coil; 9 - cylinder head; 10 - exhaust gas recirculation valve; 11 - nozzle; 12 - fuel rail; 13 - the actuator of the system for changing the length of the intake tract; 14 - inlet pipeline; 15 - intake air temperature sensor; 16 - tube for supplying fuel vapor from the adsorber purge valve to the inlet pipeline; 17 - generator; 18 - adsorber purge valve; 19 - intake manifold bracket; 20 - starter; 21 - inlet pipe of the coolant pump.
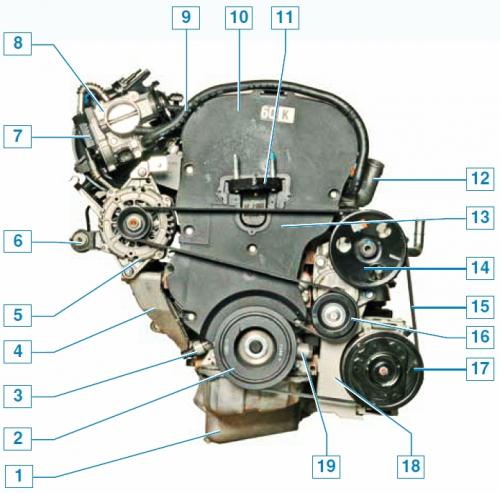
Engine (right side view of the car): 1 - oil pan; 2 - auxiliary drive pulley; 3 - oil pressure sensor; 4 - generator bracket; 5 - generator; 6 - adsorber purge valve; 7 - block throttle position sensor and idle speed controller; 8 - throttle assembly; 9 - hose for supplying coolant to the throttle assembly; 10 - upper front cover of the timing drive; 11 - bracket for the cylinder block for fastening the right support of the power unit; 12 - thermostat cover; 13 - lower front cover of the timing drive; 14 - power steering pump pulley; 15 - drive belt for auxiliary units; 16 - roller of the automatic tensioner of the auxiliary drive belt; 17 - air conditioning compressor pulley; 18 — an arm of auxiliary units; 19 - oil pump.
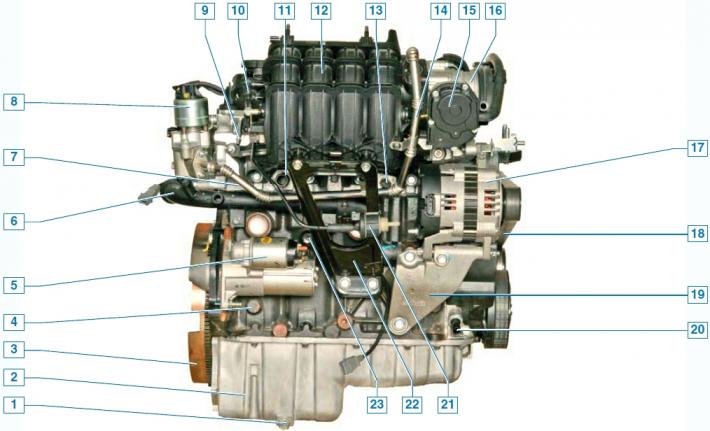
Engine (rear view of the car): 1 - oil drain plug; 2 - oil pan; 3 - flywheel; 4 - cylinder block; 5 - starter; 6 - inlet pipe of the coolant pump; 7 - cylinder head; 8 - exhaust gas recirculation valve; 9 - fuel rail; 10 - actuator for changing the length of the intake tract; 11 - branch pipe for supplying coolant to the stove radiator; 12 - inlet pipeline; 13 - coolant temperature sensor; 14 - tube for supplying exhaust gases to the intake pipeline; 15 - block throttle position sensor and idle speed controller; 16 - throttle assembly; 17 - generator; 18 - drive belt for auxiliary units; 19 - generator bracket; 20 - low oil pressure sensor; 21 - adsorber purge valve; 22 - intake manifold bracket; 23 - knock sensor.
The engine is gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, sixteen-valve, with an overhead arrangement of two camshafts. The location in the engine compartment is transverse. The order of operation of the cylinders: 1–3–4–2, the countdown is from the auxiliary drive pulley. The power system is a phased distributed fuel injection.
An engine with a gearbox and clutch form a power unit - a single unit mounted in the engine compartment on three elastic rubber-metal supports. The right support through the bracket is attached to the cylinder block, and the left and rear - to the gearbox housing.
Right side of the engine (in the direction of the car) located: timing gear drive and coolant pump (toothed belt); drive of auxiliary units - generator, air conditioning compressor and power steering pump (V-ribbed belt with automatic tensioner); oil pump.
On the left are: the ignition coils and the exhaust gas recirculation valve.
Front: exhaust manifold; exhaust gas catalytic converter; oil filter; oil level indicator; crankshaft position sensor; power steering pump (top right); air conditioning compressor (bottom right).
Rear: intake manifold with throttle assembly, absolute pressure and intake air temperature sensors, mechanism for changing the length of the intake tract, fuel rail with injectors; generator (top right); starter (bottom left), low oil pressure sensor; adsorber purge valve; knock sensor; coolant pump inlet pipe; coolant temperature gauge sensor.
Top: spark plugs, phase sensor.
The cylinder block is cast iron, the cylinders are bored directly in the block. The engine cooling jacket and oil channels are made in the body of the cylinder block.
In the lower part of the cylinder block there are five crankshaft main bearing supports with removable covers, which are attached to the block with special bolts. Holes in the cylinder block for bearings are machined with covers installed, so the covers are not interchangeable and are marked on the outer surface with numbers (account from the timing pulley).
The crankshaft is made of ductile iron, with five main and four connecting rod journals.
The shaft is equipped with eight counterweights cast integrally with it. Inserts of main and connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft are steel, thin-walled, with an anti-friction coating.
The main and connecting rod journals of the crankshaft connect the channels located in the shaft body. The axial movement of the crankshaft is limited by two liners with thrust collars of the third main bearing.
At the front end (sock) crankshaft mounted: Timing gear pulley (timing) and accessory drive pulley.
A flywheel is attached to the crankshaft flange with six bolts. It is cast iron and has a pressed steel ring gear for starting the engine with a starter.
Connecting rods - forged steel, I-section. With their bottom (detachable) The connecting rod heads are connected through liners to the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft, and the upper heads - with the help of piston pins - to the pistons.
Pistons are made of aluminum alloy. The hole for the piston pin is offset relative to the axis of symmetry of the piston by a small amount to the rear wall of the cylinder block. Three grooves for piston rings are machined in the upper part of the piston. The two upper piston rings are compression, and the lower one is an oil scraper composite (two disks and an expander). Piston pins steel, tubular section.
In the holes of the pistons, the fingers are installed with a gap, and in the upper heads of the connecting rods - with an interference fit (pressed in).

Cylinder head assembly: 1 - intake camshaft; 2 - exhaust camshaft.
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy, common to all four cylinders.
The head is centered on the block with two bushings and fastened with ten bolts. A gasket is installed between the block and the cylinder head. On opposite sides of the cylinder head are the intake and exhaust ports. Spark plugs are installed in the center of each combustion chamber.
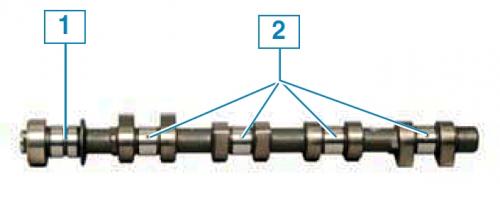
Camshaft: 1 - groove and hole for supplying oil inside the shaft; 2 - holes for supplying oil to the bearings.
At the top of the cylinder head are two camshafts made of cast iron. One shaft drives the intake valves of the gas distribution mechanism, and the other drives the exhaust valves. Eight cams are made on the shaft - an adjacent pair of cams simultaneously controls two valves (inlet or outlet) each cylinder. supports (bearings) camshafts (five bearings for each shaft) made detachable. The holes in the supports are machined complete with covers.
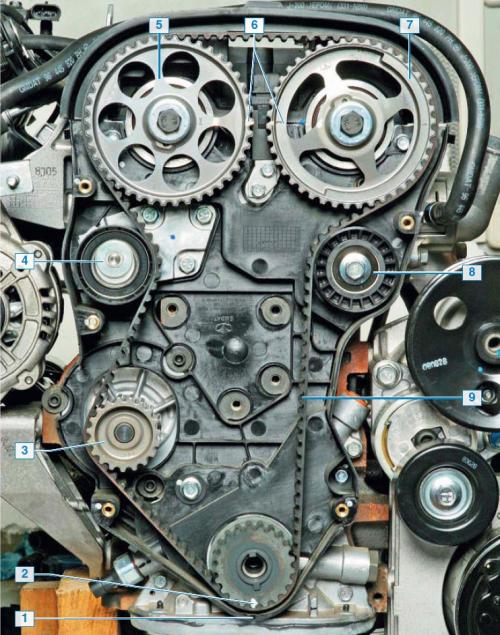
Timing gear drive: 1 - mark on the back cover of the timing drive; 2 - mark on the gear pulley of the crankshaft; 3 — a pulley of the pump of a cooling liquid; 4 - belt tensioner roller; 5 — a pulley of a camshaft of inlet valves; 6 - marks on the camshaft pulleys; 7 — a pulley of a camshaft of final valves; 8 - belt support roller; 9 - belt.
Camshaft drive - toothed belt from the crankshaft pulley. The semi-automatic tensioner ensures the required belt tension during operation.
The valves in the cylinder head are arranged in two rows, in a V-shape, with two intake and two exhaust valves for each cylinder. Steel valves, outlet valves with heat-resistant steel plate and welded chamfer.
The intake valve has a larger diameter than the exhaust valve. Seats and valve guides are pressed into the cylinder head. On top of the valve guide bushings, oil-slinger caps made of oil-resistant rubber are put on.
The valve closes under the action of one spring. Its lower end rests on a washer, and its upper end rests on a plate held by two crackers. The crackers folded together have the shape of a truncated cone, and on their inner surface there are beads that enter the grooves on the valve stem.
The valves are actuated by camshaft cams through hydraulic pushers.

Hydraulic pusher: 1 - groove for supplying oil; 2 - plunger pair.
For the operation of hydraulic pushers, channels are made in the cylinder head that supply engine oil to them. When the engine is running, oil under pressure fills the internal cavity of the hydraulic pusher and moves its plunger pair, compensating for the thermal gap in the valve drive. Thus, constant contact between the pusher and the camshaft cam is ensured.
Engine lubrication - combined. Under pressure, oil is supplied to the main and connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft, pairs of "support-camshaft neck" and hydraulic pushers.
The pressure in the system is created by an oil pump with internal gears and a pressure reducing valve. The oil pump is attached to the cylinder block on the right.
The pump drive gear is mounted on the toe of the crankshaft. The pump takes oil from the oil pan through the oil receiver and delivers it through the oil filter to the main oil line of the cylinder block, from which oil channels depart to the crankshaft main bearings and the oil supply channel to the cylinder head.
To lubricate the camshaft bearings, oil is supplied through the channels in the cylinder head to the first (from the timing drive) shaft supports.
Through the groove and drilling made on the first neck, the oil enters the shaft and then through the holes in the necks to other shaft bearings.
The oil filter is full-flow, non-separable, equipped with bypass and anti-drainage valves. By spraying, oil is supplied to the pistons, cylinder walls and camshaft lobes. Excess oil flows through the channels of the cylinder head into the oil pan.
Hydraulic pushers are very sensitive to the quality of the oil and its purity. In the presence of mechanical impurities in the oil, a quick failure of the plunger pair of the hydraulic pusher is possible, which is accompanied by increased noise in the gas distribution mechanism and intensive wear of the shaft cams. A defective hydraulic pusher cannot be repaired - it should be replaced.
The crankcase ventilation system is forced, closed type.
Through channels in the cylinder head, gases from the crankcase enter under the cylinder head cover. Passing through the oil separator (located in the cylinder head cover), the gases are cleaned of oil particles and, under the action of vacuum, enter the engine intake tract through the hoses of two circuits: the main and the idle circuit, and then into the cylinders. Through the hose of the main circuit, crankcase gases are supplied to the throttle assembly at partial and full engine loads.
Through the hose of the idle circuit, gases are discharged into the space behind the throttle valve, both in partial and full load modes, and in idle mode. Engine management, power supply, cooling and exhaust systems are described in the relevant chapters.
