Chevrolet Lacetti is equipped with wheels with the following parameters: — width and diameter of the wheel rim in inches: 6JЧ15 (steel and light alloy) or 5.5JH14 (5½JH14) (only steel).
Station wagons only have 15-inch wheels; - the number of mounting holes and the diameter on which their centers are located (PCD), in millimeters: 4×114.3 - wheel offset (ET) in millimeters: 44 is the diameter of the central hole (DIA) in millimeters: 56.6; – number of humps: 2 (designation H2 possible).
If you have a need to purchase one or more new wheels for your car for replacement or wear, you must remember that the new wheels must exactly match these parameters - with the exception of the wheel offset (deviation up or down no more than 5 mm is allowed, while the deviation must be the same on both wheels of the same axle), as well as the diameter of the central hole (deviation is allowed only in the big direction).

Alloy wheel marking on the inner surface of its rim (central part)

Steel wheel marking Wheel offset is the distance from the symmetry plane of the wheel rim to the mating plane of the disc (wheel center).
The international departure designation is ET. Departure is measured in millimeters. The smaller the wheel offset (negative values are also possible), the more the wheel protrudes out of the vehicle's wheel arch. When installing wheels with a reduced offset, the load on the wheel bearings of the car increases greatly. With an increased reach, the wheel turns out to be "drowned" inside the wheel arch and can touch the body and suspension elements, especially when turning the car. However, a deviation of the wheel offset of about 5 mm up or down is considered acceptable.
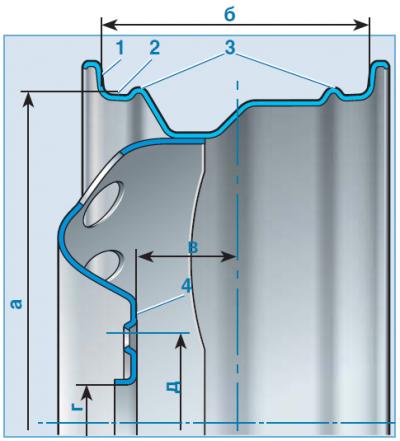
The main elements and dimensions of the wheel: 1 - rim flange; 2 - rim shelf; 3 - humps; 4 - mating plane of the wheel disk; a - rim diameter corresponding to the tire diameter; b - rim width; c - wheel offset; d is the diameter of the central hole; d - the diameter on which the centers of the wheel mounting holes are located (PCD) Do not use wheels with a PCD size other than the nominal size. This will lead to a strong beating of the wheel while driving, to damage to the mounting holes and studs, and in the worst case, to the destruction of the wheel and its disconnection from the car on the move, which will inevitably lead to an emergency.
It is unacceptable to bore and adjust the wheel mounting holes to the location of the studs on the hub using a file or drill. Mounting holes are made in the wheel disc with high precision, which is impossible to achieve in homemade conditions.
To fasten the wheel, use only special nuts with a conical chamfer. The chamfers of the nuts ensure that the wheel is centered on the hub. It is unacceptable to start driving a car if any of the wheels is not secured with all the nuts, or any of the nuts cannot be tightened (spinning on pins). If the threads in the nut or stud are damaged, immediately replace these parts with new ones yourself or at a service station.

wheel nuts
Wheel center hole diameter (international designation - DIA) important for the reason that each hub of the car has a protruding belt that performs an auxiliary function when installing the wheel. The diameter of the central hole of the wheel must not be less than the outer diameter of this belt, otherwise the wheel simply cannot be installed. Contrary to popular belief, this belt does not center the wheel on the hub (this function is performed by the wheel nuts), therefore, the installation of spacer rings on the girdle in cases where the diameter of the central hole and the outer diameter of the girdle differ significantly, by and large is not necessary.
Humps - ring protrusions on the inside of the wheel rim. Usually two hampas are performed (the designation H2 in the wheel marking may not be present, but the humps are quite clearly visible).
Humps serve for a more secure fit and better sealing of the tubeless tire on the wheel. Wheels with one hump or no hump at all when using tubeless tires are better not to use (however, such wheels are now very rare).
If you install wheels on your car that are significantly different from the standard ones, Chevrolet authorized service stations may refuse to provide you with warranty repairs for those vehicle systems that are directly related to the wheels: suspension elements, steering, brake system, hub bearings, etc.
In the SE and SX trim levels, the car has steel wheels, and only in the CDX trim level - alloy wheels. The main advantage of alloy wheels compared to steel wheels is their lighter weight, which improves suspension performance (the wheels quickly "obey" the restoring action of the elastic suspension elements and restore lost contact with the road). This improves driving comfort and driving safety. The car's handling and braking dynamics are improved, and fuel consumption is also slightly reduced. In addition, due to the high manufacturing precision and material characteristics, the alloy wheel holds the tubeless tire better on the rim and provides better sealing of the tubeless tire.
However, alloy wheels also have disadvantages. So, for example, aluminum alloys from which they are made are very susceptible to corrosion, especially in those places where the protective varnish coating of the wheel is damaged. You can damage the varnish not only on a bad road or under the influence of winter salt, but also with inept mounting / dismounting of the tire.
When balancing light-alloy wheels, special weights are glued to the surface of the rim. If there are no such weights in the tire shop, the tire shop may try to install ordinary weights on steel brackets and thus damage the varnish coating on the rim flange.
The impact resistance of alloy wheels is higher than that of steel wheels. However, the steel wheel, even with a strong impact, is not destroyed, but only deformed.
If at the same time it is able to keep air in the tire, it can even drive on its own to the place of repair. A light-alloy wheel can break from a strong impact. In this regard, it is dangerous to purchase fake wheels that have not passed special certification and strength tests. Hidden shells, cracks, delaminations may be present in their metal, which significantly reduces their strength.
Therefore, when buying wheels in a store or on the market, you should carefully consider their markings, be interested in information about the manufacturer, and require sellers to provide a certificate for the goods.
During the operation of the car, its wheels should be regularly checked for the absence of jamming of the flanges and other types of rim deformation, the absence of cracks in the spokes and the disk (the central part, where the holes for its fastening are located), the integrity of the mounting holes, severe corrosion (especially for light alloy wheels). A slight jamming of the rim flange of a steel wheel usually does not affect the tightness of the tire and does not cause the wheel to wobble while driving. Don't try to straighten the dent by hand with a hammer or sledgehammer - you risk damaging the wheel even further. It is better to give such a wheel for repair to a specialized workshop, where they can straighten it ("roll") on the machine. Ideally, it is desirable to replace the wheel.
Restoring an alloy wheel is much more difficult. Many experts tend to believe that damaged - deformed or cracked - light-alloy wheels are suitable only for remelting, because the guarantee of the strength of such a wheel is in the uniformity of its structure, which is inevitably violated during deformation, and even more so when cracks appear. However, there is another opinion: an alloy wheel can be restored using special technologies and high-quality equipment. In any case, there are plenty of services offering repair of light-alloy wheels.
