
Rear suspension elements: 1 - front transverse lever; 2 - rubber pad anti-roll bar; 3 — bracket of the anti-roll bar; 4 — an arm of the trailing arm; 5 — trailing arm; 6 - anti-roll bar; 7 - hub assembly with bearing and wheel speed sensor; 8 - fist; 9 - shock absorber; 10 - rear transverse lever; 11 - subframe; 12 - bar stabilizer bar.
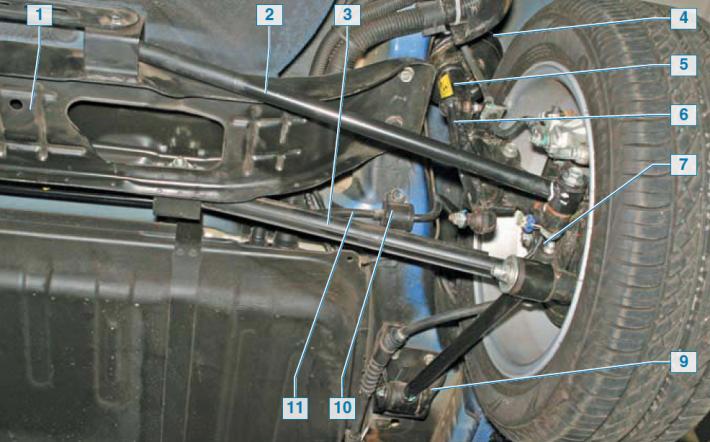
Elements of the rear suspension on the car: 1 - subframe; 2 - rear transverse lever; 3 - front transverse lever; 4 - shock absorber spring; 5 - telescopic stand; 6 - anti-roll bar; 7 - fist; 8 — trailing arm; 9 - bracket; 10 - bracket; 11 — a bar of the stabilizer of cross stability
The rear suspension is independent, assembled on a subframe.
Each wheel is suspended on longitudinal and two transverse levers, the shock absorber and spring are installed coaxially, forming a telescopic shock absorber strut that allows the rear wheel to move up and down when driving through bumps and at the same time dampen body vibrations.
An anti-roll bar reduces vehicle roll.
The shock absorber strut consists of a telescopic strut in which a double-acting hydraulic gas-filled shock absorber is installed, a cylindrical helical spring, a compression stroke buffer and an upper rubber-metal support. The spring rests on the spring cups through rubber gaskets. The shock absorber rod is connected to the upper support, which is attached to the rear wheel arch with three nuts. Due to its elasticity, the support allows the strut to swing during suspension strokes and dampens vibrations when passing small irregularities.
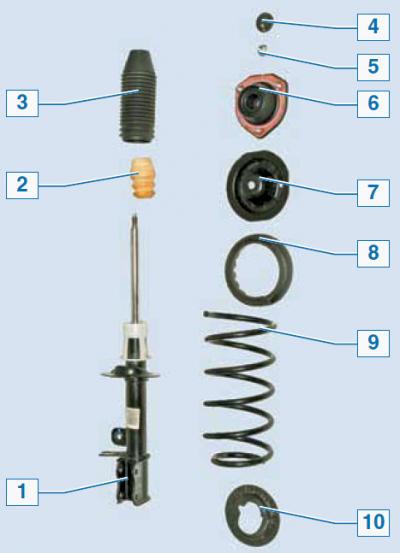
Shock absorber elements: 1 - telescopic stand; 2 - compression stroke buffer; 3 - protective cover; 4 - plug; 5 - rod fastening nut; 6 — the top support of a rack; 7 - the upper cup of the spring; 8 — the top laying of a spring; 9 - spring; 10 - bottom spring pad
A bracket is welded to the bottom of the strut body for attachment to the forged knuckle of the rear suspension.
A cylindrical belt of the hub enters the fist socket, and its flange is bolted to the fist flange.

The hub is a non-separable assembly with a bearing and a wheel speed sensor of the anti-lock braking system.
The braking forces during the movement of the car are perceived by the trailing arms, and the forces in the direction perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the car - by the transverse suspension arms.
To ensure the mobility of the levers in the joints with the body and fists, silent blocks are pressed into the eyelets of the levers. The front end of the trailing arm is attached to the bracket mounted on the body, and the rear end to the fist eye. Each wishbone is attached at one end to the fist eye, and at the other end to a subframe mounted on the body.
The bolt of the front transverse arm to the subframe has an eccentric belt and an eccentric washer, and the hole in the subframe for the bolt is oval. When the bolt is turned, the position of the lever relative to the subframe changes, thereby adjusting the wheel toe.
To increase lateral stability and reduce the roll angles of the car, a stabilizer bar is installed. The stabilizer bar in its middle part is fastened with brackets through rubber split cushions to the body. Stabilizer strut rods are made of polymeric material, and ball bearings are made at the ends of the rods. The stabilizer links connect the ends of the stabilizer bar to the telescopic strut housings.
