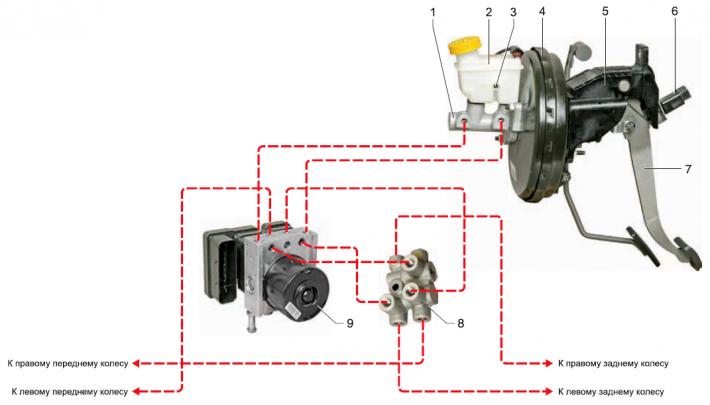
Elements of the brake system of the car: 1 — the main brake cylinder; 2 - hydraulic reservoir; 3 - brake fluid level sensor; 4 - vacuum amplifier; 5 - pedal assembly bracket; 6 — the switch of signals of braking; 7— brake pedal; 8 - splitter, 9 - ABS unit.
The working brake system is hydraulic, dual-circuit, with a diagonal separation of circuits. In normal mode, when the system is working, both circuits work. In case of failure (depressurization) one of the circuits, the other circuit provides braking of the car, although with less efficiency. The working brake system includes wheel brakes, pedal assembly, vacuum booster, brake master cylinder, hydraulic reservoir, anti-lock block, as well as connecting pipes and hoses.
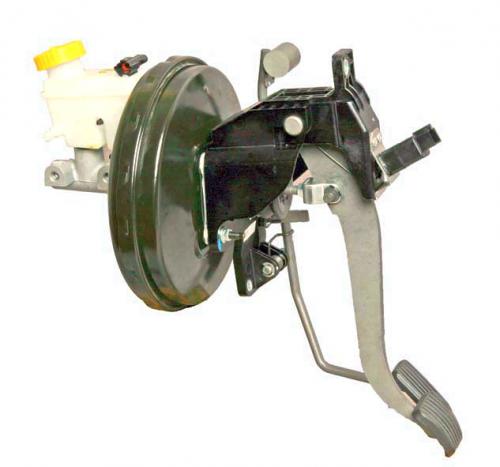

Brake pedal - suspension type. A brake light switch is installed in the pedal assembly bracket - its contacts close when the brake pedal is pressed.
The vacuum brake booster is located between the brake pedal and the brake master cylinder and is attached with four nuts to the pedal assembly bracket. The vacuum booster is non-separable; in case of failure, it is replaced with a new one.

Master brake cylinder
The main brake cylinder is attached to the vacuum booster housing with two nuts. On top of the cylinder there is a common reservoir for the hydraulic drive of the brake system and clutch, in which there is a supply of fluid. The tank body is marked with maximum and minimum liquid levels. A liquid level sensor is installed in the tank, which, when the liquid level drops below the MIN·mark, turns on a signaling device in the instrument cluster. When the brake pedal is pressed, the pistons of the master cylinder move, creating pressure in the hydraulic drive, which is supplied through pipes and hoses to the working cylinders of the wheel brakes.

Elements of the brake mechanism of the front wheel: 1 - brake pads; 2 — a disk of the brake mechanism; 3 — a bolt of fastening of a support to a directing finger; 4 - support; 5 - copper sealing washers; 6 — a bolt of fastening of a brake hose; 7 - guide pads; 8 - spring clips; 9 — a cover of a directing finger; 10 - guide pin
The brake mechanism of the front wheel is disc, with a floating caliper, which includes a single-piston wheel cylinder.
For more efficient cooling, the brake disc is ventilated.
The brake shoe guide is attached to the steering knuckle, and the caliper is attached with two bolts to the guide pins installed in the holes of the shoe guide. Protective rubber covers are installed on the fingers. The holes for the pins of the guide pads are filled with grease.
When braking, the fluid pressure in the hydraulic drive of the brake mechanism increases and the piston, moving out of the wheel cylinder, made as one piece with the caliper, presses the inner brake pad against the brake disc.
Then the caliper (due to the movement of the guide pins in the holes of the guide shoes) moves relative to the disc, pressing the outer brake pad against it. A piston with a sealing rubber ring is installed in the cylinder body. Due to the elasticity of this ring, a constant optimal gap is maintained between the disc and the brake pads.
The brake mechanism of the rear wheel is disc, with a floating caliper, which includes a single-piston working cylinder.
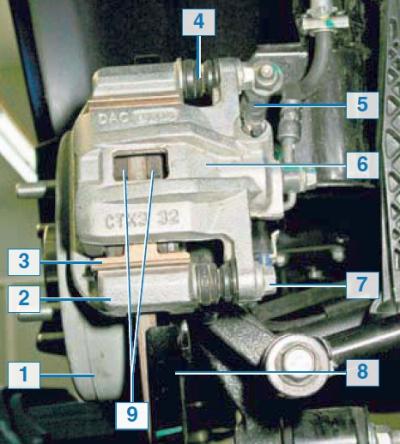
Rear wheel brake: 1 — a disk of the brake mechanism; 2 - guide pads; 3 - spring clip; 4 — a cover of a directing finger; 5 - bleed valve for hydraulic brakes; 6 - support; 7 — a bolt of fastening of a support to a directing finger; 8 - shield of the brake mechanism; 9 - brake pads
The design and principle of operation of the rear wheel brake mechanism is similar to the front wheel brake mechanism.
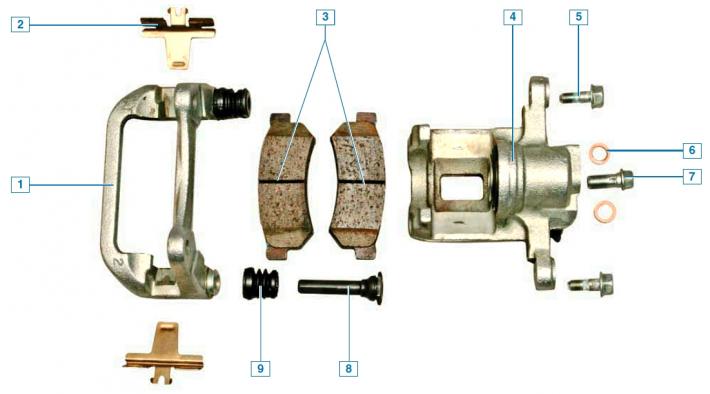
Elements of the brake mechanism of the rear wheel: 1 - guide pads; 2 - spring clip; 3 - brake pads; 4 - support; 5 — a bolt of fastening of a support to a directing finger; 6 - copper sealing washer; 7 — a bolt of fastening of a brake hose; 8 - guide pin; 9 - guide pin cover
The shoe guide is attached to the rear suspension knuckle.
The brake disc, unlike the front wheel brake disc, is not ventilated.
The parking brake mechanism is located in the central part of the brake disc. The parking brake mechanism is drum, with two brake shoes. By design, it resembles a conventional drum brake mechanism.
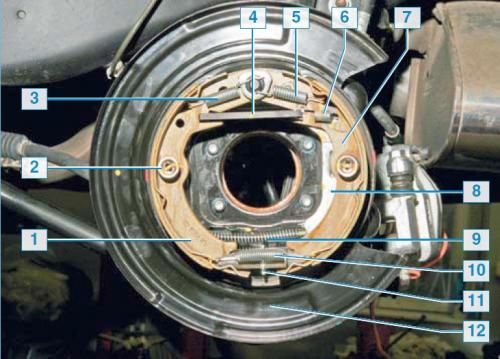
Parking brake mechanism: 1 - front block; 2 - spring cup; 3 - coupling spring of the front shoe; 4 - spacer bar; 5 — a coupling spring of a back block; 6 - clamping spring of the spacer bar; 7 - rear block; 8 - parking brake lever; 9 - parking brake cable; 10 - lower coupling spring; 11 - clearance regulator; 12 - brake shield
The brake drum for it is the inner side of the central part of the brake disc.
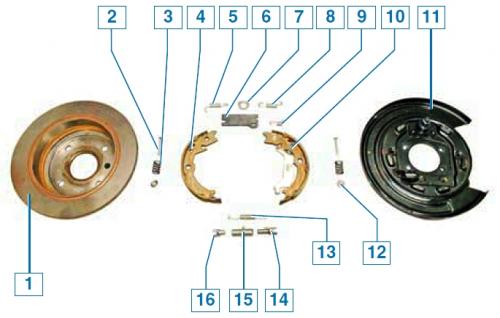
Elements of the parking brake mechanism: 1 — a disk of the brake mechanism; 2 - support post; 3 - clamping spring pads; 4 - front block; 5 - coupling spring of the front shoe; 6 - spacer bar; 7 - fixing plate; 8 — a coupling spring of a back block; 9 - clamping spring of the spacer bar; 10 - rear block; 11 - shield of the brake mechanism; 12 - spring cup; 13 - lower coupling spring; 14 - threaded tip of the regulator; 15 - regulator nut; 16 - regulator tip
All parts of the parking brake mechanism are fixed on the shield of the brake mechanism. The parking brake lever is mounted on the rear block, for which the parking brake cable is hooked. The upper ends of the pads are pressed by the coupling springs to the spacer bar, and the lower ends - to the gap adjuster between the pads and the inner surface of the disc. The regulator is a spacer bar, consisting of two tips and a nut. One threaded tip. When the nut is rotated, the length of the regulator changes due to the threaded tip, as a result of which the regulator spreads or brings the pads together.
The drive of the parking brake system is manual, mechanical, cable, on the rear wheels. It consists of a lever with a rod and an adjusting nut, an equalizer, two cables and parking brake mechanisms in the rear wheel brakes.
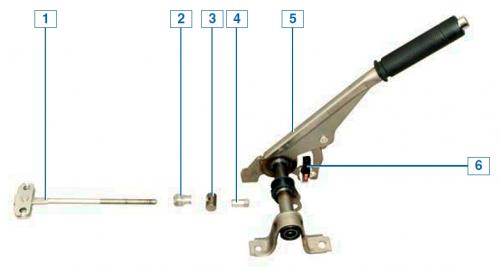
Parking brake lever: 1 - traction with cable equalizer; 2 - nut retainer; 3 - thrust finger; 4 - adjusting nut; 5— parking brake lever; 6 - switch of the signaling device for turning on the parking brake and malfunctioning of the brake system
The parking brake lever, fixed between the front seats on the floor tunnel, is connected to two cables through a link and an equalizer. The rear tips of the cables are connected to the levers of the parking brake actuator, mounted on the rear shoes.
The parking brake is adjusted by turning the adjusting nut located on the rod with the cable equalizer.
All vehicles are equipped with anti-lock brakes (ABS).
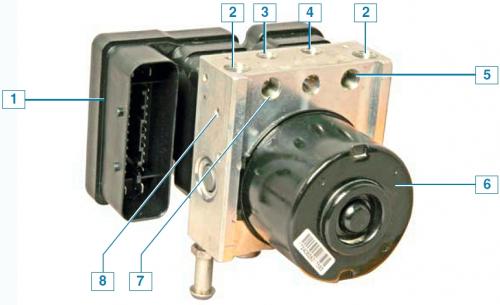
ABS block: 1 - control unit; 2 - hole for connecting the tube of the main brake cylinder; 3 - hole for connecting the tube of the brake mechanism of the left front wheel; 4 - hole for connecting the tube of the brake mechanism of the right front wheel; 5 - hole for connecting the tube of the brake mechanism of the left rear wheel; 6 - pump; 7 - hole for connecting the tube of the brake mechanism of the right rear wheel; 8 - hydraulic block;
Brake fluid from the master brake cylinder enters the ABS unit, and from it to the brake mechanisms of all wheels. The ABS block, mounted in the engine compartment on the left side member, near the bulkhead, consists of a hydraulic unit, a modulator, a pump and a control unit. ABS operates depending on the signals from the wheel speed sensors. Sensors - inductive type.
The front wheel speed sensor is installed in the steering knuckle hole and secured with a screw.

Front wheel speed sensor
The encoder driving disk is pressed onto the body of the drive's outer joint.
The rear wheel speed sensor is built into the rear wheel hub.
In the event of a failure of the rear wheel speed sensor, it is necessary to replace the hub together with the sensor. When the vehicle is braked, the ABS control unit detects the start of the wheel lock and opens the corresponding modulator valve to release the pressure of the working fluid in the channel. Valve opens and closes several times
per second, so you can make sure that the ABS is working by a slight trembling of the brake pedal at the time of braking. ABS has a built-in brake force distribution system (EBD), which performs the function of a pressure regulator in the hydraulic drive of the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels. If the rear wheels start to lock up when the car is braking, the rear wheel brake inlet valves in the modulator switch to a constant pressure mode, preventing a further increase in pressure in the rear brake working cylinders. If the ABS fails, the braking system remains functional, but the wheels may lock. In this case, a fault code is written to the memory of the unit, which is read using special equipment at the service center. Anti-slip control combined with ABS (TCS), which uses signals from wheel speed sensors.
The ABS control unit controls the anti-lock braking system.
