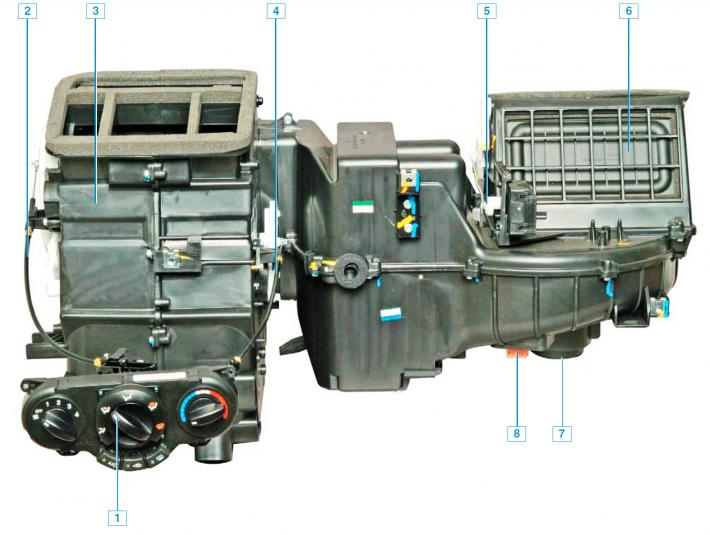

Heater with heating, ventilation and air conditioning control unit: 1 - control unit for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning; 2 - thrust distribution dampers; 3 - heater; 4 — thrust of the damper of the temperature controller; 5 - recirculation damper drive; 6 - air recirculation damper; 7 - fan motor; 8 - electronic fan motor speed controller.
The vehicle can be equipped with either a HVAC system or an HVAC system that serves to create the most comfortable conditions for the driver and passengers, regardless of weather conditions.
The heating and ventilation system includes: a heater, a heater fan, air ducts and deflectors. Through the air ducts, the air from the heater is supplied to the windshield and side window vents, to the central and side vents on the instrument panel, as well as to the ventilation openings in the heater casing to supply air to the feet of the driver and passengers. The system is controlled by turning the handles located on the heating, ventilation and air conditioning control unit. The control unit is installed on the instrument panel console.
The heater is installed under the instrument panel on the right, air ducts are fixed under the instrument panel. The following are installed in the heater housing: heater fan; electronic fan motor speed controller; distribution dampers directing air flows to certain areas; heater radiator (connected by hoses to the engine cooling system), through which coolant constantly circulates. Depending on the position of the damper associated with the temperature controller, outside air can pass through the heater core or bypass it.
The air is heated by the heat of the engine coolant circulating through the tubes of the heater radiator. For example, at an outside temperature of -18°C, the air after passing through the heater radiator heats up to 54°C, at -4°C - respectively, up to 59°C, at 10°C - up to 64°C, at 24°C - up to 68°C.
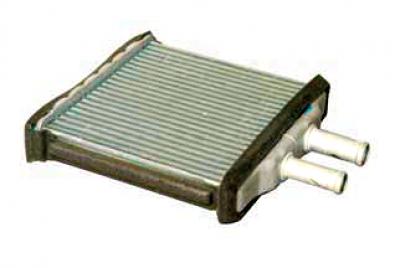
heater radiator
When the car is moving, air enters the heater through grilles located in front of the windshield. To increase the air supply to the passenger compartment while the car is moving, as well as in the parking lot, a heater fan is used.

Heater Fan and Electronic Heater Fan Motor Speed Controller
The air supply intensity is determined by the fan speed. The fan motor can rotate at four different speeds.
The distribution of air flows in the cabin is carried out by the air distribution regulator, which is connected by rods to the dampers.
By controlling the dampers, the regulator directs air flows through the air ducts to the central and side vents, to the lower ventilation openings in the heater casing, as well as to the windscreen grilles located in the instrument panel.
From the passenger compartment, air exits through valves installed behind the sidewalls of the rear bumper.
To accelerate the warm-up of the passenger compartment and prevent the entry of outside air into the passenger compartment (when driving on smoky, dusty sections of the road) is an air recirculation system. When you press the button to turn on the air recirculation mode, the recirculation damper blocks the access of outside air to the car interior and the air in the cabin begins to circulate in a closed circuit without exchanging with outside air. At the same time, the indicator in the button lights up.
Some cars are equipped with an air conditioning system. The air conditioning system is designed to reduce the temperature and humidity in the cabin. The air conditioner is turned on by pressing the air conditioner switch button located in the heating, ventilation and air conditioning control unit, while the heater fan must be turned on. When the air conditioner is turned on, the indicator located in the air conditioner switch button lights up.
The A/C compressor is mounted on the engine bracket at the front, below the power steering pump. The compressor is driven by a V-ribbed belt from the accessory drive pulley. An electromagnetic clutch is built into the compressor pulley, which turns the compressor shaft on and off from the pulley according to ECU signals.
After the compressor, the refrigerant vapor enters the condenser located in front of the radiator of the engine cooling system.
Next, the refrigerant enters the receiver, which is mounted on the condenser on the right side.
From the receiver, the refrigerant enters the gearbox, and then to the evaporator, located under the instrument panel in the heater housing.
The air thus cooled enters the passenger compartment. From the evaporator, the refrigerant is again sucked in by the compressor, and the working cycle is repeated. The high and low pressure pipelines are equipped with valves for charging and discharging refrigerant from the air conditioning system. A refrigerant pressure sensor is installed on the high pressure pipe.
The pressure sensor sends a signal to the ECU, which controls the electric fan of the engine cooling system, depending on the amount of coolant pressure and vehicle speed. In addition, according to the pressure sensor signals, the ECU turns off the air conditioning compressor if the refrigerant pressure in the system is too low or too high.
A shut-off valve is installed in the pipe fitting under the pressure sensor, which closes when the sensor is unscrewed. Therefore, when the pressure sensor is replaced, there is no refrigerant leakage from the air conditioning system.
The refrigerant in the air conditioning system is under high pressure. During work related to the depressurization of the air conditioning system, contact with eyes, skin and respiratory tract should be avoided. Any work with refrigerant must be carried out only in a ventilated area. When filling the air conditioning system, use only materials recommended by the manufacturer. It is forbidden to carry out welding or soldering work on the components of the air conditioning system. Work on the repair and maintenance of the air conditioning system should be carried out at specialized services. To search for leaks in the system, special equipment is used, while a special contrast agent is introduced into the system, which makes it possible to detect even minor leaks. After removing the refrigerant, be sure to pump air out of the system to remove any remaining moisture.
Before refueling, it is necessary to add special oil recommended by the manufacturer to the system.
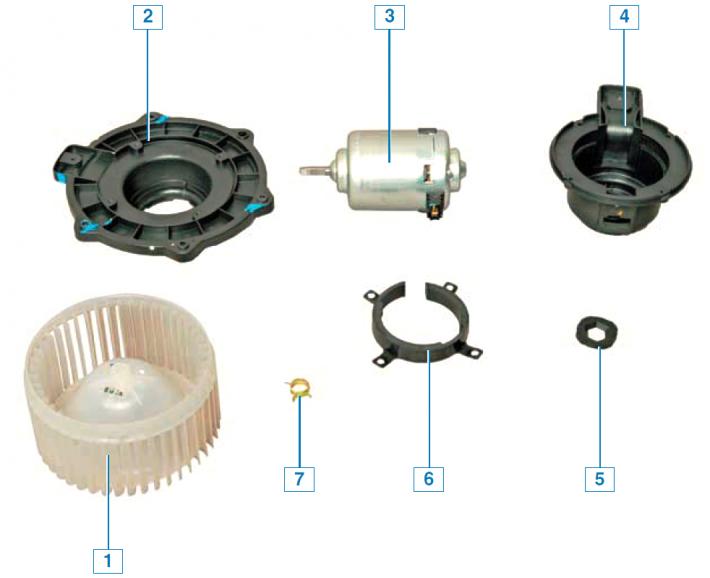

Heater Fan Details: 1 - impeller; 2 - base; 3 - fan motor; 4 - motor casing; 5 - lining of the electric motor; 6 - motor holder; 7 - clamp.
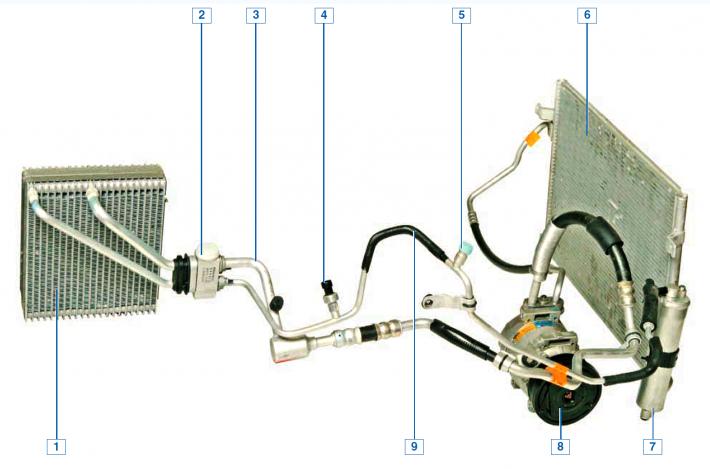
Air conditioning system: 1 - evaporator; 2 - reducer; 3—low pressure pipeline; 4 - refrigerant pressure sensor; 5 - valve for charging and refrigerant release; 6 - capacitor; 7 - receiver; 8 - compressor; 9 - high pressure pipeline.
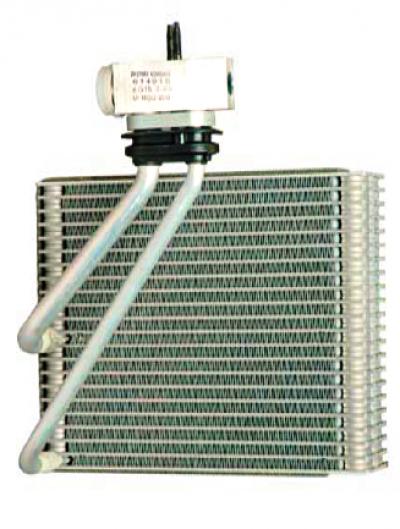
Air conditioner evaporator.

Air conditioner receiver.

Air conditioner condenser.
