Manual Transmission (pic. 6.4, 6.5) made according to a two-shaft scheme with five synchronized forward gears and one non-synchronized reverse gear. The gearbox and final drive with differential have a common crankcase, and in addition, the gearbox has an additional intermediate crankcase and cover. The input shaft is pressed into the gear block and connected to it with splines.
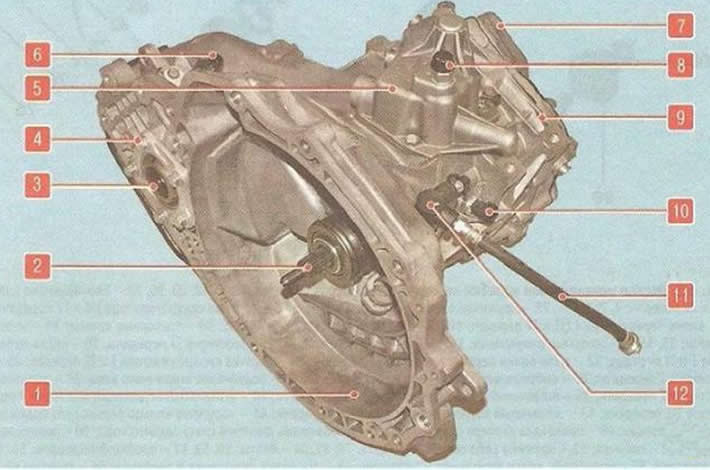
Pic. 6.4. Manual Transmission: 1 - gearbox housing; 2 - input shaft; 3 - axle shaft seal; 4 - main gear housing; 5 - gear shift mechanism; b - speed sensor; 7 - rear cover of the gearbox; 8 - breather; 9 - intermediate crankcase; 10 - reverse light switch; And - a hose of a hydraulic drive of deenergizing of coupling; 12 - clutch release hydraulic hose adapter
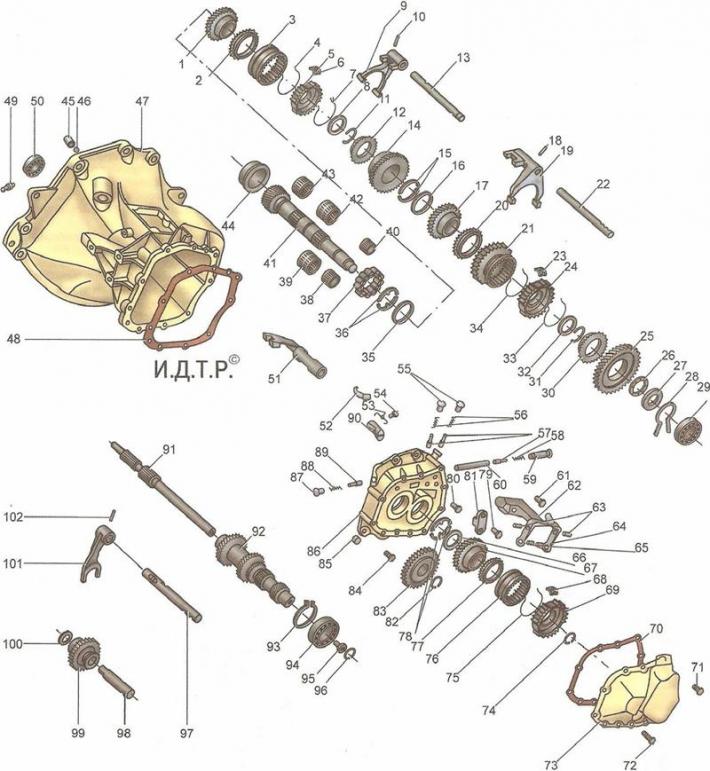
Pic. 6.5. Manual transmission details: 1 - gear IV gear; 2, 12, 20, 30, 77 - blocking synchronizer rings; 3 - clutch for switching on the synchronizer of III and IV gears; 4, 7, 33, 34.75 - synchronizer spring rings; 5 - synchronizer hub of III and IV gears; b, 23, 68 - crackers of synchronizers; 8, 32 - thrust washers; 9 - shift fork III and IV gears; 10, 18, 102 - pins; 11, 31, 74, 82, 93, 96 - retaining rings; 13 - rod of the shift fork of III and IV gears; 14 - third gear gear; 15, 36, 78 - thrust half rings; 16, 35, 66 - locking rings; 17 - gear 2nd gear; 19 - shift fork of I and II gears; 21 - clutch for switching on the synchronizer of I and II gears; 22 - rod of the shift fork of I and II gears; 24 - synchronizer hub of I and II gears; 25 - gear of the 1st gear; 26 - thrust needle bearing of the gear of the 1st gear; 27 - support washer; 28 - spring ring; 29 - output shaft bearing; 37 - roller bearing of the secondary shaft; 38 - needle bearing gear 1st gear; 39 - needle bearing gear II gear; 40 - needle bearing gear V transmission; 41 - secondary shaft; 42 - needle bearing gear III gear; 43 - needle bearing of gear IV gear; 44 - the outer ring of the roller bearing of the secondary shaft; 45 - cork; 46 - magnet; 47 - gearbox housing; 48 - clutch housing gasket; 49 - switch for reversing lights; 50 - roller bearing of the input shaft; 51 - a leash with a V gear rod; 52 - doggy; 53 - pawl spring; 54, 61, 71, 72, 79, 81, 84 - bolts; 55, 59, 87 - stopper plugs; 56, 58, 88 - springs; 57, 89 - clamps; 60 - pin of the locking mechanism; 62 - bracket for the V gear engagement fork; 63 - axis of the fork of inclusion of the V transfer; 64 - fork of inclusion of V transfer; 65 - fork crackers; 67 - driven gear V gear; 69 - synchronizer hub V transmission; 70 - cover gasket; 73 - rear cover of the gearbox; 76 - clutch for switching on the synchronizer of the V transmission; 80 - pawl bracket; 83 - drive gear V gear; 85 - magnet; 86 - intermediate crankcase; 90 - dog bracket; 91 - input shaft; 92 - gear block; 94 - ball bearing of the gear block; 95 - screw; 97 - rod of the fork for switching on the intermediate reverse gear; 98 - axis of the intermediate reverse gear; 99 - intermediate reverse gear; 100 - washer; 101 - fork of inclusion of an intermediate gear wheel of a backing
On the secondary shaft of the gearbox are the main gear spur gear, driven gears and gear synchronizers. Pairs of forward gears of the gearbox are in constant engagement. The gears of the IV gear in the neutral position rotate freely on the secondary shaft.
The forward gears are switched on by axial movement of the corresponding synchronizer clutches mounted on the secondary shaft. The reverse gear is engaged by moving the reverse intermediate gear along its axis.
The gearshift mechanism is located in a cover mounted on top of the gearbox housing.
Cable-type manual transmission control drive. Lever 1 (see fig. 6.7) shifting manual transmission together with bracket 2 is installed in the passenger compartment at the base of the body in the floor tunnel. The lever is connected to the levers 5 of the control unit on the gearbox by cables 3 and 4.
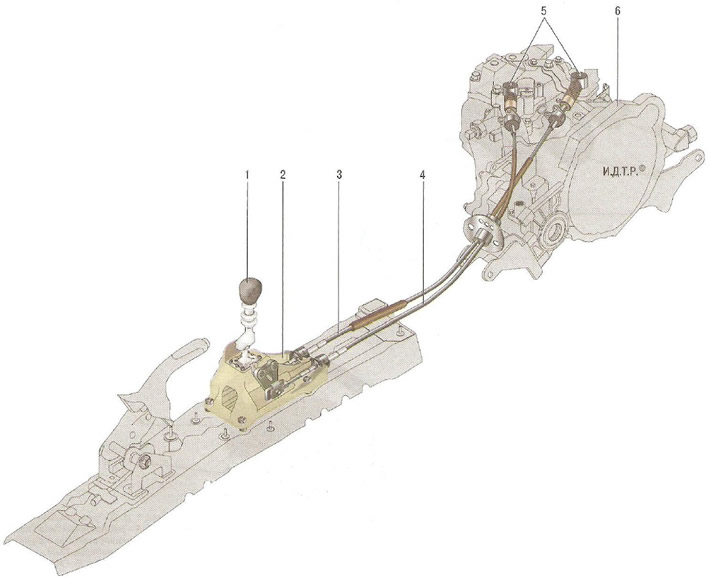
Pic. 6.7. Manual transmission control drive: 1 - gear lever; 2 - gear lever bracket; 3 - shift cable; 4 - gear selection cable; 5 - levers of the gear shift mechanism; 6 - manual transmission
main gear (pic. 6.6) made in the form of a pair of cylindrical gears, matched by noise. Torque is transmitted from the driven gear of the final drive to the differential and then to the front wheel drives.
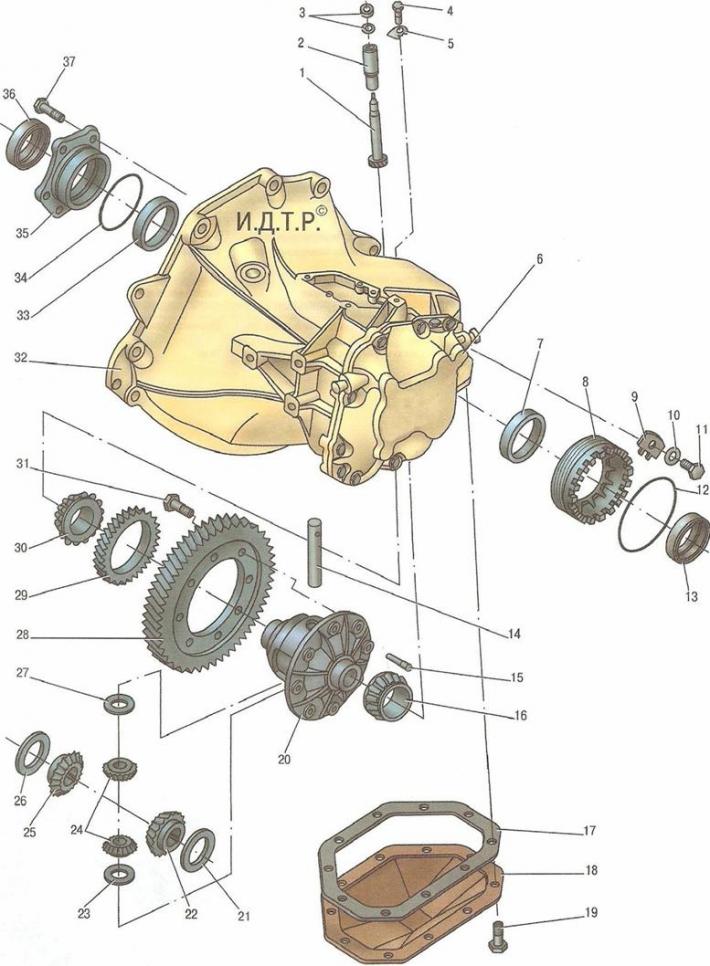
Pic. 6.6. Main gear and differential: 1 - gear shaft of the speedometer drive gearbox; 2 - speedometer drive gearbox housing; 3, 12, 34 - sealing rings; 4, 11, 19, 31, 37 - bolts; 5 - locking plate; 6 - rear cover of the gearbox; 7, 33 - outer rings of differential bearings; 8 - adjusting nut bearings; 9 - retainer plate; 10 - washer; 13, 36 - oil seals; 14 - axis of differential satellites; 15 - retainer axis satellites; 16, 30 - differential tapered roller bearings; 17 - gasket; 18 - lower cover of the gearbox; 20 - differential case; 21, 26 - thrust washers; 22, 25 - side gears; 23, 27 - thrust washers of satellites; 24 - satellites; 28 - driven gear of the main gear; 29 - speedometer drive gear; 32 - gearbox housing; 35 - right differential bearing cover
Differential conical, two-satellite. The tightness of the connection of the internal hinges of the front wheel drives with the differential gears is ensured by oil seals 3 (see fig. 6.4), 13 (see fig. 6.6) and 36.
Automatic transmission (pic. 6.8) allows you to choose the optimal gearshift mode for almost any driving style and road conditions.
It is arranged according to the traditional planetary circuit with friction braking and is connected to the engine crankshaft through a torque converter. A feature of the Chevrolet Cruze gearbox is the ability to switch from fully automatic control mode to semi-automatic mode, in which the driver, depending on driving conditions, can forcibly block automatic shifting to higher gears. The automatic transmission control algorithm is described in detail in «Gearbox control».
Cable drive for automatic transmission control. Lever 7 (pic. 6.9) The gearbox control selector is installed in the same place on the floor tunnel as the manual gearbox control lever. The selector lever is connected to the lever 11 of the control unit on the gearbox with a cable 4.
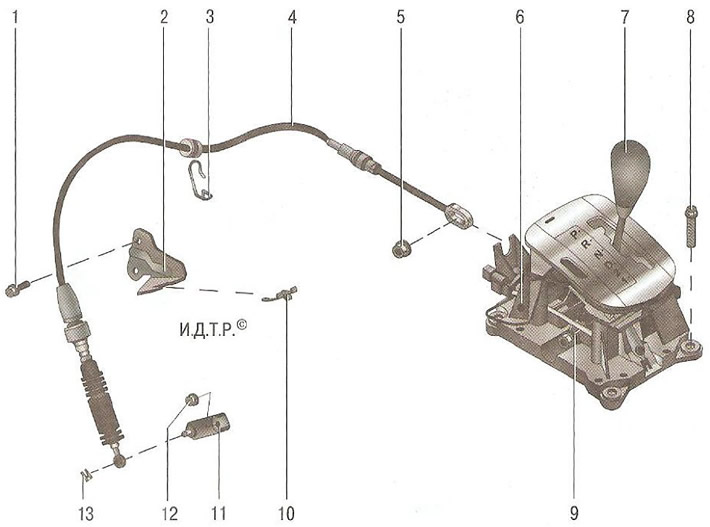
Pic. 6.9. Automatic transmission control drive: 1 - a bolt of fastening of an arm of a cable of management to a transmission; 2 - bracket for fastening the control cable to the gearbox; 3 - control cable holder on the body; 4 - gearbox control cable; 5 - nut for fastening the cable tip to the gearbox control selector lever; 6 - bracket for gear selector lever; 7 - automatic transmission control selector lever; 8 - bolt for fastening the bracket to the base of the body; 9 - mechanism bracket; 10 - cable sheath retainer; 11 - gearbox control lever; 12 - nut for fastening the gearbox control lever to the shaft of the gearbox control unit; 13 - cable tip retainer
Differential The design of an automatic transmission is completely similar to that of a manual transmission differential.
To repair an automatic transmission, a large set of special tools and appropriate training of the performer are required, so if repair of the transmission is necessary, contact a specialized service.
