- fuel supply, including fuel tank, fuel module, fuel filter and fuel pressure regulator (part of the fuel module), pipelines and fuel rail with injectors;
- air supply, which includes an air filter, an air supply sleeve, a throttle assembly;
- catching fuel vapors, consisting of an adsorber, an adsorber purge valve and connecting pipelines.
Note: The evaporative emission system is described in a separate subsection (see «Evaporative Emission System»), since it only serves to fulfill environmental requirements to reduce toxicity.
Functional purpose fuel supply systems - ensuring the supply of the required amount of fuel to the engine in all operating modes. The engine is equipped with an electronic control system with distributed fuel injection. In the distributed injection system, the functions of mixture formation and dosing of the air-fuel mixture supply to the engine cylinders are separated: air is supplied by an air supply system consisting of a throttle assembly, and the amount of fuel required at each moment of engine operation is injected by injectors into the intake pipe. This control method makes it possible to ensure the optimal composition of the combustible mixture at each particular moment of engine operation, which allows obtaining maximum power with the lowest possible fuel consumption and low exhaust gas toxicity. Manages the fuel injection system (as well as the ignition system) an electronic unit that continuously monitors, with the help of appropriate sensors, the engine load, the vehicle speed, the thermal state of the engine, and the optimal combustion process in the engine cylinders.
A feature of the Chevrolet Cruze injection system is the synchronous operation of the injectors in accordance with the valve timing (the engine control unit receives information from the phase sensor). The control unit turns on the nozzles sequentially, and not in pairs, as in asynchronous injection systems. Each nozzle is activated through 720°of crankshaft rotation. However, in starting and dynamic modes of engine operation, an asynchronous method of fuel supply is used without synchronization with the rotation of the crankshaft.
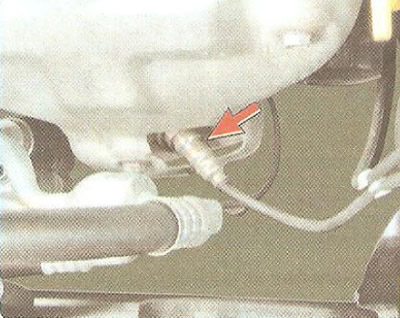
The main sensor for ensuring an optimal combustion process is control oxygen concentration sensor in exhaust gases (Lambda probe). It is installed in the exhaust manifold of the exhaust gas system and, together with the engine control unit and injectors, forms a control loop for the composition of the air-fuel mixture supplied to the engine. Based on the sensor signals, the engine control unit determines the amount of unburned oxygen in the exhaust gases and, accordingly, evaluates the optimal composition of the air-fuel mixture entering the engine cylinders at any given time. Having fixed the deviation of the composition from the optimal 1:14 (fuel/air), providing the most efficient operation of the catalytic converter of exhaust gases, the control unit changes the composition of the mixture using injectors. Since the oxygen concentration sensor is included in the feedback circuit of the engine control unit, the air-fuel ratio control loop is closed.
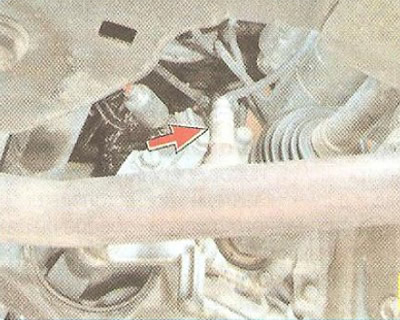
A feature of the engine management system of a Chevrolet Cruze car is the presence, in addition to the control sensor, of a second, diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor, installed in the exhaust pipe of the exhaust system. According to the composition of the gases that have passed through the converter, it determines the efficiency of the engine control system. If the engine control unit, according to information received from the diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor, detects an excess of exhaust gas toxicity that cannot be eliminated by calibrating the control system, then it turns on the engine malfunction warning light in the instrument cluster and stores the error code in memory for subsequent diagnostics.

Fuel tank made of polymeric materials is installed under the bottom of the body in its rear part and is attached to it with two clamps. In order to prevent fuel vapor from entering the atmosphere, the tank is connected by a pipeline to the adsorber. An electric fuel pump is installed in a flanged hole at the top of the tank. From the pump, fuel is supplied to the engine fuel rail mounted on the intake pipe. From the fuel rail, fuel is injected by injectors into the intake pipe.
Fuel lines power systems are tubes connecting various elements of the system.
Warning: Power system hoses are made using a special technology from oil and petrol resistant materials. Use of hoses other than those recommended may result in failure of the power system and, in some cases, fire.

fuel pump module includes electric pump, fuel pressure regulator and fuel gauge sensor.
The fuel pump module delivers fuel and is installed in the fuel tank, reducing the chance of vapor lock because fuel is supplied under pressure rather than vacuum. The lubrication and cooling of the fuel pump parts is also improved.
The fuel pump is submersible, rotary type, with an electric drive.
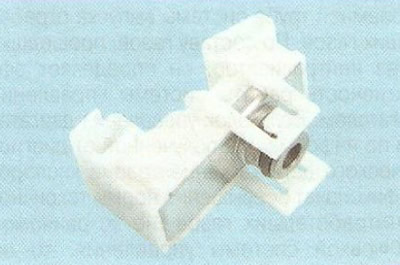
Fuel pressure control installed in the fuel pump module and designed to maintain constant fuel pressure in the fuel rail. The regulator is connected to the beginning of the supply line (immediately after the fuel filter) and is a bypass valve with a spring having a strictly calibrated force.
Fuel filter full-flow, structurally integrated with the fuel module body. If the filter becomes clogged, the housing assembly must be replaced.
fuel rail 2 (pic. 5.18) is a hollow part with holes for injectors, with fitting 1 for connecting a high-pressure fuel line and brackets 4 for attaching to the intake pipe. The injectors 6 are sealed in the openings of the ramp and in the sockets of the inlet pipe with rubber rings 5 and secured with spring clips 3. The complete assembly with injectors is inserted into the openings of the inlet pipe with the injector shanks and secured with two bolts.
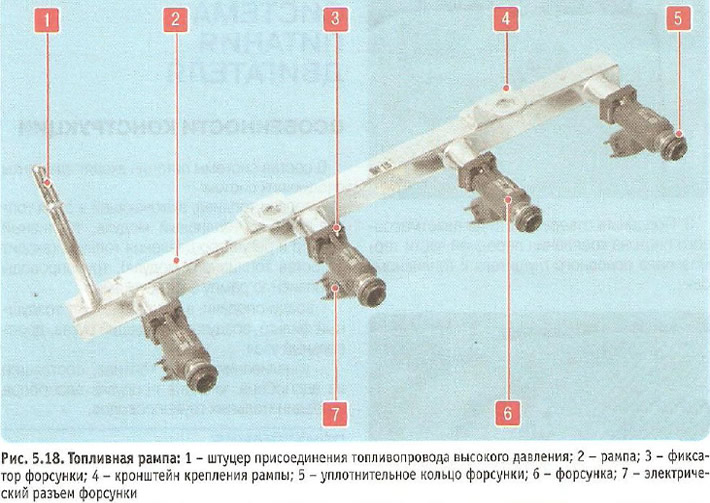

nozzles (pic. 5.19) attached to the ramp from which fuel is supplied to them, and with their atomizers they enter the openings of the intake pipe. The nozzles are sealed with rings 2 and 4 in the openings of the ramp and the intake pipe. The nozzle is designed for metered fuel injection into the engine cylinder and is a high-precision electromechanical valve. Pressurized fuel flows from the rail through channels inside the nozzle body to the shut-off valve. A spring compresses the check valve needle against the taper hole in the atomizer plate, keeping the valve in the closed position. The voltage supplied from the engine control unit through the electrical connector 1 to the injector solenoid winding creates a magnetic field in it, which draws the core together with the shut-off valve needle into the solenoid. The conical annular hole in the atomizer plate opens, and fuel is injected through the diffuser of the atomizer body into the inlet channel of the cylinder head and further into the engine cylinder. After the electrical impulse stops, the spring returns the core and the shut-off valve needle to its original state - the valve closes. The amount of fuel injected by the injector depends on the duration of the electrical impulse.


Air filter installed in the right front of the engine compartment on the car body. The lower pipe of the filter is inserted into the air duct of the intake silencer, installed under the right front fender.

The filter is connected by a plastic pleated air supply sleeve with throttle body.
Air filter element paper, flat, with a large area of the filtering surface.
Throttle assembly (pic. 5.20) is the simplest control device and serves to change the amount of main air supplied to the engine intake system. It is installed on the inlet flange of the inlet pipe. A molded plastic sleeve is put on the inlet pipe of the throttle assembly, fixed with a clamp and connecting the throttle assembly with the air filter.
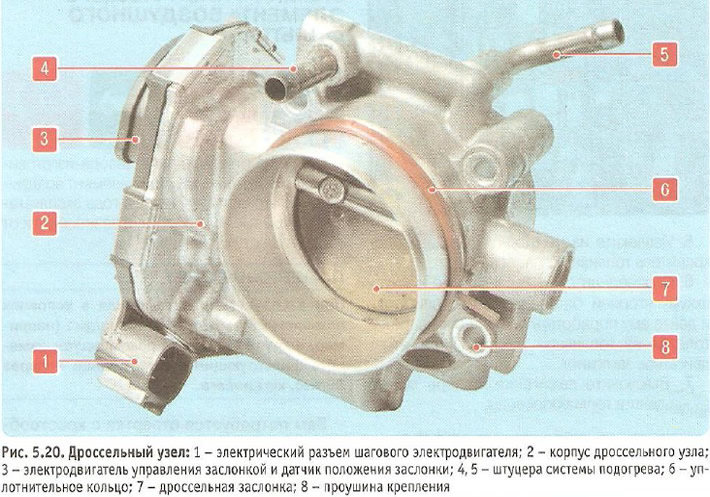
The throttle assembly includes a throttle position sensor and a stepper motor 3 for throttle control. There is no mechanical connection between the throttle assembly and the throttle control pedal. So-called «electronic» the throttle control pedal transmits information about the degree of depression on the pedal to the electronic engine control unit, which, in turn, taking into account the vehicle speed, the gear engaged, the engine load and the crankshaft speed, opens the throttle valve to the desired angle.
There is no seasonal adjustment device in the air filter, so the throttle assembly is equipped with a heating system that prevents icing of the throttle valve in the cold season and is connected to the engine cooling system by hoses.
During operation, the throttle assembly does not require maintenance and adjustment, only monitor the condition of the rubber seals to avoid air leakage.
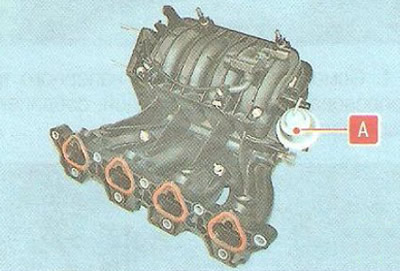
The inlet pipe is equipped system for changing the length of the intake tract, which allows you to develop increased power at high engine speeds (minimum intake tract length) and maximum torque in the low and medium speed range (increased length of the intake tract). The length of the intake pipe channels is changed at the signal of the engine control unit by turning the damper inside the intake pipe using pneumatic chamber A, which is connected to the engine vacuum system through a solenoid valve.
