There are many reasons for the deterioration of the dynamics, the main ones can be defined as follows.
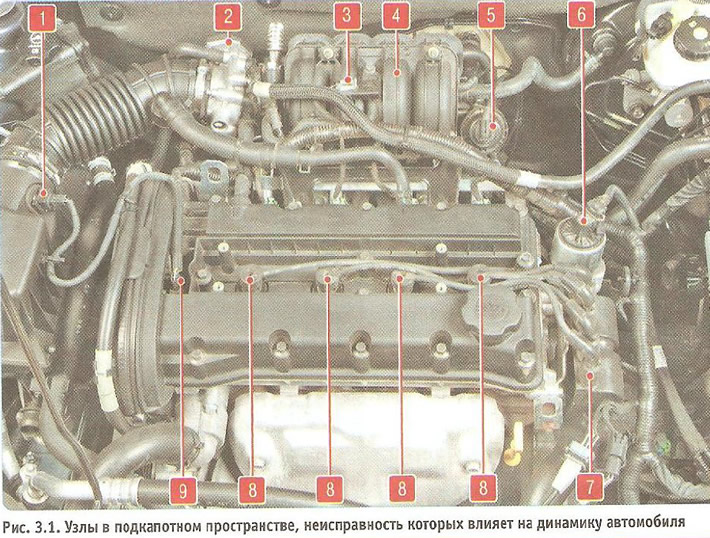
1. Engine malfunction - low compression in one or more cylinders, additional air is sucked into the intake pipe 4 (pic. 3.1). Coking of the exhaust system or damage to the catalytic converter (see «Exhaust system»).
2. Malfunction of the power supply system - clogging of the nozzles, fuel filter and hoses of the fuel supply system. Insufficient fuel pump supply, Use of low-quality fuel.
3, Malfunction of the ignition system - failure of the spark plug, ignition coils 7, breakdown of high-voltage wires 8 (see «Checking the ignition system»).
4, Malfunction of the engine management system - failure of the system sensors: intake air temperature sensor 1, throttle position sensor 2, absolute pressure sensor 3, phase sensor 9 (see «Engine management system»). If any sensor fails, the electronic control unit switches to work according to a backup program that allows you to get to a garage or car service, but at the same time, the power and economic characteristics of the engine are reduced.

5. Malfunction of the system for changing the geometry of the inlet pipe - failure of the solenoid valve 6 and pneumatic actuator 5 of the system.
6. Clutch slip due to wear or malfunction of the elements of the hydraulic drive to turn it off.
7. Malfunction of the brake system - braking of one or more wheels while driving, incorrect adjustment of the parking brake.
8. Insufficient tire pressure.
9. Car overload.
A complete diagnosis of the car should be carried out by highly qualified craftsmen using special diagnostic equipment, so contact a car service.
You can independently carry out the following work.
1. Check and adjust the air pressure in the tires.
2. Check the operation of the service brake system and parking brake. It is not necessary to remove the wheels for this. Find a flat section of the road and in dry, calm weather, conduct a ride to determine the run-out of the car. The car must be fully fueled, only the driver is in the cabin. Accelerate the vehicle to 50 km/h, level off the speed, and then disengage the gear and coast to a complete stop. Take another ride in the opposite direction. The overrun should be about 500 m.
3. Check the operation of the ignition system as described above.
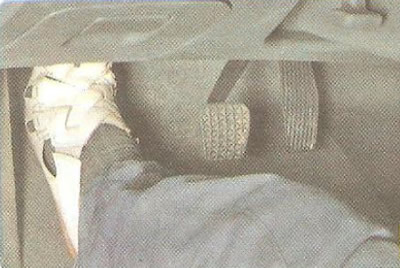
4. Check clutch operation. The initial check is carried out on a flat, obstacle-free area. Set the accelerator pedal to a higher idle speed - approximately 1500 min-1. Brake the vehicle with the parking brake. Depress the clutch and engage first gear. Then begin to slowly release the clutch pedal. If the engine stalls, the clutch is working and not slipping. If the engine does not stall, the clutch is worn and needs to be replaced.
