Description of the checkpoint
New automatic transmission (AISIN 55-51LE) is a five-speed electronically controlled automatic transmission.
The main elements of the gearbox are torque converter, planetary gear, hydraulic control system and electronic control system.
Electronic components
Gearbox controller
The main function of the automatic transmission controller is to determine the moments of gear shifting and engagement of the torque converter lock-up clutch. It is located under the instrument panel on the driver's side.
Automatic transmission shifting is controlled by an electronic system. The controller processes the signals coming to it. Based on the information received, the TCM controls the hydraulic system.
The electronic control system consists of the following elements:
- Automatic transmission controller
- Shift Solenoid Valves (SS1, SS2, SS3, SS4 and SS5)
- Transmission input shaft speed sensor
- Transmission output shaft speed sensor
- Automatic transmission fluid temperature sensor
- Gearbox range switch
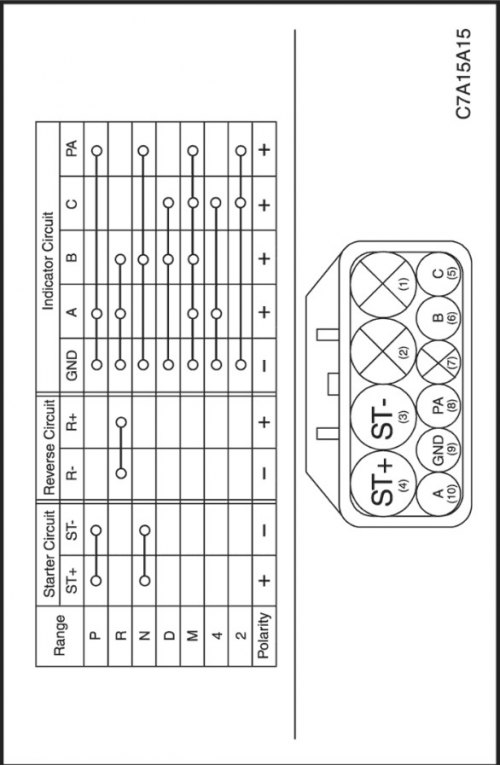
Gearbox range switch
The range switch sends information to the starter and the automatic transmission controller depending on the position of the gear lever.
- The engine can only be started if the range switch is in the "P" or "N". (Protection against starting the engine with the gear engaged.)
- When reversing, the automatic transmission range switch gives the command to turn on the reverse lights.
- The received information is used to control gear shifting.
The automatic transmission range switch sends signals to the starter and to the reverse circuit, bypassing the automatic transmission controller.
Switching solenoid valve No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (SS1, SS2, SS3, SS4, SS5)
5 switching solenoid valves are installed in the valve body. The solenoid valves turn on and off based on a control signal from the TCM. Combinations of 5 shift solenoid valves, SS1, SS2, SS3, SS4 and SS5, change gear ranges.
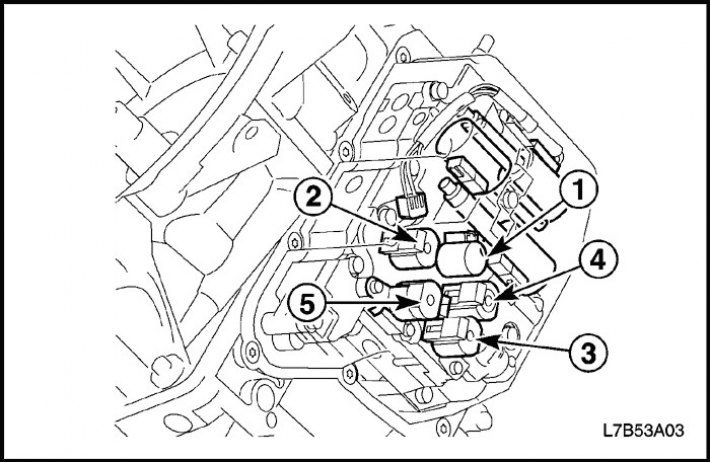
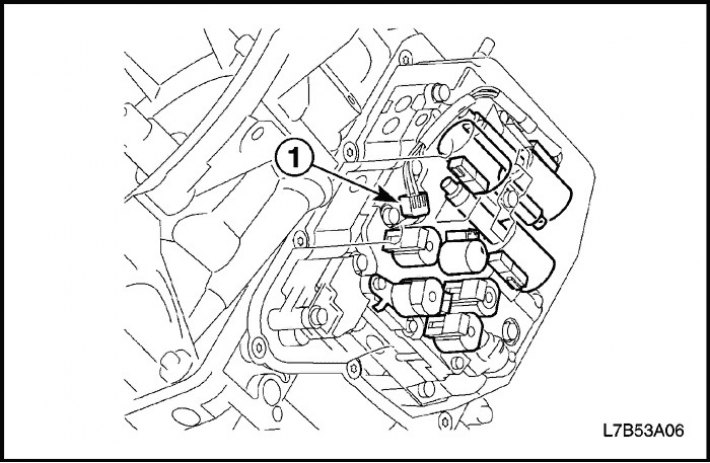
Solenoid valve for pressure control in hydraulic lines (SLT)
Solenoid valve for pressure control in hydraulic lines (SLT) regulates the line pressure upstream of the throttle valve using a control signal from the TCM and the pressure in the hydraulic lines of the clutches and brakes to reduce shock during gear changes.
Torque converter clutch lock-up solenoid valve (SLU)
Torque converter clutch lock-up solenoid valve (SLU) regulates SLU line pressure with control signal from TCM and hydraulic clutch lockout pressure to reduce shift shock.
1st gear, engine braking - 1st gear and reverse brake (B3)
2nd gear - 2nd gear brake (B2)
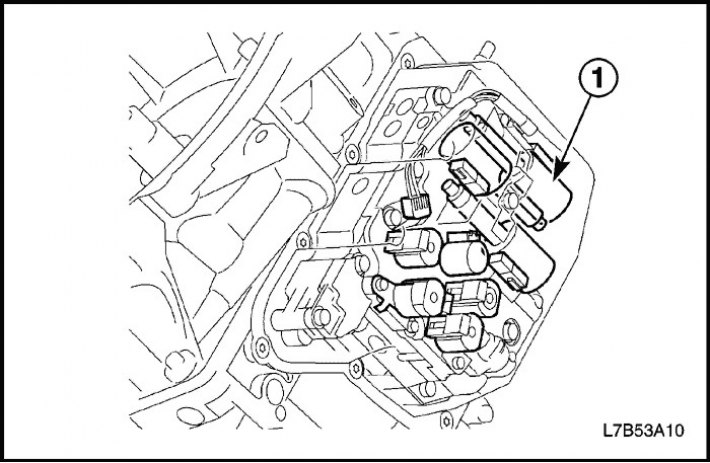
Shift pressure control solenoid valve (SLS)
Shift pressure control solenoid valve (SLS) regulates SLS line pressure using a control signal from the TCM.
2nd, 3rd, 4th gears - 2nd gear inertia brake (B1)
5th gear, reverse gear - direct clutch (C2)
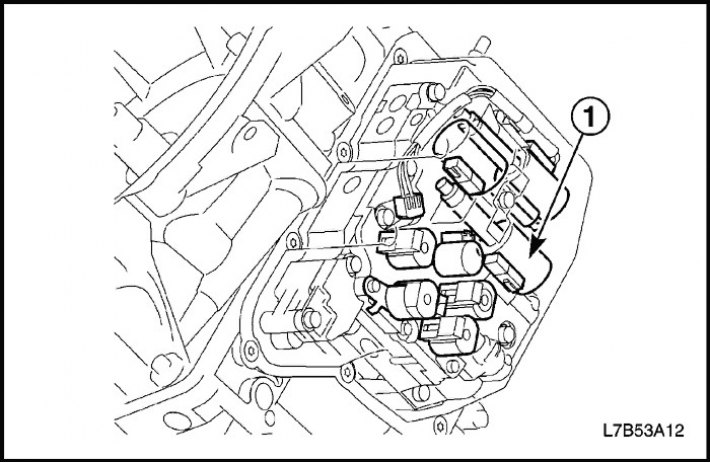
Automatic transmission fluid temperature sensor
The transmission fluid temperature sensor is located in the valve block.
The automatic transmission fluid temperature sensor sends information about the temperature of the automatic transmission fluid to the TCM.
The controller uses the received data to calculate the moments of gear shifting and engagement of the torque converter lock-up clutch.
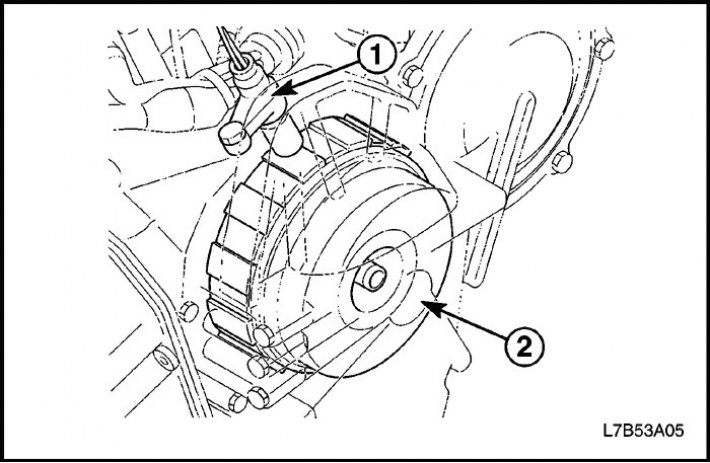
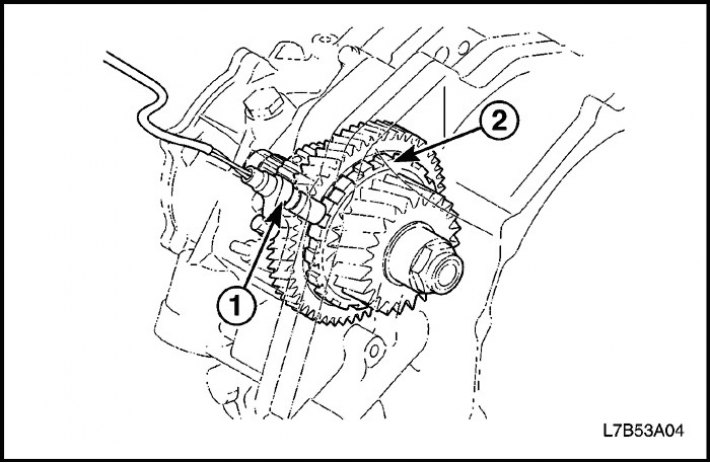
Transmission input shaft speed sensor
Transaxle Input Shaft Speed Sensor Assembly (1), mounted on top of the gearbox with final drive assembly, determines the speed of rotation of the input shaft by the number of revolutions of the drum (2) direct drive clutches.
The sensor sends a shaft speed signal to the TCM.
Transmission output shaft speed sensor
Transaxle Output Shaft Speed Sensor Assembly (1), mounted on top of the transaxle assembly, senses vehicle speed from the number of revolutions of the park gear (2).
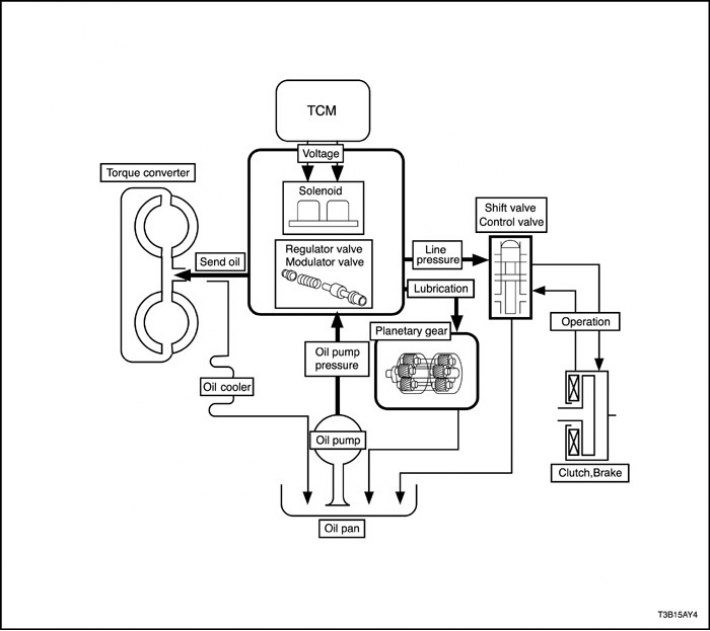
Hydraulic control system
Depending on the pressure supplied by the oil pump, the TCM commands the on/off solenoid valves of the hydraulic system, which controls the operation of the torque converter, planetary gear, clutches and brakes in accordance with the driving mode of the vehicle.
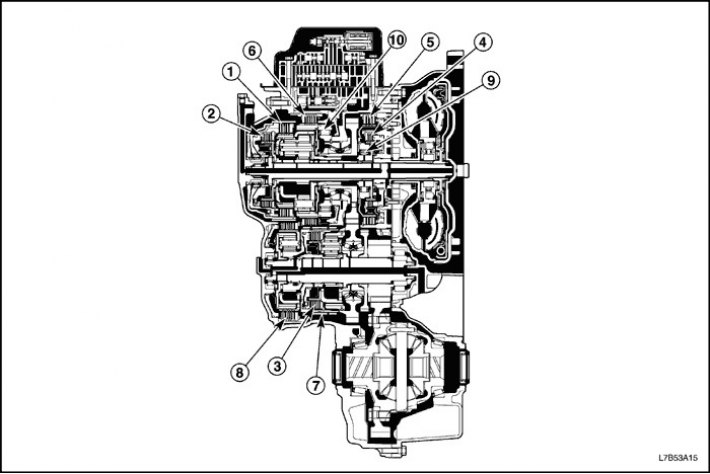
Automatic transmission (automatic transmission)
Purpose of components
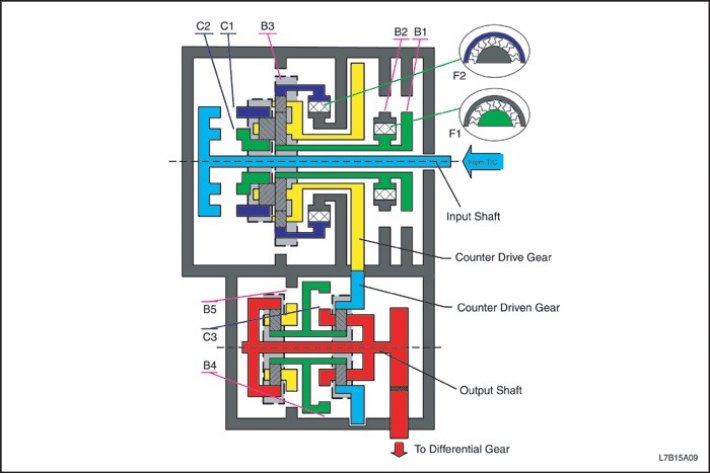
|
Clutch and brake
|
Purpose
|
|
|
C1
|
Forward clutch (1)
|
Ensuring the connection of the input shaft with the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set.
|
|
C2
|
Direct clutch (2)
|
Ensuring the connection of the input shaft with the sun wheel of the rear planetary gear set.
|
|
C3
|
underdrive clutch (3)
|
Provision of communication of the sun wheel of the reduction gear with the carrier of the front planetary gear set of the reduction gear.
|
|
B1
|
Inertia brake 2nd gear (4)
|
Ensuring the blocking of the sun wheel of the front planetary gear set.
|
|
B2
|
2nd gear brake (5)
|
Ensuring locking the rotation of the sun wheel of the front planetary set counterclockwise.
|
|
B3
|
1st gear and reverse brake (6)
|
Providing locking of the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set.
|
|
B4
|
Underdrive brake (7)
|
Ensuring blocking of the undershift sun wheel.
|
|
B5
|
Brake B5 (8)
|
Ensuring the blocking of the carrier of the rear planetary gear set.
|
|
F1
|
Overrunning Clutch #1 (9)
|
Ensuring that the sun wheel of the front planetary gear set does not rotate counterclockwise when the B2 brake is applied.
|
|
F2
|
Freewheel No. 2 (10)
|
Ensuring locking the rotation of the epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary set counterclockwise.
|
Operation of friction clutches and brakes
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
|||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
|||
|
P
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
||
|
R
|
V<=7
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
|
V>7
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
||
|
N
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
||
|
D, M
|
D
|
1st
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
|
M
|
1st
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
|
|
2nd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
||
|
3rd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
||
|
4th
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
||
|
5th
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
||
|
4
|
1st
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
|
|
2nd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
||
|
3rd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
||
|
2
|
1st
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
|
|
2nd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
||
D - 1st gear
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
||
|
D
|
1st
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
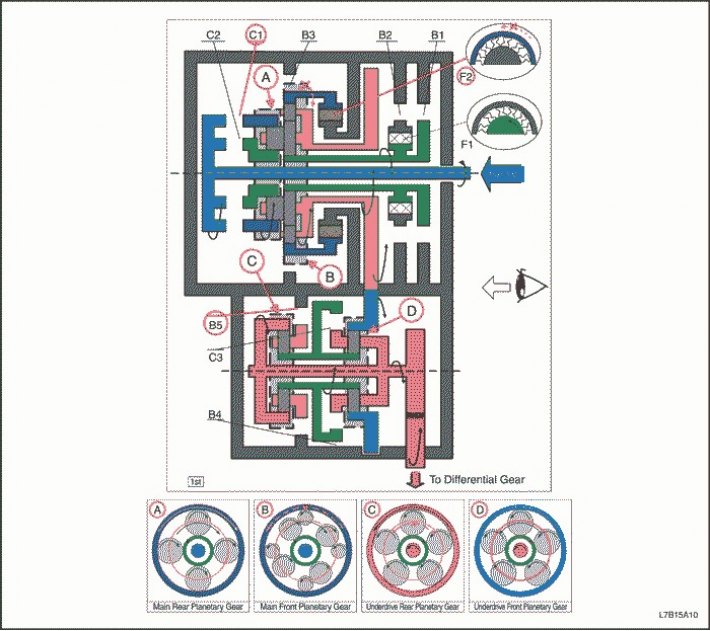
"D" - 1st gear
1. The input shaft rotates clockwise.
- Enabled C1 (Connects the input shaft to the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
2. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
3. The rear planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
4. The large front planetary pinion itself rotates clockwise, and the rear planetary pinion rotates with it.
5. The small pinion of the front planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
6. The front epicyclic gear will rotate counterclockwise.
- Enabled F2 (Ensuring locking the rotation of the epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary set counterclockwise).
7. The front and rear planetary carrier rotates clockwise due to the reactive force of the front planetary gear small pinion.
8. The intermediate shaft drive gear rotates clockwise, and the carrier of the front and rear planetary gears rotates with it.
9. The intermediate shaft driven gear rotates counterclockwise.
10. The epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise, and the countershaft driven gear rotates with it.
11. The front planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
12. The sun wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
13. The rear planetary sun gear rotates clockwise and the front planetary sun gear rotates with it.
14. The rear planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
- Enabled B5 (Blocks the rotation of the carrier of the rear planetary gear set).
15. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise.
16. The front row carrier and differential pinion rotate counterclockwise, and the rear epicyclic gear rotates with them.
17. The driven gear of the final drive rotates clockwise.
(Engine braking)
1. The intermediate shaft drive gear and the main carrier of the front and rear planetary gears rotate clockwise.
2. The rear planetary carrier rotates clockwise, but the rear planetary pinion rotates clockwise, although it itself rotates counterclockwise due to the resistance of the rear planetary gear epicyclic gear.
3. The large front planetary pinion rotates clockwise although it rotates counterclockwise, and the small front planetary gear rotates clockwise while itself rotates clockwise. And the carrier of the front planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
4. The front epicyclic gear rotates clockwise due to the fact that the small front gear rotates clockwise itself, but the driving force is lost due to the release of F2. Therefore, engine braking is not activated.
D - 2nd gear
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
||
|
D
|
2nd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
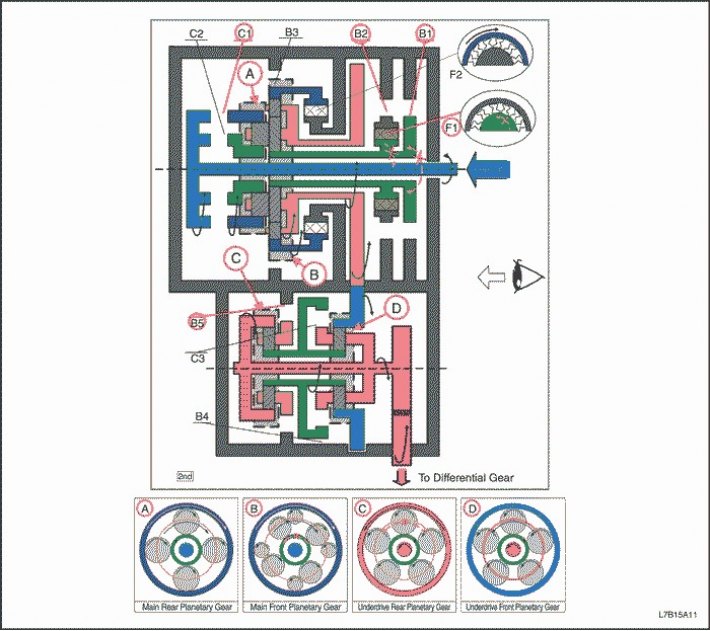
"D" - 2nd gear
1. The input shaft rotates clockwise.
- Enabled C1 (Connects the input shaft to the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
2. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
3. The rear planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
4. The large front planetary pinion itself rotates clockwise, and the rear planetary pinion rotates with it.
- Included B2 with F1 and B1 (Block the rotation of the sun wheel of the front planetary gear set)
5. The front and rear planetary carrier turns clockwise due to the reaction force of the large front planetary pinion.
6. The intermediate shaft drive gear rotates clockwise, and the carrier of the front and rear planetary gears rotates with it.
7. The intermediate shaft driven gear rotates counterclockwise.
8. The epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise, and the countershaft driven gear rotates with it.
9. The front planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
10. The sun wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
11. The rear planetary sun gear rotates clockwise and the front planetary sun gear rotates with it.
12. The rear planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
- Enabled B5 (Blocks the rotation of the carrier of the rear planetary gear set)
13. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise.
14. The front row carrier and differential pinion rotate counterclockwise, and the rear epicyclic gear rotates with them.
15. The driven gear of the final drive rotates clockwise.
(Engine braking)
1. The driving force is transferred to the input shaft without the intervention of the overrunning clutch. Engine braking works.
D - 3rd gear
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
||
|
D
|
3rd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
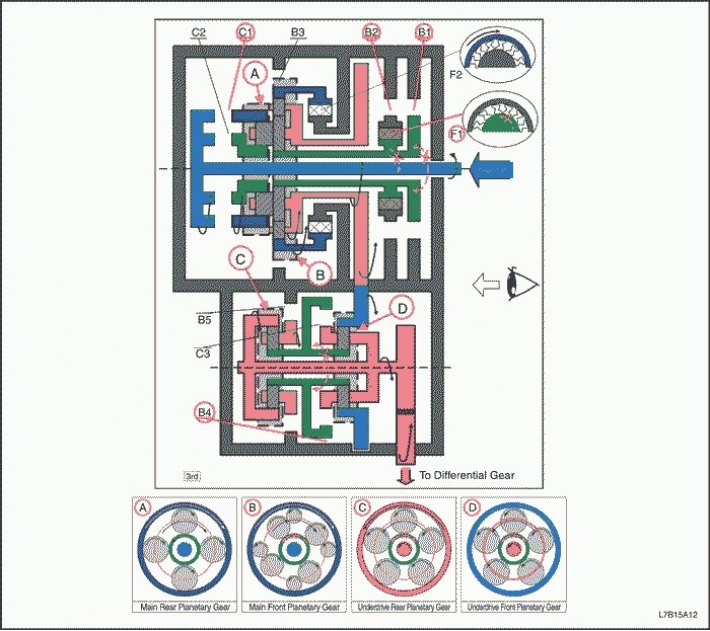
"D" - 3rd gear
1. The input shaft rotates clockwise.
- Enabled C1 (Connects the input shaft to the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
2. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
3. The rear planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
4. The large front planetary pinion itself rotates clockwise, and the rear planetary pinion rotates with it.
- Included B2 with F1 and B1 (Block the rotation of the sun wheel of the front planetary gear set)
5. The front and rear planetary carrier turns clockwise due to the reaction force of the large front planetary pinion.
6. The intermediate shaft drive gear rotates clockwise, and the carrier of the front and rear planetary gears rotates with it.
7. The intermediate shaft driven gear rotates counterclockwise.
8. The epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise, and the countershaft driven gear rotates with it.
9. The front planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
- Enabled B4 (Blocks the rotation of the sun wheel of the front and rear planetary gear set)
10. The front planetary carrier turns counterclockwise due to the reaction force of the front planetary pinion.
11. The rear epicyclic gear and differential pinion rotate counterclockwise, and the front row carrier rotates with them.
12. The driven gear of the final drive rotates clockwise.
(Engine braking)
- The driving force is transferred to the input shaft without the intervention of the overrunning clutch. Engine braking works.
D - 4th gear
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
||
|
D
|
4th
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
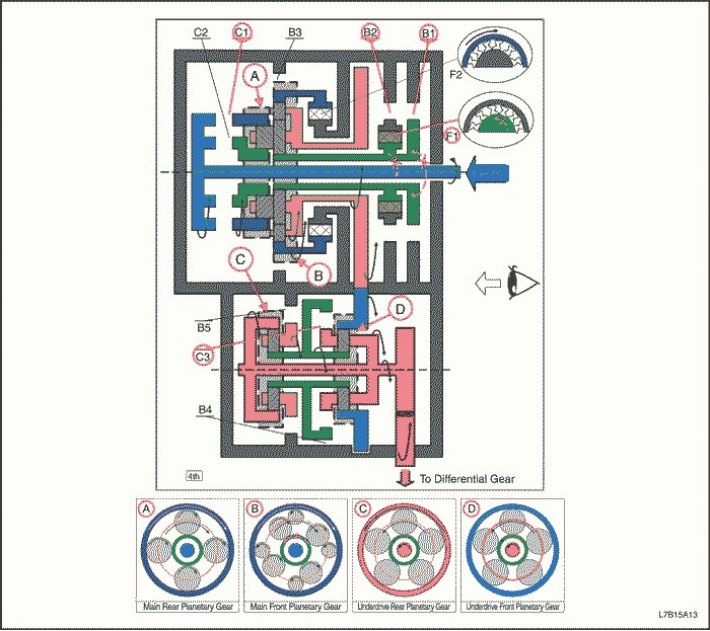
"D" - 4th gear
1. The input shaft rotates clockwise.
- Enabled C1 (Connects the input shaft to the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
2. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
3. The rear planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
4. The large front planetary pinion itself rotates clockwise, and the rear planetary pinion rotates with it.
- Included B2 with F1 and B1 (Block the rotation of the sun wheel of the front planetary gear set)
5. The front and rear planetary carrier turns clockwise due to the reaction force of the large front planetary pinion.
6. The intermediate shaft drive gear rotates clockwise, and the carrier of the front and rear planetary gears rotates with it.
7. The intermediate shaft driven gear rotates counterclockwise.
8. The epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise, and the countershaft driven gear rotates with it.
- Enabled C3 (Ensuring the connection of the sun wheel of the planetary gear set with the carrier of the front planetary gear)
9. The front planetary pinion cannot rotate by itself, and the underdrive unit rotates counterclockwise alone.
10. The differential gear pinion rotates counterclockwise and the downshift unit rotates with it.
11. The driven gear of the final drive rotates clockwise.
1. The driving force is transferred to the input shaft without the intervention of the overrunning clutch. Engine braking works.
D-5th gear
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
||
|
D
|
5th
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
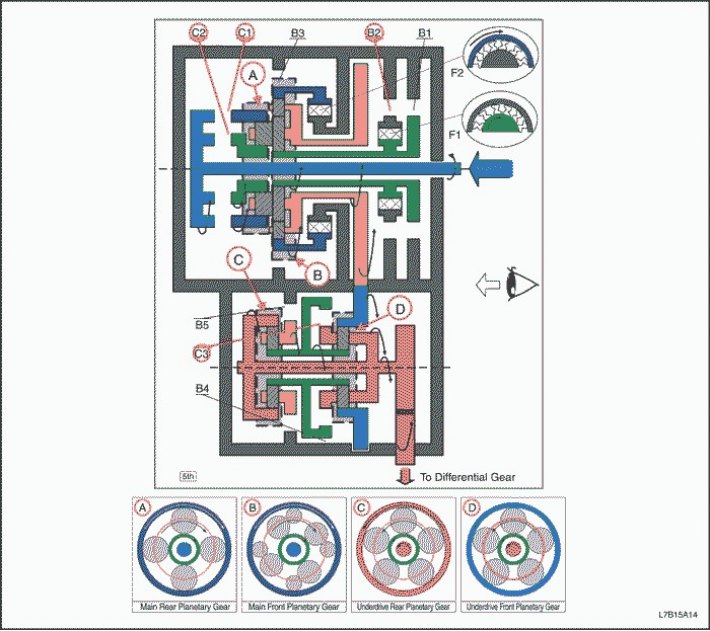
"D" - 5th gear
1. The input shaft rotates clockwise.
- Enabled C1 (Connects the input shaft to the epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
- Enabled C2 (Ensuring the connection of the input shaft with the sun wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
2. The rear planetary pinion cannot rotate by itself, and the rear planetary gear unit rotates clockwise alone.
3. The large front planetary pinion cannot rotate on its own with the rear planetary pinion, and the front planetary gear unit rotates clockwise alone.
4. The countershaft drive gear rotates clockwise and the front planetary gear assembly rotates with it.
5. The intermediate shaft driven gear rotates counterclockwise.
6. The epicyclic gear wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise, and the countershaft driven gear rotates with it.
- Enabled C3 (Ensuring the connection of the sun wheel of the planetary gear set with the carrier of the front planetary gear)
7. The front planetary pinion cannot rotate by itself, and the underdrive unit rotates counterclockwise alone.
8. The differential gear pinion rotates counterclockwise and the downshift unit rotates with it.
9. The driven gear of the final drive rotates clockwise.
1. The driving force is transferred to the input shaft without the intervention of the overrunning clutch. Engine braking works.
Reverse
|
Position
|
Solenoid
|
Coupling
|
Brake
|
Freewheel
|
||||||||||||
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
C1
|
C2
|
C3
|
B1
|
B2
|
B3
|
B4
|
B5
|
F1
|
F2
|
||
|
R
|
V<=7km/h
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
V>7 km/h
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
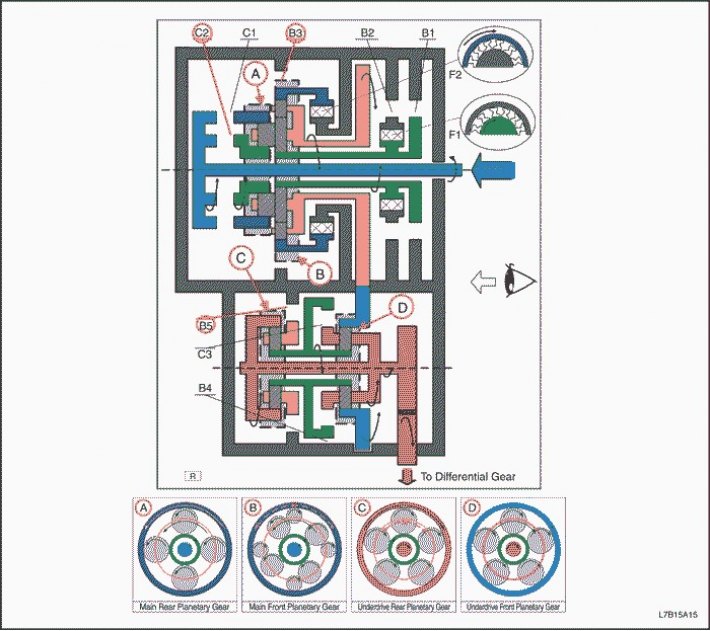
Reverse
1. The input shaft rotates clockwise.
- Enabled C2 (Ensuring the connection of the input shaft with the sun wheel of the rear planetary gear set)
2. The sun wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
3. The rear planetary gear itself rotates counterclockwise.
4. The large front planetary pinion rotates counterclockwise on its own, and the rear planetary pinion rotates with it.
5. The small pinion of the front planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
- Enabled B3 (Blocks the rotation of the epicyclic gear of the front planetary gear set)
6. The front and rear planetary carrier turns counterclockwise due to the reactive force of the front planetary gear small pinion.
7. The intermediate shaft drive gear rotates counterclockwise, and the carrier of the front and rear planetary gears rotates with it.
8. The countershaft driven gear rotates clockwise.
9. The epicyclic gear of the front planetary gear rotates clockwise, and the countershaft driven gear rotates with it.
10. The satellite of the front planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
11. The sun wheel of the front planetary gear set rotates counterclockwise.
12. The rear planetary sun gear rotates counterclockwise, and the front planetary sun gear rotates with it.
13. The rear planetary gear itself rotates clockwise.
- Enabled B5 (Blocks the rotation of the carrier of the rear planetary gear set)
14. The epicyclic gear wheel of the rear planetary gear set rotates clockwise.
15. The front row carrier and differential pinion rotate clockwise, and the rear epicyclic gear rotates with them.
16. The driven gear of the final drive rotates counterclockwise.
1. The driving force is transferred to the input shaft without the intervention of the overrunning clutch. Engine braking works.
TCM control functions
Switching control and blocking control
According to the shift program, the TCM sends a signal to the electronic valves S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5, which actuate the on/off control "Switching control", and the torque converter clutch lock-up solenoid valve (SLU), which actuates the linear control "Blocking management", based on vehicle speed and throttle opening.
Operation of each solenoid valve
|
Broadcast
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
|
1st
|
On
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
2nd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
Off
|
|
3rd
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
On
|
Off
|
|
4th
|
Off
|
Off
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
|
5th
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
On
|
Off
|
The 55-51LE automatic transaxle does not provide some user-selectable driving modes. Essentially, the TCM is programmed to "Economy mode", but under specific conditions, the TCM will automatically switch to multiple shift programs. However, only "Winter mode" can be selected with a switch.
1. Adaptive shift control for the driver (Eco, Medium, Sport modes)
Economy mode is used for normal driving conditions after the ignition is turned on. And the driver's preference is detected using fuzzy logic, based on the operation of the accelerator. This control changes gearshift points to Economy (low speed), Average (average speed) and Sports (high speed) according to preference.
|
Start (1) And (2)
|
(1) "D"
|
(2) Vehicle speed >= 5 km/h (3 mph)
|
|
Ending (1), or (2) or (3)
|
(1) Except "D"
|
(2) Vehicle speed > 240 km/h (149 mph)
|
|
(3) Found that the driver prefers "Economy mode"
|
||
2. Winter mode
This mode is used to start the vehicle on a slippery road by pressing the winter mode switch. (Car pulls off in 3rd gear)
|
Range
|
Winter
|
|
|
D
|
3 (L) ↔ 4 (L) ↔ 5 (L)
|
|
↔: up/down switch, (L): Lock operation
3. Hill driving mode
When the TCM detects uphill movement based on engine torque load and acceleration reduction, this mode changes the shift points in the high speed section according to the degree of uphill and prevents the automatic transmission from actively shifting.
4. Downhill driving mode
When the TCM detects a downhill movement based on the increase in full throttle acceleration, this mode activates moderate engine braking, changing shift points in the high speed portion.
5. HOT mode control (Hot)
This regulator reduces the temperature of the automatic transmission fluid, changing the shift points when it rises excessively. (Automatic transmission fluid temperature> 140°C (284°F))
6. Control "Height"
This governor compensates for reduced engine power by setting shift points in a slightly higher vehicle speed range when the vehicle is high above sea level where the air pressure is reduced.
7. Cold shift management
This control compensates for reduced engine torque by setting shift points in a slightly higher vehicle speed range when the air temperature is extremely cold. (Engine coolant temperature < -30°C (-22°F))
Manual shift control (Step mode (TAP))
The driver can select their favorite gearshift mechanism and enjoy the sporty driving style and feel of a manual transmission by shifting the gear selector lever from the range "D" to manual transmission position and M+ range (up switching) / M- (down switching). But the blocking control works automatically. Shift control is again actuated by shifting from manual transmission to range "D".
Lock release control
This control disables the downshift or idle lockout action and prevents the engine from stalling due to the brake pedal being pressed at low speed.
Upshift/downshift learning control
This regulator learns pressure on each clutch or brake to reduce shock with every gear shift (Raise, Lower, Mechanical lower, Coast down).
(1) 65°C (149°F) =< Oil temperature < 110°C (230°F)
(2) Constantly low throttle opening (about 20-30%)
(3) Sufficient switching interval (about 3 sec.)
(4) Repeat each switch about 10 times
ND switch control
This regulator improves ND shift quality by controlling the hydraulic line pressure control solenoid valve to match the forward clutch piston stroke (C1), learned in ND learning control and applying the best hydraulic pressure to the forward clutch (C1) when switching ND.
ND Learning Management
This regulator learns the hydraulic pressure of the forward clutch (1) by monitoring the on-time and rate of change of rotation of the forward clutch (1).
|
Start (1), And (2), And (3) And (4)
|
(1) 500 rpm =< Engine speed < 1200 rpm
|
|
|
(2) 65°C (149°F) =< Oil temperature < 110°C (230°F)
|
||
|
(3) 450 rpm =< forward clutch rotation (C1) < 1200 rpm
|
||
|
(4) Throttle opening < 3.0%
|
||
(1) When above trigger conditions
(2) Switching interval more than 3 sec.
(3) Repeat ND switching about 10 times
NR switch control
This regulator improves NR shift performance by controlling the shift pressure control solenoid valve to match the forward clutch piston stroke (C2), learned in NR learning control, and applying the best hydraulic pressure to the clutch (C2) when switching NR.
NR Learning Management
This regulator learns direct clutch hydraulic pressure (C2) by monitoring the on-time and the rate of change of rotation of the C2 clutch.
|
Start (1), And (2), And (3) And (4)
|
(1) 500 rpm =< Engine speed < 1200 rpm
|
|
|
(2) 65°C (149°F) =< Oil temperature < 110°C (230°F)
|
||
|
(3) 450 rpm =< forward clutch rotation (C1) < 1200 rpm
|
||
|
(4) Throttle opening < 3.0%
|
||
(1) When above trigger conditions
(2) Switching interval more than 3 sec.
(3) Repeat NR switching about 10 times
Torque reduction control
This regulator improves shift performance by sending a torque reduction request signal from the TCM to the ECM and disabling shift torque boost during ND, NR and 1↔2↔3↔4↔5 shifts.
When the accelerator pedal is pressed quickly, this control sets the upper limit of the engine torque and prevents such a circumstance as "Brief overrevving of the engine", when switching "clutch to clutch" 2↔3, 3↔4 and 4=>2.
CPR Adaptive Learning Procedure
Perform the Transmission Adaptive Learning procedure after any of the following maintenance activities:
- TCM Replacement
- Changing TCM Calibration
- Replacing the control valve block
- Overhaul of the gearbox with final drive assembly
- Replacing the gearbox with final drive assembly
1. Drive a car to warm up the transmission fluid to a temperature of 65-110°C (150-230°F). The adaptive learning procedure will not be performed if the automatic transmission fluid is not heated to the appropriate temperature.
2. Reset the adaptive learning results of the final drive assembly.
3. Complete the following steps for adaptive garage shift learning.
- Apply the parking brake and depress the brake pedal.
- Toggle out of NEUTRAL range for 3 seconds (Neutral) in range REVERSE (Reverse).
- Switch out of range REVERSE (Reverse) to NEUTRAL range (Neutral).
- Repeat the above two steps five times.
- Toggle out of NEUTRAL range for 3 seconds (Neutral) to the MOTION range (Drive).
- Switch from MOVE (Drive) to NEUTRAL (Neutral).
- Repeat the above two steps five times.
4. Perform the following steps for adaptive up/down switch learning.
- Drive a car in range "DRIVE" with low throttling (15-20 %) up to speed exceeding 50 km/h (31 mph) in 4th gear.
- Reduce speed and apply the brake until the car comes to a complete stop. Carry out braking of the car in such a way that it takes at least 14 seconds.
- Repeat the above steps five times.
5. If the shift indicator positions are P, R, N, D, 4, 2:
- Perform the following steps for adaptive 4→2 mechanical downshift learning (Non-Step TAP Switching).
- Drive a car in range "4" up to speed exceeding 25 km/h (16 mph) in 2nd at any throttle position.
- Slow down, manually change gear from "4" on "2" and stop the car.
- Repeat the above two steps ten times.
If the shift indicator positions are P, R, N, D, M:
- Perform the following steps for adaptive learning step down switching (TAP-DOWN) 2→1 (TAP step by step).
- Drive a car in range "TAP 2" up to speed exceeding 25 km/h (16 mph) or in 2nd gear at any throttle position.
- Slow down, manually switch from "TAP 2" on "TAP 1" and stop the car.
- Repeat the above two steps ten times.
Important: If shift quality does not improve, verify that the TCM is properly calibrated.
6. Confirm switching quality.
