Disassembly
1. Remove screw (1) oil nozzle mounts (2) (three places).
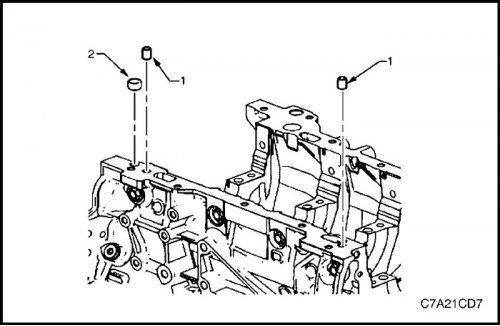
2. Remove pins (1) for installing an oil pan on the cylinder block and front flared plug (2) oil channel of cylinder block bank 1.
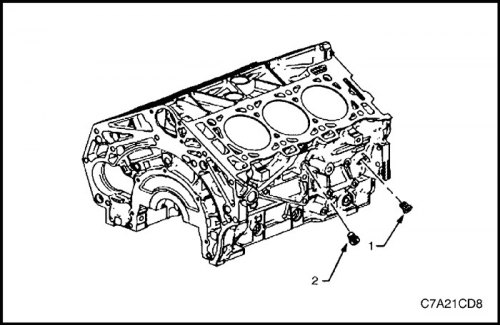
3. Remove the side screw plug (1) bank 1 cylinder block oil passage and screw plug (2) drain hole for coolant.
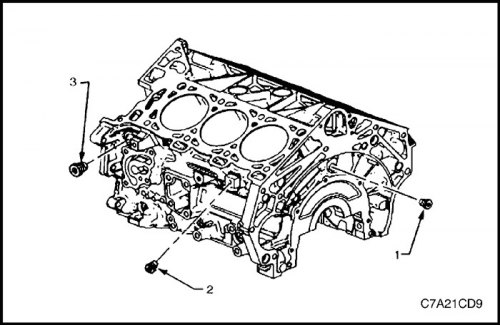
4. Remove rear screw plug (1) oil channel, side screw plug (2) coolant drain hole for cylinder bank 2 and the left-hand side screw plug (3) oil channel.
Attention! When removing the expanding coolant plugs, do not apply downward force, so as not to damage the cylinder block.
5. Remove expanding coolant plugs (1) and pins (2) for mounting the cylinder head to the cylinder block.
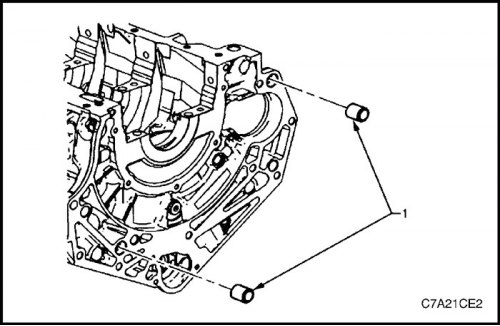
6. Remove pins (1) for mounting the gearbox on the cylinder block.
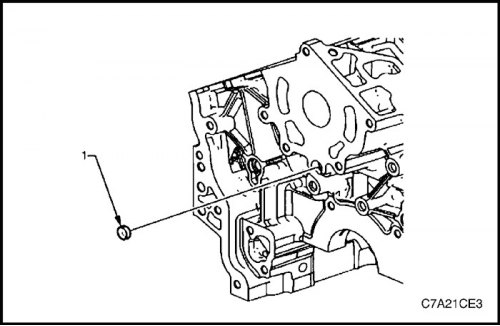
7. Remove the front expanding plug (1) oil channel.
Clear
1. Completely remove the thread sealant, gasket material and sealant using a conventional wooden or plastic scraper.
2. Clean all areas listed below with a suitable solvent:
- Sealing surfaces
- coolant channels,
- oil channels,
- bearing supports.
3. Clean all threaded and through holes with a suitable solvent.
4. Dry the cylinder block with compressed air.
Inspection
Measurement of cylinder diameters
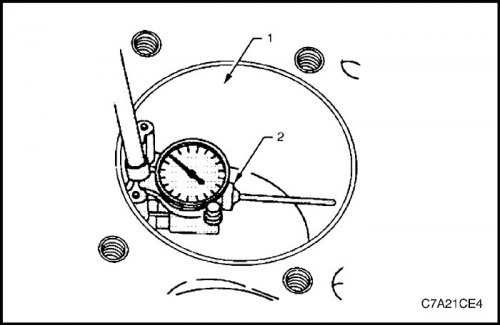
1. Measure the diameter of the cylinder at a distance of 37 mm from the top plane of the block (1), using a normal bore gauge or tool J-8087 (2).
2. Record the results and compare with the dimensions given in the technical specifications.
Note: If the cylinder diameter is larger than specified in the technical specifications, then the cylinder may be bored by 0.25 mm. For maintenance, only one repair size of pistons and rings is provided. If the cylinder diameter exceeds the required value by more than 0.25 mm, then the cylinder block must be replaced.
Measuring the taper of cylinders
1. Take a measurement on the side force bearing surfaces perpendicular to the crankshaft axis, 10 mm below the top surface of the cylinder block, and record the result.
2. Take a measurement on the side force bearing surfaces perpendicular to the crankshaft axis, 100mm below the top surface of the cylinder block, and record the result.
3. Determine the difference between these two measurements. This result will be the taper of the cylinder.
4. Compare the results with the dimensions given in the technical specifications.
5. If the cylinder diameter is larger than specified in the technical specifications, then the cylinder bore can be 0.25 mm. For maintenance, only one repair size of pistons and rings is provided. If the cylinder diameter exceeds the required value by more than 0.25 mm, then the cylinder block must be replaced.
Measuring out-of-roundness of cylinders
1. Measure the cylinder bore on the side load and non side load surfaces 10 mm below the top surface of the cylinder block. Record measurement results.
2. Determine the difference between these two measurements. The result will indicate the non-circularity of the upper end of the cylinder.
3. Measure the cylinder diameter on the side load and non side load surfaces 100 mm below the top surface of the cylinder block. Record measurement results.
4. Determine the difference between these two measurements. The result will indicate the non-circularity of the lower end of the cylinder.
5. Compare the results obtained with the dimensions indicated in the technical specifications.
6. If the cylinder diameter is larger than specified in the technical specifications, then the cylinder bore can be 0.25 mm. For maintenance, only one repair size of pistons and rings is provided. If the cylinder diameter exceeds the required value by more than 0.25 mm, then the cylinder block must be replaced.
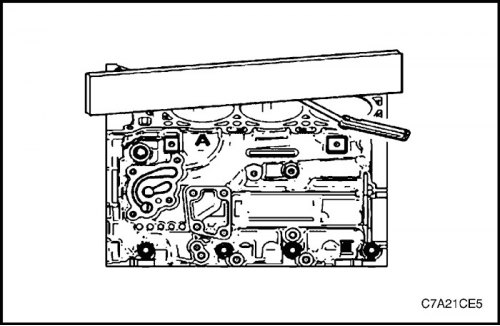
Checking the flatness of the upper surface of the cylinder block
1. The top surfaces of the cylinder block must be clean and free of gasket material.
2. Inspect the surface for blemishes or scratches that could prevent the gasket from sealing when the cylinder head is installed.
3. Lay a ruler diagonally across the top face of the cylinder block.
4. Measure the gap between the ruler and the front side of the cylinder block at 4 points along the ruler with a gap gauge.
5. If warping is less than 0.05 mm, then machining of the upper surface of the cylinder block is not required.
6. If warping is in the range of 0.05±0.20 mm, or there are any defects or scratches that may prevent the gasket from sealing when installing the cylinder head, then the upper surface of the cylinder block must be ground.
7. If grinding is required, then the maximum allowable thickness of the layer to be removed is 0.25 mm.
8. If more than 0.25 mm thick material needs to be removed from the top surface of the cylinder block, the block must be replaced.
Assembly
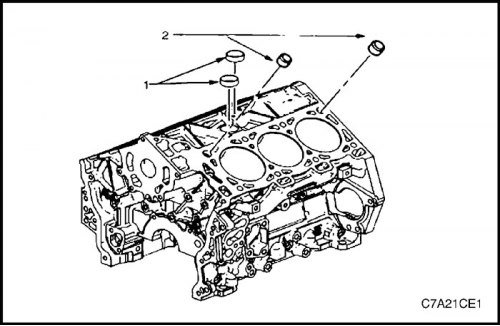
1. Apply RTV sealant to new flared plugs (1) coolant and reinstall them.
2. Install pins (2) for mounting the cylinder head to the cylinder block.
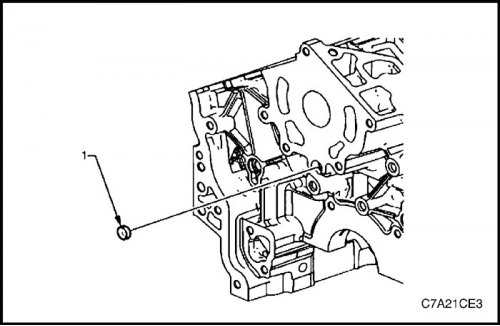
3. Install new front expanding plug (1) oil channel.
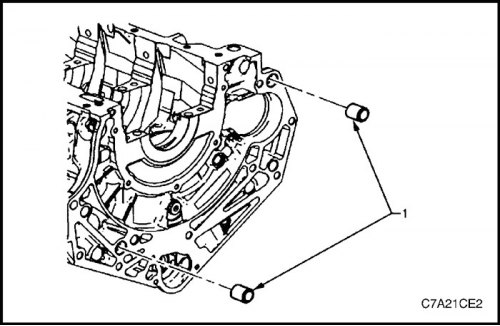
4. Install pins (1) for mounting the gearbox on the cylinder block.
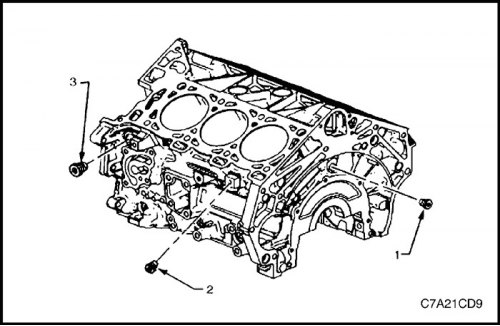
5. Install rear screw plug (1) oil channel, side screw plug (2) coolant drain hole for cylinder bank 2 and the left-hand side screw plug (3) oil channel.
Tighten
Tighten the rear screw plug of the oil channel of the cylinder block to a torque of 31 Nm (33 lb-ft).
Tighten the bank 2 cylinder block side screw plug to 31 Nm (23 lb-ft).
Tighten the bank 2 cylinder block side screw plug to 31 Nm (23 lb-ft).
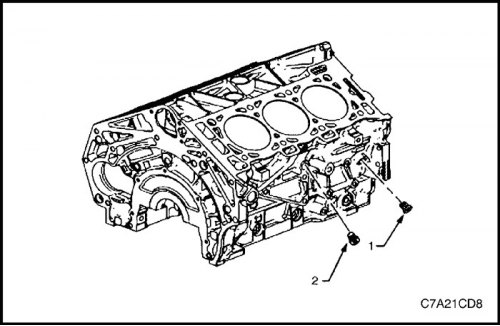
6. Install screw plug (1) oil channel and screw plug (2) coolant channel on the right side.
Tighten
Tighten the bank 1 cylinder block side screw plug to 31 Nm (23 lb-ft).
Tighten the bank 1 cylinder block side screw plug to 31 Nm (23 lb-ft).
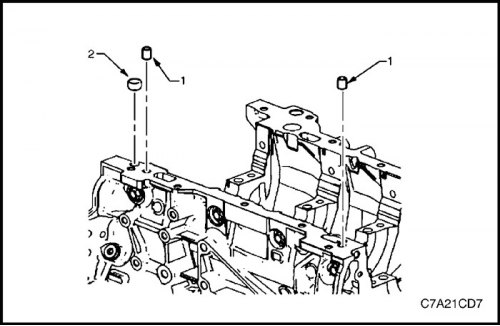
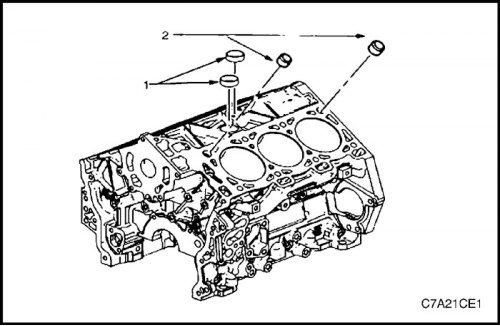
7. Install new expanding plug (1) oil passage on the front bearing surface of the oil pan, on the bank 1 side, and the pins (2) for installing the oil pan on the cylinder block.
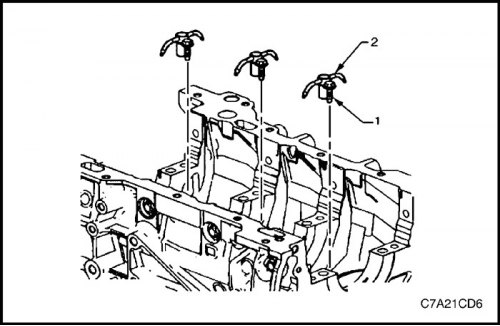
8. Install (three places) oil nozzle (2).
9. Install (three places) screw (1) oil nozzle mountings.
Tighten
Tighten the oil nozzle screw to 10 Nm (89 lb-in).
