Replacing keys
If the required number of memorized master keys is not available to perform the key addition procedure, it is necessary to perform the key programming procedure.
Adding Keys
Important:
- To start this procedure, you must have a memorized master key.
- In total, up to 10 master or service keys can be programmed for one car.
- This procedure only serves to add keys. This procedure does not delete previously learned keys.
- Keys prepared for memorization must have a mechanical configuration similar to the current key.
- If more than one service key is to be stored, each service key must be immediately preceded by the memorized master key.
1. Using the previously memorized master key, turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
2. Switch off the ignition and remove the key.
3. Within 4 seconds, insert the key to be memorized.
Turn on the ignition without starting the engine. After that, the car will remember the new key.
Programming parts of the anti-theft system
Important: After replacing the anti-theft controller (TDM), before the key programming procedure, it is necessary to complete the procedure for setting up a new anti-theft system controller.
Setting up a new anti-theft controller
From the main menu of the scan tool, select Service Programming System, then follow the instructions on the screen.
Key encoding procedure.
Important: To perform the first key memorization procedure, you must use only the master key. If you use a service key first, the TDM controller will not allow additional keys to be stored.
This procedure must be performed after replacing any of the following components:
- car keys;
- TDM controller;
- ECM controller.
Important: After replacing the TDM controller, before the key programming procedure, it is necessary to complete the procedure for setting up a new anti-theft system controller.
From the main menu of the scan tool, select Service Programming System, then follow the instructions on the screen.
Anti-theft system
Anti-theft system (CTD) when activated, it is designed to prevent theft of property from the vehicle by sounding an intermittent horn and flashing the exterior lights for approximately 30 seconds when unauthorized access to the vehicle is detected. However, the CTD system does not affect engine starting.
When the CTD system is enabled, unauthorized access is considered to be one of the following:
- Opening the rear compartment without using the remote lock system.
- Opening any door without unlocking it using the remote control locks.
The system includes the following parts:
- body controller;
- door opening switches;
- rear compartment door open switch.
Activating the CTD system
Important: Anti-theft system (CTD) can be activated with windows or roof open.
To activate the system, you need to perform the following steps.
1. Switch off the ignition.
2. Get out of the car.
Important: The system will not activate if the doors are locked manually. The keyless remote control must be used to activate the CTD system.
3. Lock the doors by pressing the LOCK button (LOCK) on the control panel. The system will go into activation delay mode and will not start the activation timer until all doors are closed. The security indicator flashes quickly, the CTD system is open at this time. The CTD system will enter the locked state when the last door is closed.
When locked, the security indicator lights up continuously. If the LOCK button is pressed after all vehicle doors are closed, the open state will be skipped and the system will go directly to the locked state with the security light on continuously.
4. The system will activate approximately 30 seconds after entering the locked state. When the indicator starts blinking slowly, the system is activated. Otherwise, if you press the LOCK button on the lock remote control again, the system will activate immediately, skipping the 30 second delay.
Locking the vehicle without activating the CTD system.
The car can be locked without activating the theft deterrence system (CTD), by manually locking the car door locks.
Shutdown of the activated system/disable the alarm
If the system was activated using the remote control, it must be disabled.
Important: Manually unlocking the doors does not disable the CTD activation mode. Also, disconnecting the battery or removing the fuses does not disable wakeup mode, as the body controller (BCM) stores the state of the CTD system in memory.
To disable the CTD system, follow these steps:
1. Press the UNLOCK button (UNLOCK) on the remote control locks.
2. Insert a valid key into the ignition and start the engine.
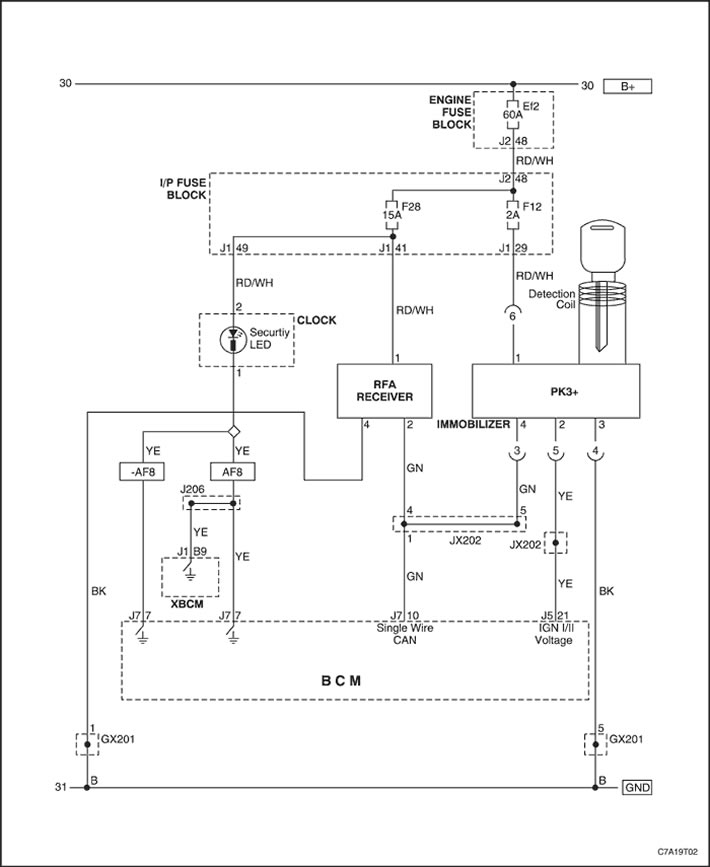
Description of the CTD circuit
The following is a description of all components used in the anti-theft system (CTD).
Body controller (BCM)
The CTD system is an internal function of the body controller (BCM), which uses serial data and inputs from various switches to perform CTD functions.
When the BCM detects unauthorized access, it will turn on the horn and exterior lights.
When the BCM detects tampering, it will first go into scare mode. The scare function issues a command for short beeps with an audible signal. If tampering continues after 10 seconds, the BCM goes into alarm mode. An intermittent beep sounds and the lights flash for 30 seconds. The 30 second alarm period is followed by a 10 second pause. Then the system is activated again.
Door opening switches
In the CTD system, door open switches in the door frames are used as one of the methods for activating the alarm.
The BCM controls all door open switches via binary inputs from each open switch. If the BCM receives a short to ground signal from the door open switch while the CTD system is active, the BCM will generate an alarm.
Input signals
The BCM monitors the following input signals:
- switches for opening the doors of the driver and passenger;
- rear compartment door open switch.
- LOCK buttons (LOCK) and UNLOCK (UNLOCK) on the control panel; internal function of the BCM controller;
- code key status - The BCM uses the code key status to disable the system or stop the alarm when the correct vehicle key is used to start the engine.
Output signals
BCM manages the following devices:
- horn relay;
- outdoor lights.
Car anti-theft system (VTD)
Car anti-theft functions (VTD) performed by the anti-theft controller (TDM) and engine controller (ECM). When the ignition key is inserted into the ignition lock cylinder and the ignition is turned on, the transponder built into the key head is energized by the excitation coil located around the ignition lock cylinder. This exciter coil is part of the TDM controller. On power-up, the transponder transmits a signal containing a unique value, which is received by the TDM controller. The TDM controller then compares this value with the value stored in memory. If the values match, the TDM sends the fuel enable password over the serial link to the ECM. If the unique transponder value is incorrect, the TDM sends a fuel inhibit password to the ECM. It is important to note that despite the fact that the password is called "permission / prohibition of fuel supply", the starter may also be blocked to prevent the engine from starting.
When the ECM receives the fuel enable password from the TDM, the ECM sends a password request. The ECM sends this password request back to the TDM over the serial link. Both controllers, ECM and TDM, perform calculations on this request. If the calculated response from the TDM matches the calculation made in the ECM, the ECM allows the engine to start.
The VTD system includes the following components:
- anti-theft controller (TDM);
- Engine control controller (ECM)
- ignition (transponder);
- security indicator.
Anti-theft controller (TDM, immobilizer)
On vehicles with steering-column ignitions, the exciter is built into the anti-theft controller (TDM), located in the steering column. TDM controller can store up to 10 keys (transponder values).
The TDM controller uses the following inputs: battery voltage, ignition on voltage, and ground circuit. The anti-theft controller controls the following outputs:
- password exchange and request/response with the engine management controller (ECM).
When the ignition key is inserted into the ignition lock cylinder and the ignition is turned on, the transponder built into the key head is powered by the excitation coils located around the ignition lock cylinder. When power is applied, the transponder transmits a signal containing a unique value, which is received by the anti-theft controller. The anti-theft controller then compares this value with the learned key code stored in memory. The anti-theft controller performs one of the following functions.
- If the transponder value matches the value stored in the TDM memory, the TDM sends a fuel enable command to the ECM via the serial link.
- If the unique transponder value does not match the value stored in the TDM, the TDM sends a fuel disable command to the ECM via the serial link.
- If the TDM cannot get the transponder value in the ignition key, no message will be sent to the ECM.
Engine control controller (ECM)
When the engine controller (ECM) receives from the anti-theft controller (TDM) fuel enable command, the ECM generates a password request. The ECM sends this password request back to the TDM over the serial link. Both controllers, ECM and TDM, perform calculations on this request. If the calculated response from the TDM matches the calculation made in the ECM, the ECM allows the engine to start.
The ECM will prevent the vehicle from starting if one of the following conditions is detected.
- The fuel enable password is invalid.
- The TDM controller has sent a fuel inhibit password.
- No password received - communication with the TDM controller is broken.
- The password response calculated by the TDM controller does not match the calculation performed in the ECM.
Ignition (transponder)
Ignition key for vehicles equipped with the Passkey III+ immobilizer system (PK3+), is a standard ignition key with a transponder located in the plastic head of the key. The transponder value is fixed and cannot be changed. In the car's anti-theft system (VTD) the ignition key transponder value is used to determine that a valid ignition key is being used to start the engine. There are approximately 3 trillion possible transponder values.
Parking keys provide full access to the vehicle, just like a master key. However, unlike the master keys, which can only be memorized on a single car, the number of car park keys that can be memorized on one car is not limited. Parking keys are only used on vehicles configured for use in police fleets.
- Starting the car engine.
- Locking/unlocking all doors and rear compartment.
- Locking/unlocking all luggage compartments.
Security indicator
Anti-theft controller (TDM) can only command the clock to turn on the security light if the ignition key is in the ON position (INCLUDED). The TDM controller issues a command to turn on the safety indicator each time a malfunction is detected in the VTD system and the engine is prohibited from starting.
Scheme of the immobilizing anti-theft system