General diagnostics
Faults in steering, suspension, tires and wheels can manifest themselves in the operation of several systems. When diagnosing, pay attention to all systems. Some problems, such as unusual or excessive tire wear and one-sided tread wear, can result from vigorous driving. First of all, do a test drive. If possible, conduct this trip with the participation of the customer.
Then proceed to the pre-checks below. Eliminate all deviations from the norm.
Preliminary checks
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check if the tires are inflated and wear evenly.
|
Inflate tires to the required pressure.
|
|
Check for play or wear at the junction of the steering column and steering gear.
|
Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace intermediate shaft if required.
|
|
Check for loose or damaged parts on the front and rear suspension, steering gear, linkages and linkages.
|
Tighten the front and rear suspension mounts. Tighten the steering gear bracket bolts. Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace front and rear suspension as needed. Replace steering gear if required. Replace intermediate shaft if required.
|
|
Check if the tires are warped.
|
Perform a free-running runout test. Select and mount tires.
|
|
Check the wheel balance, make sure that there is no deformation of the wheels, as well as wear or insufficient fixation of the wheel bearings.
|
Perform wheel balancing. Replace wheels. Replace wheel bearings.
|
|
Check the tension of the power steering pump drive belt.
|
Tension the power steering pump drive belt.
|
|
Check for leaks in the power steering system. Also check the fluid level in the power steering.
|
Eliminate leaks. Check power steering. Add power steering fluid if necessary.
|
Side slip of the car
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the correct selection and uniformity of tires.
|
Replace tires.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
|
Check the lateral force acting on the radial tire.
|
Check wheel alignment. Rearrange the wheels and tires as an assembly. Change tires if necessary.
|
|
Check the front wheel alignment.
|
Adjust the angles of the front wheels.
|
|
Check the front wheel alignment.
|
Reinstall the gear and control valve assembly. Replace gear and directional valve assembly if required.
|
|
Check for sticking front brakes.
|
Adjust front brakes.
|
Unusual or excessive tire wear
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the alignment of the front and rear wheels.
|
Adjust the angles of the front and rear wheels.
|
|
Check if the toe angle of the front and rear wheels is too large.
|
Adjust the toe angle of the front and rear wheels.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
|
Check tire balance.
|
Balance tires.
|
|
Check shock absorbers for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
|
Check tires for rotation.
|
Swap tires. Change tires if necessary.
|
|
Check if the car is overloaded.
|
Do not overload your vehicle.
|
|
Check if the tire pressure is sufficient.
|
Inflate tires to the required pressure.
|
One-sided tread wear
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the correct toe angle of the front and rear wheels.
|
Adjust the toe angle of the front and rear wheels.
|
|
Check that the suspension arm is not twisted or bent.
|
Replace suspension arm.
|
Wheel bouncing
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check tire and wheel balance.
|
Balance the tire or wheel.
|
|
Check the correct operation of the shock absorbers.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
Shimmy, shaking or vibrating
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check tire and wheel balance.
|
Balance the tire or wheel.
|
|
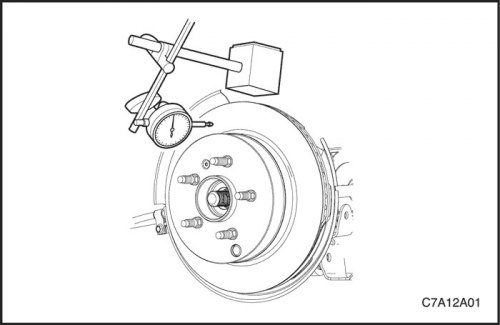
Check if the wheel hub runout is too high.
|
Measure the hub flange runout. Replace hub if required.
|
|
Check if the imbalance of the brake drum or brake disc is too great.
|
Adjust the brakes. Replace brake disc or brake drum if required.
|
|
Check the tie rod ends for wear.
|
Replace the outer tie rods.
|
|
Check wheel balance.
|
Perform wheel balancing.
|
|
Check the lower ball joint for wear.
|
Replace lower ball joint.
|
|
Check if the wheel runout is too high.
|
Measure wheel runout. Replace wheel if necessary.
|
|
Check if the radial runout of the tire and wheel assembly is too great under load.
|
Carry out the selection and mounting of the tire on the wheel.
|
Difficult steering
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check steering gear preload.
|
Adjust rack bearing preload.
|
|
Check the hydraulic system. Measure the pressure in the power steering system with a pressure gauge.
|
Replace seals and hoses as needed.
|
|
Check if there is any binding or seizing in the steering mechanism.
|
Lubricate the steering gear. Repair or replace the steering gear as needed.
|
|
Check tightness of steering gear fasteners.
|
Tighten the nuts and bolts of the steering gear mounting brackets.
|
Excessive steering play
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check for wear and tightness of the front wheel bearings.
|
Replace front wheel bearings.
|
|
Check tightness of steering gear fasteners.
|
Tighten the nuts and bolts of the steering gear mounting brackets.
|
|
Check for play or wear at the junction of the steering column and steering gear.
|
Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace intermediate shaft if required.
|
|
Check steering gear preload.
|
Adjust rack bearing preload.
|
Poor ability to self-return to the middle position
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check that ball joints and tie rod ends are sufficiently lubricated.
|
Replace ball joints and outer tie rods.
|
|
Check ball joints for binding.
|
Replace ball joint
|
|
Check the steering column for binding.
|
Lubricate the steering column. Replace steering column if required.
|
|
Check the front wheel alignment.
|
Adjust the angles of the front wheels.
|
|
Check steering gear preload.
|
Adjust rack bearing preload.
|
|
Check if the valve is stuck.
|
Lubricate the gear and control valve assembly. Replace gear and directional valve assembly if required.
|
|
Check if the intermediate shaft is binding in the steering gear.
|
Replace intermediate shaft.
|
Unusual noise in the front suspension
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check that ball joints and tie rod ends are sufficiently lubricated.
|
Replace ball joints and outer tie rods.
|
|
Check for damaged suspension parts.
|
Replace damaged suspension parts.
|
|
Check for wear on the arm bushings and tie rod ends.
|
Replace arm bushings or tie rods.
|
|
Check the stabilizer bar link fastenings.
|
Tighten the stabilizer bar link fasteners.
|
|
Check if the wheel nuts are tight.
|
Tighten wheel nuts.
|
|
Check that the suspension bolts and nuts are tight.
|
Tighten the suspension bolts or nuts.
|
|
Check the shock absorbers and telescopic strut mounts for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers. Tighten the strut mounting bolts.
|
|
Check that the telescopic strut springs are correctly positioned.
|
Set the strut spring to the correct position.
|
Vehicle yaw or poor handling
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the correct selection and uniformity of tires.
|
Replace tires.
|
|
Check that ball joints and tie rod ends are sufficiently lubricated.
|
Replace ball joints and outer tie rods.
|
|
Check shock absorbers for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
|
Check the stabilizer bar link fastenings.
|
Tighten the stabilizer bar link fasteners.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
|
Check steering gear preload.
|
Adjust rack bearing preload.
|
|
Check the alignment of the front and rear wheels.
|
Adjust the angles of the front and rear wheels.
|
Instability of driving when braking
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check for wear and tightness of the front wheel bearings.
|
Replace front wheel bearings.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
|
Check for leakage from the wheel brake cylinder or caliper.
|
Replace wheel cylinder or caliper.
|
|
Check if the discs are warped.
|
Replace disks.
|
|
Check the correctness and uniformity of the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheels.
|
If the caster angle is out of range, check the frame and repair if necessary.
|
Reduced or uneven body height relative to the wheels
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
|
Check if the car is overloaded.
|
Do not overload your vehicle.
|
|
Check if the spring is correctly selected and not weakened.
|
Replace spring.
|
Too much "soft" suspension
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check shock absorbers for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
Too much "tough" suspension
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check if the shock absorbers are correct.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
|
Check the correct spring selection.
|
Replace spring.
|
Body leans or wobbles when cornering
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the stabilizer bar link fastenings.
|
Tighten the stabilizer bar link fasteners.
|
|
Check the shock absorbers and telescopic strut mounts for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers. Tighten the strut mounting bolts.
|
|
Check if the car is overloaded.
|
Do not overload your vehicle.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
"breakdowns" pendants
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check shock absorbers for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
|
Check if the car is overloaded.
|
Do not overload your vehicle.
|
|
Check for broken or sagging springs.
|
Replace spring.
|
Recoil on the steering wheel on uneven roads
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check for air in the power steering system.
|
Bleed air from the power steering system.
|
|
Check tightness of steering gear fasteners.
|
Tighten the nuts and bolts of the steering gear mounting brackets.
|
|
Check for play or wear at the junction of the steering column and steering gear.
|
Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace intermediate shaft if required.
|
|
Check if the tie rod ends are tight.
|
Tighten the tie rod ends. Replace outer tie rods if required
|
|
Check for wear and tightness of the front wheel bearings.
|
Replace front wheel bearings.
|
Steering wheel jerking or jerking
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the hydraulic system. Measure the pressure in the power steering system with a pressure gauge.
|
Replace seals and hoses as needed.
|
|
Check if steering valve is sticking.
|
Clean gear and control valve assembly Replace gear and control valve assembly if required.
|
|
Check if the power steering pump drive belt is tight.
|
Adjust the tension of the power steering pump drive belt.
|
Tire concavity
|
Checks
|
operation, action
|
|
Check the alignment of the front and rear wheels.
|
Adjust the angles of the front and rear wheels.
|
|
Check shock absorbers for wear.
|
Replace shock absorbers.
|
|
Check for worn or loose wheel bearings.
|
Replace wheel bearings.
|
|
Check if tire or wheel runout is too high.
|
Select and mount tires. Change tires if necessary. Replace wheels if necessary.
|
|
Check the ball joint for wear.
|
Replace ball joint
|
|
Check steering gear preload.
|
Adjust rack bearing preload.
|
Car pull during acceleration
Vehicle pull to the right can occur with high throttle on some front-wheel drive vehicles with drive axles of different lengths. This pull to the right is caused by the fact that the right drive axle is longer than the left, which creates a difference in the angular position of the drive axles. For vehicles with intermediate shafts, the length of the axles is almost the same.
The inequality of the lengths of the leading axles leads to the occurrence of a moment that increases the positive convergence of the left front wheel. The moment that increases the convergence becomes noticeable when accelerating the car, started from a standstill or at a low initial speed.
Checking procedure
1. Attach a small piece of duct tape to the upper midpoint of the steering wheel.
2. Determine the amount of steering wheel turn, in inches, required to keep the vehicle in a straight line during hard acceleration.
3. Compare this value with that measured on other similar vehicles.
Vehicle pull during acceleration may increase due to the following factors:
- Differences in assemblies of tires and wheels. This factor has the greatest influence on the car's withdrawal during acceleration. The slightly smaller diameter of the right front tire results in more right side pull torque.
- Big difference in pressure between right and left tires.
- Looseness in the bushings of the suspension arms, in the tie rods or in the steering gear mounts. Torque wobble allows more forward movement and positive toe-in of the respective front wheel compared to the other wheel. Loose suspension elements can lead to a pull in the opposite direction when braking.
- Increased height of the front of the body relative to the wheels. This can lead to an increase in the angle of inclination of the drive axle and wobbling of the front wheels at speeds from 24 to 48 km/h (15 to 30 mph).
- Seizure or excessively tight connections of the drive axles. Tight drive axle connections or increased front body height relative to the wheels can also lead to front wheel wobble at speeds between 24 and 48 km/h (15 to 30 mph).
- Incorrect installation, wear or looseness of the engine mounts leads to an unfavorable deviation from the norm in the angles of the drive axles.
Corrective action for these problems is given in this part, in the section «General diagnostics».
Among the reasons for the occurrence of an effect similar to the removal of a car during acceleration, include:
- Incorrect setting of the angles of the front or rear wheels.
- Incorrect installation or frame defect.
- Front suspension damage.
- Incorrect installation of the rear cross member.
Hub and bearing
To check for play in the hub and bearing assembly, do the following:
1. Raise the vehicle and place it on the supports provided for this purpose.
2. Remove the rear wheel. See Part 2E. Tires and wheels.
3. Remove the brake caliper and disc. See Part 4E. Rear brakes.
4. Place the dial indicator with magnetic base on a fixed part of the vehicle.
5. Use your hand to move the wheel hub along the axis of rotation. If the wheel hub travel is greater than 0.04 mm (0.002 inch), replace the hub and bearing assembly. See Part 2D. Rear suspension.
6. Install the brake caliper and disc. See Part 4E. Rear brakes.
7. Install the rear wheel. See Part 2E. Tires and wheels.
8. Lower the car.