Diagnostic Trouble Codes
|
DTC
|
Description
|
|
C0035
|
Front left wheel speed sensor circuit
|
|
C0040
|
Front Right Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit
|
|
C0045
|
Rear left wheel speed sensor circuit
|
|
C0050
|
Rear Right Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit
|
|
C0110
|
fuel pump circuit
|
|
C0131
|
The working circuit of the anti-lock braking system (ABS) / traction control (TCS)
|
|
C0161
|
Brake Switch/Anti-Lock Brake Sensor Circuit (ABS) / traction control (TCS)
|
|
C0186
|
Lateral accelerometer circuit
|
|
C0196
|
Yaw rate sensor circuit
|
|
C0252
|
Vehicle Stability Enhancement System (VSES). Sensors are uncorrelated
|
|
C0280
|
The stability increase system is running too long
|
|
C0287
|
Longitudinal Accelerometer Circuit
|
|
C0292
|
VSES instrument cluster sensor circuits
|
|
C0460
|
Steering wheel position sensor
|
|
C0550
|
Controller performance (ECU)
|
|
C0551
|
Variant configuration error
|
|
C0561
|
Saving system shutdown information
|
|
C0569
|
System configuration error
|
|
C0899
|
Device {Single or 1} Low Voltage
|
|
C0900
|
Device {single or 1} High voltage
|
|
U0102
|
Lost connection with RDM (Transfer case module)
|
|
U1500
|
Communication fault on CAN bus 2 (group of sensors) (Bus disabled)
|
|
U2100
|
Communication fault on CAN bus (Bus disabled)
|
|
U2105
|
Lost communication with ECM
|
|
U2106
|
Lost Communication With TCM
|
|
U2107
|
Lost Communication with VCM
|
|
U2139
|
Lost connection to gateway
|
|
U2142
|
Lost communication with a group of sensors
|
|
U2143
|
Lost Communication With Steering Angle Sensor
|
Checking the diagnostic circuit
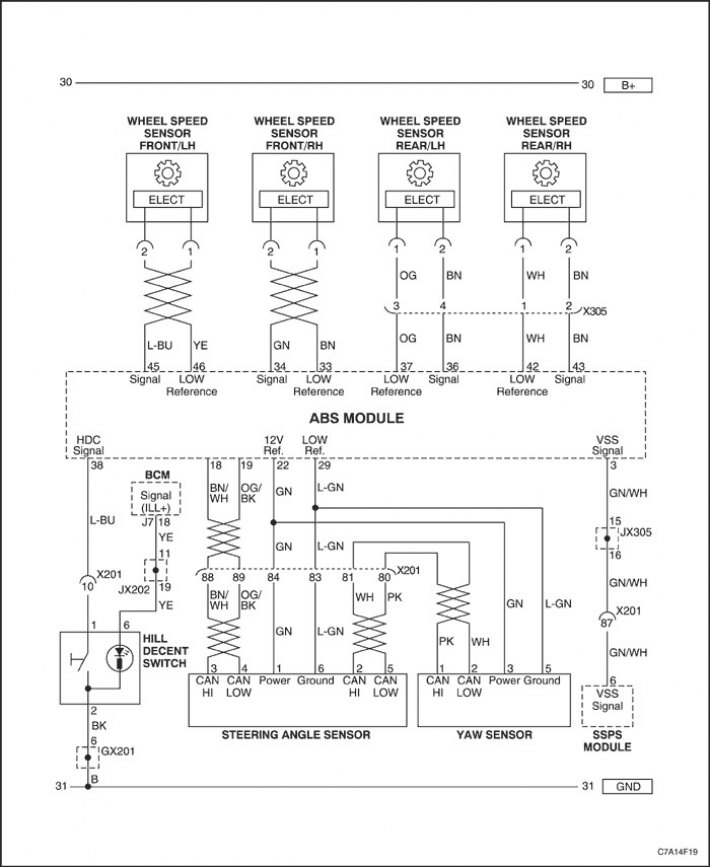
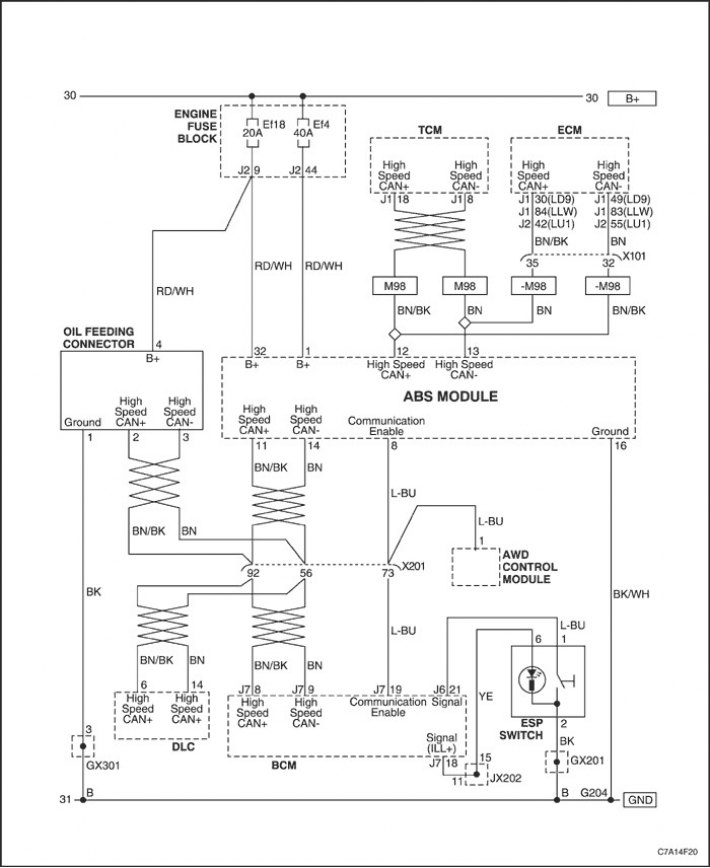
System description
The diagnostic circuit test is a systematic method for troubleshooting the ABS/DDRP system.
A service technician looking for the cause of any ABS/DDRP system problems should begin by checking the diagnostic circuits. The test of the diagnostic circuits is built in a logical sequence, the operations of which must be performed by a technician when searching for the cause of a malfunction.
The EBCM uses terminals 11 and 14 for serial transmission/reception of data from the brake system controller. DC battery power is supplied to the EBCM through terminals 1 and 32, and ignition-on voltage is applied to terminal 4. The EBCM is connected to ground through terminal 16.
Diagnostic procedure
When servicing the ABS/DDRP system, follow the sequence below.
1. Check the condition of the mechanical elements of the vehicle structure related to the brake system.
- The brake fluid level in the reservoir is normal.
- Visually check if the fluid in the master cylinder is contaminated
- Check master cylinder and modulator for leaks.
- Check master cylinder and modulator for leaks.
- Check brake parts on all wheels.
- Make sure the brakes don't stick (brake warning light switch adjustment).
- Check equal braking force on all wheels (no lateral pull)
- Check brake pads for wear and damage.
- Check wheel bearings for wear and damage.
- Check wheel speed sensors and their wires.
- Check the gear rings of the speed sensors for damage.
- Check for tire wear and determine tread thickness.
- To make sure there is a problem, perform a test drive.
2. Perform a diagnostic circuit test and go to the appropriate troubleshooting table.
3. After all faults in the ABS system have been eliminated, messages with system fault codes should be erased.
Checking the diagnostic circuit
| Step | Operation | Values | Yes | No |
| 1 |
Does the scan tool communicate with the EBCM?
|
-
|
Go to operation 2
|
Go to operation 4
|
| 2 |
Are there any DTCs, current or historical?
|
-
|
Go to operation 3
|
Jump to Operation 7
|
| 3 |
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
| 4 |
Check DLC connector harness, battery and cable.
Are all positions in order?
|
-
|
Go to operation 5
|
Go to operation 6
|
| 5 |
Is any DTC found?
|
-
|
Jump to operation 1
|
System OK
|
| 6 |
Is any DTC found?
|
-
|
Jump to operation 1
|
System OK
|
| 7 |
Did the ABS warning light and brake warning light come on for 3 seconds (lamp test)?
|
-
|
Jump to operation 8
|
Go to operation 9
|
| 8 |
System functioning is normal.
|
-
|
System OK
|
-
|
| 9 |
Did the lamp stay on?
|
-
|
Jump to operation 10
|
System OK
|
| 10 |
Refer to the corresponding table for troubleshooting instructions for DTCs.
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Diagnostic test run
When servicing vehicles, anti-lock system (ABS) and anti-slip braking system (TCS), to carry out all the tests and run all the functions of the system, test runs are required. A test run may also be required to reset the individual DTCs described in this section. Diagnostic system check (including test drive) should be carried out after the completion of the repair of the vehicle in order to verify the effectiveness of the repairs carried out.
The diagnostic test run mode depends on the nature of the problems in the ABS/TCS.
1. Read Diagnostic Aids and Conditions for Setting the DTC.
2. Connect all previously disconnected components.
3. Start the engine.
4. Drive a car for at least 10 minutes subject to the following conditions. While driving, no illegal or unsafe maneuvers are allowed.
- Freeway traffic
- Rough roads
- Check customer complaints and re-create the necessary driving conditions.
- With the engine running, connect a scan tool and test for any DTCs. If any DTCs are set, follow the troubleshooting instructions for those DTCs in the appropriate table.
Initialization sequence
Brake controller (ECBM) executes the initialization program at the beginning of each ignition cycle until the vehicle speed reaches 15 km/h (9 mph). The initialization program establishes the sequence of operation of each solenoid valve and pump motor, as well as the necessary relays, in order to verify the operation of the components. If any DTC is detected, the brake system controller (EBCM) sets a specific fault code. The initialization sequence can be felt and heard and is a normal part of the job.
