Checking the refrigeration system
If a malfunction in the refrigeration system is suspected, the following checks should be carried out:
1. Check the outside surfaces of the radiator and condenser coils to make sure that the air flow is not obstructed by dirt, leaves or other foreign material. Check between the condenser and the radiator, as well as all external surfaces.
2. Check for obstructions or kinks in the condenser coil, hoses and pipes.
3. Check the operation of the electric fan.
4. Check all air ducts for leaks or obstructions. Weak air flow may indicate that the evaporator heat exchanger is clogged.
5. Check compressor clutch slip.
6. Check drive belt tension.
Quick Check Procedure for Insufficient Cooling
Perform the following procedure "touching by hand", to quickly check that the A/C system is properly charged with R-134a refrigerant. Air temperature must be above 21°C (70°F) for most models,
1. Warm up the engine. Let the engine run at idle.
2. Open the hood and all doors.
3. Turn on the air conditioner.
4. Set the temperature control to the maximum cooling position.
5. Set the fan speed switch to the maximum speed position.
6. Feel the temperature of the evaporator outlet pipe by hand. The tube must be cold.
7. Check other issues. See «Checking the refrigeration system» in this section.
8. Check system for leaks. See «Refrigeration System Leak Check» in this section. If a leak is found, discharge the system and repair the leak. At the end of the repair, evacuate the system and charge it.
9. If there is no leak, see «Insufficient Cooling Diagnosis» in this section.
Pressure versus temperature in R-134A system
|
TEMPERATURE°C (°F) *
|
PRESSURE kPa (psig) *
|
TEMPERATURE°C (°F) *
|
PRESSURE kPa (psig) *
|
|
-8 (17.6)
|
113.1 (16.4)
|
9 (48.2)
|
296.2 (43.0)
|
|
-7 (19.4)
|
121.5 (17.6)
|
10 (50.0)
|
309.6 (44.9)
|
|
-6 (21.2)
|
130.2 (18.9)
|
15 (59.0)
|
383.7 (55.7)
|
|
-5 (23.0)
|
139.1 (20.2)
|
20 (68.0)
|
467.7 (67.8)
|
|
-4 (24.8)
|
148.4 (21.5)
|
25 (77.0)
|
567.5 (82.3)
|
|
-3 (26.6)
|
157.9 (22.9)
|
30 (86.0)
|
667.8 (96.9)
|
|
-2 (28.4)
|
167.6 (24.3)
|
35 (95.0)
|
785.6 (113.9)
|
|
-1 (30.2)
|
177.8 (25.8)
|
40 (104.0)
|
916.4 (133.0)
|
|
0 (32.0)
|
188.2 (27.3)
|
45 (113.0)
|
1 062.2 (154.0)
|
|
1 (33.8)
|
198.8 (28.8)
|
50 (122.0)
|
1 222.1 (177.2)
|
|
2 (35.6)
|
209.9 (30.4)
|
55 (131.0)
|
1 398.2 (202.8)
|
|
3 (37.4)
|
221.2 (32.1)
|
60 (140.0)
|
1 589.6 (230.5)
|
|
4 (39.2)
|
232.9 (33.8)
|
65 (149.0)
|
1 799.0 (260.9)
|
|
5 (41.0)
|
245.0 (35.5)
|
70 (158.0)
|
2 026.6 (293.9)
|
|
6 (42.8)
|
257.4 (37.3)
|
75 (167.0)
|
2 272.2 (329.5)
|
|
7 (44.6)
|
269.8 (39.1)
|
80 (176.0)
|
2 544.0 (369.0)
|
|
8 (46.4)
|
282.9 (41.0)
|
-
|
-
|
* All calculated values are rounded to one decimal place.
Evaporator range: -7 to 7°C (19,4 - 44,6°F), these values represent the temperature of the gas inside the coil, not on its surface. Add 2-6°C (4-11°F) to the temperature of the coil and the air around it.
Capacitor range: 45 to 70°C (113-158°F), is not the ambient temperature. Add 19-22°C (34-40°F) to the ambient temperature to ensure normal heat exchange. Then see pressure graph.
Example: 32°C (90°F) Outside temperature +22°C (40°F) = 54°С (130°F)
Condenser temperature at which a pressure of 1379 kPa is reached (200 psig), with an air flow of 50 km/h (31 mph).
Refrigeration system leak test; Refrigerant Leak Check
Check for leaks if you suspect a refrigerant leak from the system. In addition, it is necessary to check for leakage after all maintenance work related to the dismantling of pipes or connections. As a rule, leaks occur at the fittings of the refrigeration system and at the joints. Typically, leaks are caused by the following reasons:
- Wrong tightening torque.
- Damage to O-rings
- Dirt or fibers on O-rings.
Liquid Leak Detectors
Liquid detection solutions are used to detect leaks on fittings. Apply the solution to the suspected leak with the swab supplied with the solution. Watch for bubbles to appear. They indicate the presence and location of a leak.
For locations where this method is difficult to apply, such as the evaporator and condenser sections, an electronic leak detector is more convenient.
Electronic leak detectors
Follow the manufacturer's instructions for calibrating, operating and maintaining the electronic leak detector. To ensure the accuracy of the portable model, the condition of the battery is of particular importance. Before starting the test, set the detector to R-134a mode.
Note: Electronic leak detectors are sensitive to windshield cleaning solutions, solvents and cleaners, and some types of automotive adhesives. In order to avoid false detections, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the surface. Make sure all surfaces are dry to avoid damage to the detector.
General instructions for testing
1. Trace the entire circuit of the refrigeration system.
2. Describe a full circle around each joint at a speed of 25-50 mm/s (1-2 inch/s).
3. Hold the stylus tip up to 6 mm (1/4 inch) from the surface.
4. Do not close the air intake.
5. An intermittent beep of 1-2 clicks per second will change to a continuous tone when a leak is detected. Adjust the balance control to maintain a frequency of 1-2 clicks per second.
6. Check all of the following areas even after the leak has been found and confirmed:
- Evaporator inlet and outlet.
- Inlet and outlet of the receiver-drier.
- Condenser inlet and outlet.
- Places for soldering and welding.
- Locations of damage.
- Hose connections.
- Compressor rear cover
- All fittings and connections.
Checking Service Ports/Access Valves
Service ports are protected by sealing caps. Care must be taken to ensure that these caps are not unscrewed or lost. Each port has its own cap.
Checking the evaporator heat exchanger
Leaks on the evaporator heat exchanger are hard to find. Check the evaporator heat exchanger by following the procedure below:
1. Turn on the electric fan at maximum speed for at least 15 minutes.
2. Turn off the fan.
3. Wait 10 minutes.
4. Remove the blower resistor. See section 7A, "Heating and ventilation system".
5. Insert the leak detector probe as close as possible to the evaporator coil. The detector will indicate a leak with a continuous beep.
6. To search for compressor oil on the surface of the heat exchanger, use a lantern.
Compressor Shaft Seal Check
1. Blow compressed air behind and in front of the compressor clutch/pulley for at least 15 minutes.
2. Wait 1-2 minutes.
3. Check the area in front of the pulley. If the detector beeps continuously, there is a leak.
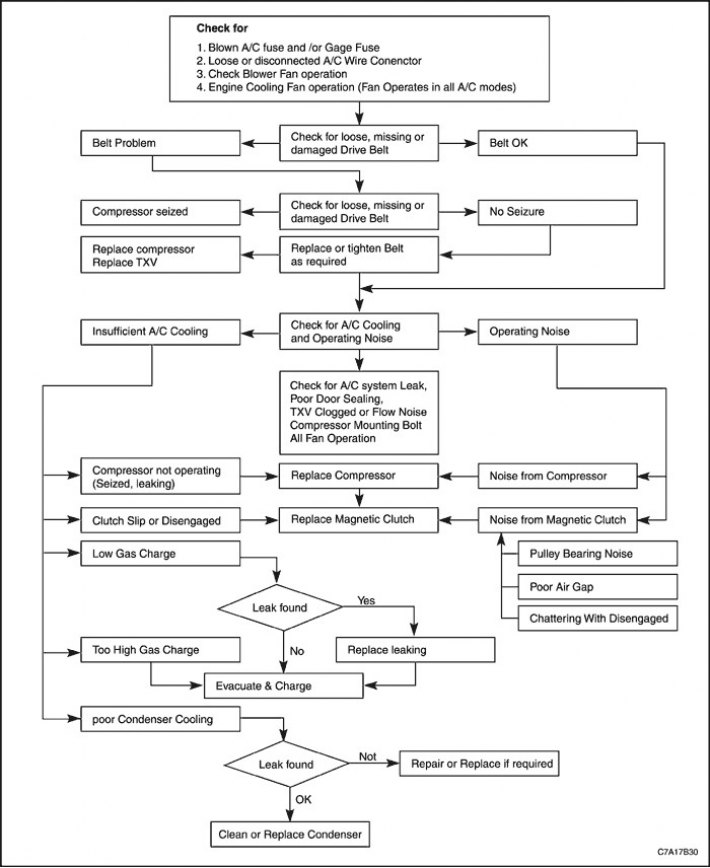
SP Compressor/Refrigerant System Diagnosis
Complaints about an air conditioning system generally fall into three types: Refrigerant/oil leaks, operating noise, and insufficient cooling.
Refer to the following diagnostic description for proper maintenance of the air conditioning system.