The main indicator for determining the health of the engine power system is the fuel pressure in the fuel rail.
With insufficient fuel pressure, the following malfunctions are possible:
- unstable engine operation;
- stop the engine at idle;
- increased or decreased idle speed of the crankshaft;
- poor vehicle handling (engine does not develop full power);
- jerks and dips in the engine when the car is moving.
To begin with, we recommend checking the reliability of the electrical contacts in the wiring harness blocks of the injection system units responsible for fuel supply (fuel pump, injectors).
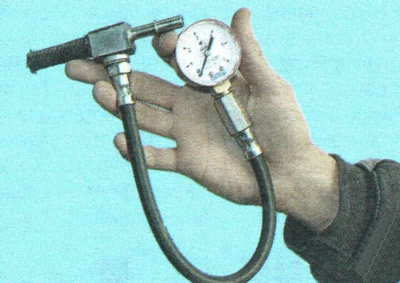
You can only check the fuel pressure in the power system with a pressure gauge with a hose and an adapter for connecting to the fuel rail. Moreover, you can connect the pressure gauge to the fuel rail in two ways: either into the break of the fuel supply pipeline, disconnecting it from the rail fitting...

...or to a special diagnostic socket, the design of which is similar to that of the tire valve. Due to the fact that the connection to the diagnostic socket is self-explanatory (it is only necessary that the pressure gauge hose end is the same as the tire pump hose end), this subsection describes the connection of a pressure gauge to the break in the fuel supply pipeline as more laborious and requiring additional operations.
1. Turn on the ignition and listen - you should hear the sound of the electric fuel pump for a few seconds. If the sound of the operation of the electric fuel pump is not audible, check the electric power supply circuit of the pump.
NOTE: If you turned on the ignition three times without trying to start the engine and the next time the electric fuel pump did not start, this is not a sign of a malfunction. It will turn on simultaneously with the start of the engine start by the starter.
2. Reduce the pressure in the supply system (see «Reducing the pressure in the power system»).

3. Slide the retainer of the fuel supply hose end attached to the fuel pulsation compensator.

4. Press the release button...

5....and disconnect the hose tip from the fuel pulsation compensator fitting.
NOTE: When removing the hose, some fuel may leak out. Wipe it off with a rag.
6. To check the fuel pressure, connect a pressure gauge with a measurement limit of at least 500 kPa into the gap between the fuel hose and the fitting of the fuel pulsation compensator.
7. Start the engine. With the engine idling, the pressure in the line should be about 380 kPa.
The following causes of low fuel pressure are possible:
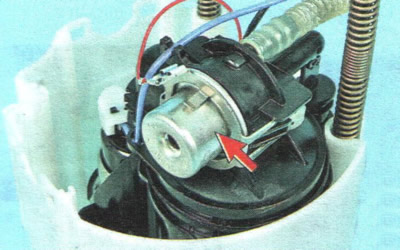
- faulty fuel pressure regulator (installed in the fuel module);
- clogged fuel filter (installed in the fuel module);

- fuel pump defective.
8. Stop the engine and reduce the pressure in the power system (see «Reducing the pressure in the power system»).
9. Connect the fuel hose to the fuel pulsation compensator.
