P0100. Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Malfunction.

1. Check that the wiring harness connector is securely attached to the combined mass flow and intake air temperature sensor connector.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0101. Mass fuel flow sensor signal output out of acceptable range.

1. Check the condition of the air filter element (see «Replacing the air filter element»)...
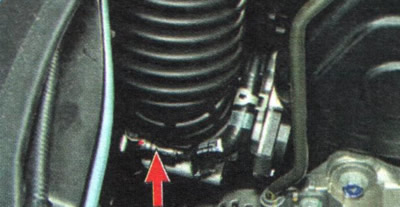
2.... reliable tightening of the clamps of the air supply hose...

3.... and the reliability of fastening the wiring harness block to the connector of the combined mass flow sensor and the temperature of the incoming air.
4. If the air cleaner element is clean and the air duct and the combined mass flow and intake air temperature sensor harness connector are secure, check the sensor circuits (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0105. Absolute pressure sensor malfunction (rarefaction) in the intake pipe.
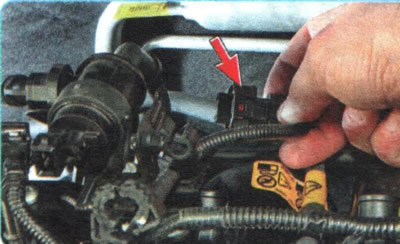
1. Check that the wiring harness connector is securely attached to the MAP sensor connector (rarefaction) in the intake pipe.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0110. Faulty intake air temperature sensor.
The troubleshooting procedure is the same as for code P0100.
P0111. Inlet air temperature sensor signal out of range.
The troubleshooting procedure is the same as for code P0101.
P0116. Coolant temperature sensor signal output out of range.
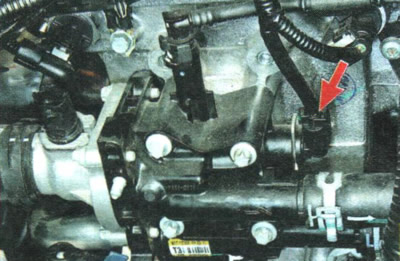
1. Check up reliability of fastening of a block of a plait of wires to a socket of the gauge of temperature of a cooling liquid.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0117. Low input voltage of the coolant temperature sensor.
The troubleshooting procedure is the same as for code P0116.
P0118. High input voltage of the coolant temperature sensor.
The troubleshooting procedure is the same as for code P0116.
P0135. Control Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction.

1. Check up reliability of connection of parts of a block of a plait of wires of the operating gauge of concentration of oxygen.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the connection of the parts of the block, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0141. Diagnostic Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction.
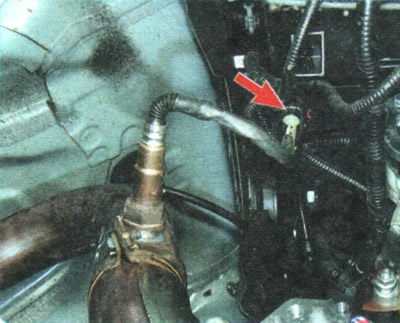
1. Install the car on a lift or an inspection ditch, remove the engine crankcase protection (see «Removal and installation of mudguards and engine crankcase protection») and check the connection of the diagnostic oxygen sensor harness connector parts.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the connection of the parts of the block, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204. Malfunction of the injector circuit, respectively, of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd or 4th cylinder.

1. Check that the wiring harness connector is securely fastened to the appropriate injector connector. To access the injector connectors, remove the engine wiring harness holders by performing operations 1-27 of subsection «Removal and installation of the fuel rail».
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, check the electrical circuit of the injector (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the injector (see «Removing, checking and installing injectors»).
P0230. Malfunction of the primary control circuit of the fuel pump.

1. Check the integrity of the fuse No. 35 and the reliability of the fastening of the fuel pump relay No. 34 in the mounting block of the engine compartment.
2. If the fuse is intact and the relay is secure, check the fuel pump relay power supply circuit (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»).
P0300. Misfires in one or more cylinders.
The troubleshooting procedure is described below for codes P0301-P0304.
P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304. Misfires respectively in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd or 4th cylinder.
If these codes are combined with fault codes of any elements of the engine management system, then misfires in the cylinders are caused by the failure of these elements. In this case, the malfunction should be searched for by the methods described above for the corresponding fault codes.
If misfiring occurs in only one cylinder, troubleshoot in the following order.
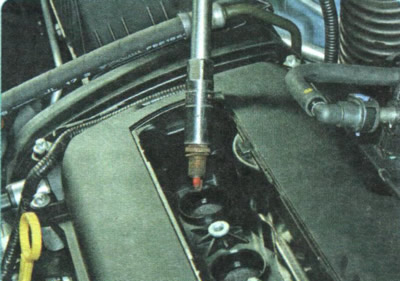
1. Remove the spark plug from the cylinder that is misfiring (see «Replacement and maintenance of spark plugs»). Examine the candle and compare its appearance with the photographs given in the subsection «Diagnostics of the engine condition by the appearance of spark plugs». If the candle is black and damp, it can be discarded.
2. If the spark plug looks good, try replacing it with a new one or swap the spark plugs.

3. If, after replacing the spark plug, misfiring in the cylinder persists, check that the wiring harness connector is securely fastened to the appropriate injector connector. To access the injector connectors, remove the engine wiring harness holders by performing operations 1-27 of subsection «Removal and installation of the fuel rail».

4. If the injector block is connected securely and the misfiring persists, try swapping the injectors (see «Removing, checking and installing injectors»).
5. If misfiring continues in the same cylinder after swapping injectors, check the electrical circuit of that cylinder's injector (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»).
6. If, as a result of the measures taken, misfires in the cylinder have not disappeared, check the compression in the cylinder (see «Cylinder compression check»). Normal compression is more than 1.0 MPa, a decrease in compression indicates the need for engine repair.
7. If all checks fail, the cause may be a malfunction of the ignition coil unit or air leaking into the cylinder through the intake pipe gasket.
If misfiring occurs in all cylinders, troubleshoot in the following order.

1. Check the condition of the air filter element (see «Replacing the air filter element»)...
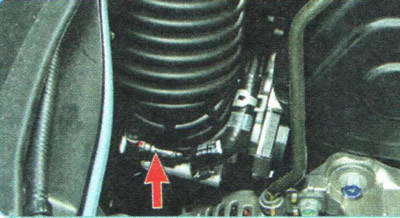
2.... and the reliability of tightening the clamps of the air supply hose.
3. Check the fuel pressure in the power system (see «Checking the pressure in the power system»). If the pressure is too low, replace the fuel module (see «Removal and installation of the fuel module»).

4. If the problem persists, remove the ignition coil pack (see «Removal and installation of the block of coils of ignition»). Check the coil block for burnouts and cracks.
5. If as a result of the measures taken misfires have not disappeared, check the compression in the cylinders (see «Cylinder compression check»). Normal compression is more than 1.0 MPa, a decrease in compression indicates the need for engine repair.
6. If all checks have failed, the cause may be a malfunction of the ignition coil unit or air leaks into the cylinders through the gaskets of the throttle assembly and the intake pipe.
P0325. Knock sensor circuit malfunction.

1. Install the car on a lift or an inspection ditch, remove the engine crankcase protection (see «Removal and installation of mudguards and engine crankcase protection») and check that the wiring harness connector is securely attached to the knock sensor connector.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0335. Malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor (when such a malfunction occurs, the engine, as a rule, stops).

1. Check the connection of the parts of the wiring harness block of the crankshaft position sensor (the pad is located at the rear of the engine block, behind the starter).
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, check the electrical circuits of the sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»).
3. If the problem persists, check the reliability of fastening of the crankshaft position sensor to the crankshaft rear oil seal (To do this, you will have to remove the gearbox and flywheel), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0340. Malfunction of the intake camshaft position sensor.
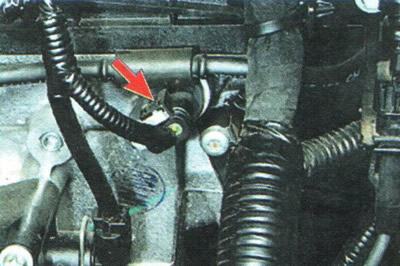
1. Check that the harness connector is securely attached to the intake camshaft position sensor connector and that the sensor is securely attached to the cylinder head.
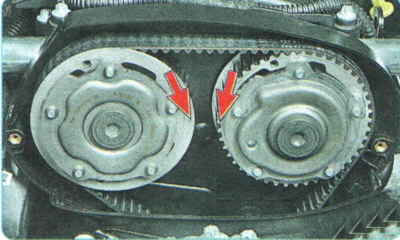
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, set the piston of the 1st cylinder of the engine to the TDC position of the compression stroke (see «Setting the piston of the first cylinder to the TDC position of the compression stroke») and check the alignment of the marks on the mechanisms for changing the valve timing of the intake and exhaust camshafts. If necessary, rearrange the timing belt, aligning the marks (see «Replacing the timing belt»).
3. If the marks on the variable valve timing mechanisms matched, check the electrical circuits of the intake camshaft position sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0365. Malfunction of the exhaust camshaft position sensor.
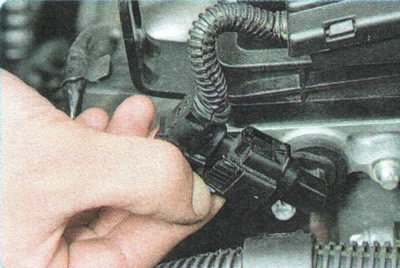
1. Check that the wiring harness connector is securely attached to the exhaust camshaft position sensor connector and that the sensor is securely attached to the cylinder head.
2. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the fastening of the shoe, set the piston of the 1st cylinder of the engine to the TDC position of the compression stroke (see «Setting the piston of the first cylinder to the TDC position of the compression stroke») and check the alignment of the marks on the mechanisms for changing the valve timing of the intake and exhaust camshafts. If necessary, rearrange the timing belt, aligning the marks (see «Replacing the timing belt»).
3. If the marks on the timing change mechanisms matched, check the electrical circuits of the exhaust camshaft position sensor (see «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment»), and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
P0420. Low efficiency of the catalytic converter.
Most often, this fault code appears as a result of chemical poisoning of the active substance of the catalytic converter (on a Chevrolet Aveo, the converter is part of the collector) combustion products of low-quality fuel, as well as melting of the converter core due to fuel burnout in the engine exhaust manifold. Therefore, the first thing to do when the code P0420 appears is to change the place of refueling. Perhaps the neutralizer can still be salvaged. If, after a run of about 500 km after changing the refueling, the engine management system malfunction warning light continues to burn, perform the following.
1. Check if there is a breakthrough of exhaust gases through the junction of the collector and the cylinder head, if necessary, replace the gasket of the collector (see «Removal and installation of the collector, replacement of its gasket»).
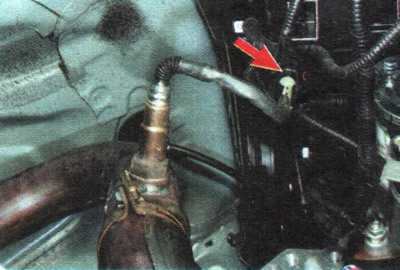
2. Install the car on a lift or an inspection ditch, remove the engine crankcase protection (see «Removal and installation of mudguards and engine crankcase protection») and check the connection of the diagnostic oxygen sensor harness connector parts.
3. If the cause of the malfunction is not in the connection of the parts of the block, check the electrical circuits of the sensor, see. «Diagnostics of malfunctions of onboard electrical equipment», and if necessary, replace the sensor (see «Removal and installation of sensors of a control system of the engine»).
If the checks did not reveal any malfunctions, then the catalytic converter is out of order. In this case, replace the collector with a new one (see «Removal and installation of the collector, replacement of its gasket»).
