General description of the cooling system
The cooling system ensures the proper temperature in all operating modes of the engine.
The cooling system consists of a radiator and circulation system, fans, thermostat, coolant pump.
The timing belt drives the coolant pump.
The pump circulates the coolant (coolant) in system. The coolant passes through the water jacket passages in the engine block, intake manifold and cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the operating temperature of the thermostat, it opens. The coolant then flows into the radiator where it cools.
The system sends some coolant to the heater heat exchanger.
The expansion tank is connected to the radiator to compensate for fluid expansion. The expansion tank provides the required level of coolant in the engine.
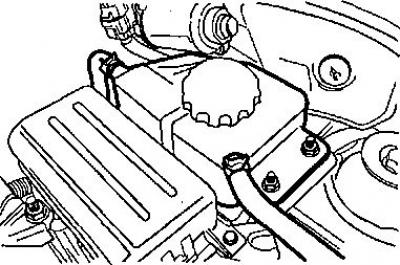
The cooling system in this vehicle is not equipped with a radiator cap or filler cap. The liquid is filled through the expansion tank.
Expansion tank
The expansion tank is a clear plastic reservoir similar to a washer fluid reservoir.
The expansion tank is connected with one hose to the radiator and the other hose to the cooling system. In the process of movement, the coolant expands. A portion of the expanded coolant exits the radiator and engine into the expansion tank. Air that has entered the radiator and engine is also forced into the expansion tank.
When the engine is stopped, the coolant cools and contracts. The displaced liquid returns back to the radiator and engine. This helps to keep the liquid level at the required level at all times and improves the quality of cooling.
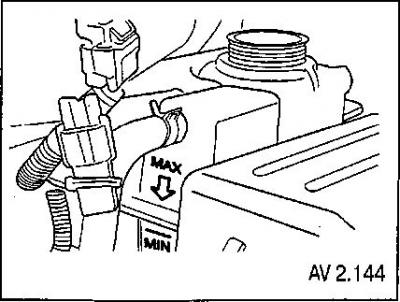
Ensure the fluid level is between the MIN and MAX marks on the expansion tank when the system is cold.
Expansion tank cap check
1. Pressurize the cap from 120 to 160Kpa.
2. Wait 10 seconds and check the pressure on the pressure tester mounted on the cap.
If the pressure measured by the cooling system pressure tester falls below 80 kPa, replace the expansion tank cap.
